Comorbid Psychiatric Disorders Impair Response to Psychosocial Treatment in Adolescents with Bipolar Disorder
At the 2019 meeting of the International Society for Bipolar Disorders, researcher Marc J. Weintraub and colleagues followed 145 adolescents with bipolar disorder over a period of two years. The adolescents with comorbid disorders (compared to those with bipolar disorder alone) fared more poorly in response to psychosocial treatment.
Weintraub and colleagues found that the adolescents who had anxiety disorders in addition to their bipolar disorder spent more weeks depressed, had more severe symptoms of (hypo)mania, and had more family conflict over the course of the study than those adolescents who had bipolar disorder alone.
Participants who had attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in addition to their bipolar disorder had more weeks with (hypo)manic symptoms, had more severe (hypo)manic symptoms, and greater family conflict than those with bipolar disorder alone.
Those participants with comorbid oppositional defiant disorder (ODD) or conflict disorder in addition to their bipolar disorder had more depressive symptoms and family conflict throughout the study.
Editor’s Note: How to better approach treatment in these diagnostically complex young people is an urgent unmet need, as most research excludes participants with more than one psychiatric disorder. Clinicians treating young people with bipolar disorder and comorbidities such as anxiety disorder, ADHD, and ODD must generally rely on inferences from children with these illnesses, using their own intuition about best treatment approaches rather than having evidence from systematic studies about how best to treat these children. It appears that both psychosocial and pharmacological treatments must be tailored to these more complicated presentations.
More Than 70% of People with Bipolar Disorder Have Additional Psychiatric Illness
At the 2019 meeting of the International Society for Bipolar Disorders, researcher Kathleen R. Merikangas reviewed large scale community studies of people with bipolar disorder in multiple countries. She reported that more than 70% of people with bipolar disorder have three or more lifetime disorders, not just bipolar disorder.
Preliminary findings suggested that adolescents with bipolar disorder did not tend to have other disorders in addition to their bipolar disorder, but as they approached young adulthood these became more common. Merikangas concluded, “These findings suggest that early intervention may prevent the secondary comorbidity that is related to greater impairment, worse course and poorer treatment response in bipolar disorder.”
Editor’s Note: It is a major deficit that not only is there limited data on early intervention in general, but virtually none about early intervention in the face of multiple comorbidities. This lack of treatment knowledge means that the majority of people with bipolar disorder are facing challenges that could be mitigated if only the needed clinical treatment research were done.
Lithium Reverses Some White Matter Abnormalities in Youth with Bipolar Disorder
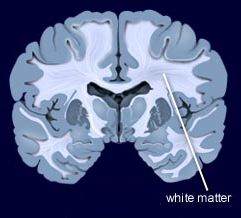 Multiple groups of researchers have reported the presence of white matter tract abnormalities in patients with bipolar disorder. Some of these abnormalities correlate with the degree of cognitive dysfunction in these patients. These white matter tract abnormalities, which are measured with diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), are widespread and can appear as early as childhood in people with bipolar disorder. Researcher Vivian Kafantaris mentioned at the 2019 meeting of the International Society for Bipolar Disorders that lithium treatment in children and adolescents normalizes these alterations, as described in an article she and her colleagues published in the journal Bipolar Disorders in 2017.
Multiple groups of researchers have reported the presence of white matter tract abnormalities in patients with bipolar disorder. Some of these abnormalities correlate with the degree of cognitive dysfunction in these patients. These white matter tract abnormalities, which are measured with diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), are widespread and can appear as early as childhood in people with bipolar disorder. Researcher Vivian Kafantaris mentioned at the 2019 meeting of the International Society for Bipolar Disorders that lithium treatment in children and adolescents normalizes these alterations, as described in an article she and her colleagues published in the journal Bipolar Disorders in 2017.
Editor’s Note: This is another reason to consider the use of lithium in children with bipolar disorder. Lithium treatment may help normalize some of the earliest signs of neuropathology in the illness.
Lithium FDA-Approved for Bipolar Disorder in Children 7–17
 In April 2019, the US Food and Drug Administration approved lithium for both the acute treatment of mania and for ongoing maintenance treatment of bipolar disorder in children and adolescents aged 7 to 17. Combined analysis of several studies indicates that lithium is effective and well-tolerated in both children and adolescents with bipolar disorder, both for acute treatment and to prevent bipolar episodes.
In April 2019, the US Food and Drug Administration approved lithium for both the acute treatment of mania and for ongoing maintenance treatment of bipolar disorder in children and adolescents aged 7 to 17. Combined analysis of several studies indicates that lithium is effective and well-tolerated in both children and adolescents with bipolar disorder, both for acute treatment and to prevent bipolar episodes.
Preventing Illness in the Offspring of a Parent with Bipolar Disorder
A 2018 article by researcher Robert Freedman and colleagues in the American Journal of Psychiatry reported that prenatal nutritional supplements can reduce mental illness in at-risk offspring. The article made a good case for supplementation with folate, phosphatidylcholine, and vitamins A and D.
Here we describe some additional ways to minimize risk of mental illness in children who are at risk for bipolar disorder or other mental illnesses.
Some efforts at prevention can begin even before a child is conceived. Avoiding smoking or drinking alcohol and maintaining a nutritious diet to prevent inflammation and excessive weight gain before conception could reduce adverse epigenetic effects on the offspring. Epigenetics refers to environmental influences on gene transcription. The impact of life experiences such as a mother or father’s substance use is not registered in their child’s DNA sequence, but can influence the structure of the child’s DNA or its packaging.
Maternal good health and wellbeing during pregnancy has also been shown to improve neonatal health and functioning.
Once a child is born, they can be encouraged in healthy habits, including a nutritious diet, good sleeping habits, regular vigorous exercise, and mindfulness/meditation training (which pediatric psychiatrist James Hudziak has suggested should be universal).
For a child who is beginning to develop mood or behavioral symptoms, more intensive intervention may be prudent. Research supports the effectiveness of family interventions such as family-focused therapy (FFT) for youth with depression, cyclothymia, or bipolar disorder not otherwise specified (BP-NOS) and a family history of bipolar disorder. Researcher David J. Miklowitz described the effects of this intervention in a 2013 article in the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.
Depression in children 3 to 6 years of age is as common as depression in older children (with rates around 1–2%), and robust improvements have been observed when families engage in parent child interaction therapy (PCIT) with a focus on emotional development. In PCIT, parents are coached while interacting with their children and encouraged to establish warm interactions while setting appropriate limits. In a study by Joan L. Luby and colleagues published in the American Journal of Psychiatry in 2018, using PCIT modified to include an emotional development component improved depression and associated symptoms in children aged 3 to 11, and it also improved mothers’ mood and behavior. Read more
Lithium Superior to Other Mood Stabilizers in a Longitudinal Study of Bipolar Youth
At a late-2018 scientific meeting, researcher Danella Hafeman and colleagues reported some results of the Course and Outcome of Bipolar Youth (COBY) study. The study includes long-term follow up of 413 youth with bipolar disorder, who ranged in age from 7 to 17 years old. Hafeman and colleagues reported that taking lithium more than 75% of the time was linked to fewer suicide attempts, fewer depressive symptoms, and fewer psychosocial difficulties than taking another mood stabilizer (such as an atypical antipsychotic, lamotrigine, or valproic acid) more than 75% of the time after adjusting for demographic variables.
Despite the limitations of observational studies such as this one, the authors concluded, “Our findings are consistent with studies in adult populations, showing that lithium (compared to other mood stabilizers) is associated with decreased suicidality, less depression, and better psychosocial functioning. Given the paucity of evidence regarding lithium in children and adolescents, these findings have important clinical implications for the pharmacological management of youth with [bipolar disorder].”
Editor’s Note: These observations are consistent with several other studies. Researcher Barbara Geller and colleagues observed in eight years of follow up of children diagnosed with bipolar disorder that those who were treated with lithium spent more time in remission than those who took other medicines. A randomized controlled study by researcher Robert Findling and colleagues documented that maintenance lithium treatment was more effective than placebo at preventing bipolar episodes. Together, these data suggest that lithium should be used more often in the long-term treatment of children with bipolar disorder.
Way ahead of his time in about 1993, the renowned child psychiatrist Dennis Cantwell said something like this: “If I had an adolescent child with a first manic episode, I would have him stay on lithium for the rest of his life.” He seems to have been prescient, as evidence of the many benefits of lithium over other alternatives in the treatment of both children and adults has been accumulating.
An open-access review article this editor (Robert M. Post) published in the journal Neuropsychopharmacology in 2017, “The New News about Lithium: An Underutilized Treatment in the United States,” argues that lithium’s many benefits have been underestimated, while its side effects have been overestimated. It is my view that it would be beneficial if lithium were more often included in the treatment regimen of adults as well as children and adolescents with bipolar disorder.
Lithium has an astounding range of effectiveness. It prevents recurrent depressions and suicide (even in those with unipolar depression), increases hippocampal and cortical volume, protects memory, and increases the length of telomeres (the end portions of chromosomes that protect them as they replicate). In multiple animal models of neurological diseases, it has also been found to be neuroprotective and to reduce the size of brain lesions.
Using Light to Improve Sleep and Depression
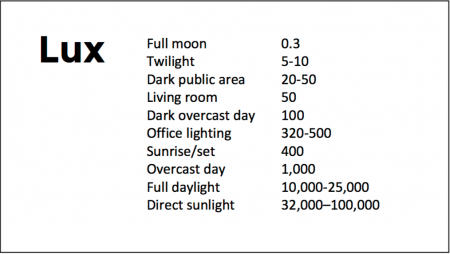
At the 2018 meeting of the North Carolina Psychiatric Association, researcher Chris Aiken described the phenomenon of sleep inertia, when people are awakened from deep sleep by an alarm, rather than waking at the end of a sleep cycle, and are groggy for 15 minutes. Depressed people may stay groggy for 4 hours. A dawn simulator may help. These lights turn on gradually over the course of 30 to 60 minutes, reaching 250 lux while the patient is still asleep. Dawn simulators have worked in eight out of ten controlled clinical trials to help people with seasonal affective disorder, adolescents, and normal adults wake up more easily. They range in cost from $25 to $90 and some brands include PER2LED or LightenUp. Aiken says dawn simulators can improve depression, sleep quality, and cognition.
Evening and nighttime light: Bright lights and blue light, like the light that comes from electronic screens, can shut down the body’s secretion of melatonin, making people awake and alert in the evening when they should be getting sleepy. Dim light or glasses that filter out blue light allow increases in melatonin secretion in the evening, while bright light suppresses it. Missing this early melatonin pulse creates “night owls” who have delayed sleep onset.
Because light still reaches our eyes through our eyelids as we sleep, even low-level light during the night impairs sleep, cognition, and learning, and increases the risk of depression by a hazard ratio of 1.8 (about double the risk). A 2017 study by Kenji Obayashi in the American Journal of Epidemiology found that bedroom light above 5 lux elevated rates of depression in older adults after two years of followup. Living room light averaged around 50 lux and increased depression further.
The treatment is turning off TVs, electronic screens, and cellphones in the evening or wearing blue-blocking glasses, which can be found for less than $10. Blue-blocking glasses can increase calmness and reduce anxiety, and even are effective in treating mania. Then, during sleep, wear an eye mask or get light-blocking blinds or curtains for windows. For a complete blackout, use blackout curtains, aluminum foil over windows, electric tape over LED lights, or try sleeping in the basement.
Aiken suggests that to re-instate healthy sleep patterns, people should institute virtual darkness from 6pm to 8am, including wearing blue-blocking glasses when out of bed. Then they should institute total darkness or wear an eye mask when in bed. When symptoms improve, this routine can gradually be shifted to begin later in the evening, such as two hours before bedtime.
Blue light filters are also available for smartphones and tablets including Apple Nightshift mode, Kindle BlueShade, and Android Twilight and Blue Light Filter.
Glasses that filter out blue light include Uvex Ultraspec 2000, 50360X ($7 on Amazon) and Uvex Skyper 351933X ($7-10 on Amazon). The website lowbluelights.com sells blue-blocking glasses from $45 and a variety of other blue-free lighting products such as lightbulbs and flashlights.
Bright light therapy for unipolar and bipolar depression: 30 minutes of bright light (7,500 to 10,000 lux) in the morning can help treat depression in unipolar and bipolar disorder and seasonal affective disorder. The effects usually take 3 to 7 days to set in, but they only last while a patient continues using the bright light in the morning. Researcher Dorothy K. Sit and colleagues found that bright light therapy in the morning sometimes caused hypomanic reactions in people with bipolar disorder, and reported in a 2018 article in the American Journal of Psychiatry that midday light therapy (from noon to 2:30pm) was also effective without this unwanted effect. However, a 2018 article by Ne?e Yorguner Küpeli and colleagues in the journal Psychiatry Research suggested that a half hour of morning light for two weeks was sufficient to bring about improvement in 81% of patients with bipolar disorder and did not cause serious side effects.
Melatonin regimen for sleep onset delay: Melatonin can be used to treat severe night-owls with a very late onset of sleep (for example, going to bed at 2 or 3am and sleeping late into the morning). Melatonin can help with sleep onset to some extent when used at bedtime, but in those with an extreme phase shift, researcher Alfred J. Lewy recommends a regimen of low dose priming with 400–500 micrograms of melatonin at 4pm and then a full dose of 3 milligrams of melatonin at midnight. The 4pm priming dose helps pull back the delayed onset of the body’s secretion of melatonin toward a more normal schedule.
Marijuana Use in Early Adolescence Triples Risk of Psychosis At Age 18
 Hannah J. Jones and colleagues reported in the journal JAMA Psychiatry in 2018 that early- and late-onset marijuana use increased the risk of psychosis at age 18 (odds ratio 3.7 to 2.97). Interestingly, early-onset cigarette use also increased risk of psychosis, but much of the link between cigarette use and psychosis disappeared after correcting for confounding variables.
Hannah J. Jones and colleagues reported in the journal JAMA Psychiatry in 2018 that early- and late-onset marijuana use increased the risk of psychosis at age 18 (odds ratio 3.7 to 2.97). Interestingly, early-onset cigarette use also increased risk of psychosis, but much of the link between cigarette use and psychosis disappeared after correcting for confounding variables.
The data on 5,300 participants born from 1991 to 1992 came from the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children. Researchers followed up with the participants about their use of marijuana and cigarettes at least three times between the ages of 14 and 19.
Editor’s Note: These data add to a host of epidemiological data that smoking marijuana doubles the risk of psychosis. Risk is further increased among people with a common genetic variant (val/val) of the gene for COMT (catechol-O-methyltransferase), which metabolizes prefrontal dopamine. The variant, which includes two valine amino acids, functions better than other variants that include methionine amino acids. People with val/met or met/met COMT genes metabolize dopamine more slowly, making them relatively protected.
The data are also pretty strong that early heavy use of marijuana is a risk factor for new onset of both bipolar disorder and schizophrenia (and not just an earlier onset in those who might have been vulnerable otherwise).
While marijuana use has become more mainstream with its legalization in many states, its recreational use still carries risks of mental illness. In addition to increasing psychosis risk, marijuana use can also make bipolar disorder more difficult to treat.
A minor component of marijuana, cannabidiol, can have some positive effects, but what you get most of when consuming marijuana is tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which produces symptoms that resemble psychosis.
Data in rats indicate that a father rat’s use of THC as an adult increases the risk that his offspring (with which he has no contact) will be prone to opiate addiction. The effect is an epigenetic one, conveyed by chemical changes in the father’s DNA that get passed on to the next generation via changes that persist in his sperm. We don’t know if this also happens with humans. So even if you are not worried about your own health, avoiding marijuana use might be good for your children.
Pilot Study Finds Intravenous Ketamine Improves Tough-to-Treat Adolescent Depression
A 2018 open study by Kathryn R. Cullen and colleagues in the Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology suggests that intravenous ketamine may improve depression in adolescents who have not responded to at least two antidepressants.
Thirteen patients ranging in age from 12 to 18 with treatment-resistant depression were given six ketamine infusions over a period of two weeks, at doses of 0.5 mg/kg of body weight. A 50% drop in scores on the Children’s Depression Rating Scale-Revised (CDRS-R) was considered a good response, and the average drop in participants’ scores was 42.5%. Five of the thirteen participants (38%) met the criteria for a good response. Three of these participants were still in remission at six weeks, while the other two relapsed within two weeks.
Ketamine was fairly well-tolerated by the young participants. Some had temporary dissociative symptoms or blood pressure changes. Higher absolute doses of ketamine were linked to better response.
The response rates in this group were not as good as in some studies of adults. More research using larger sample sizes and placebo controls is needed to optimize dosing and clarify the safety and efficacy of intravenous ketamine in adolescents with tough-to-treat depression, but this is a promising finding in a small number of adolescents.
Treatment Approaches to Childhood-Onset Treatment-Resistant Bipolar Disorder
Dear readers interested in the treatment of young children with bipolar disorder and multiple other symptoms: In 2017, BNN Editor Robert M. Post and colleagues published an open access paper in the journal The Primary Care Companion for CNS Disorders titled “A Multi-Symptomatic Child: How to Track and Sequence Treatment.” The article describes a single case of childhood-onset bipolar disorder shared with us via our Child Network, a research program in which parents can create weekly ratings of their children’s mood and behavioral symptoms, and share the long-term results in graphic form with their children’s physicians.
Here we summarize potential treatment approaches for this child, which may be of use to other children with similar symptoms.
We present a 9-year-old girl whose symptoms of depression, anxiety, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), oppositional behavior, and mania were rated on a weekly basis in the Child Network under a protocol approved by the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Institutional Review Board. The girl, whose symptoms were rated consistently for almost one year, remained inadequately responsive to lithium, risperidone, and several other medications. We describe a range of other treatment options that could be introduced. The references for the suggestions are available in the full manuscript cited above, and many quotes from the original article are reprinted here directly.
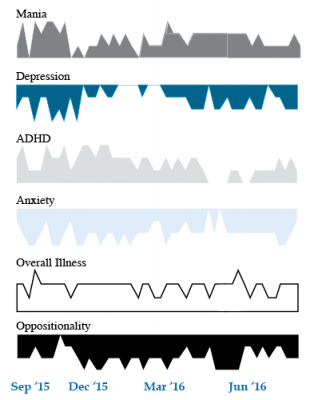
As illustrated in the figure below, after many weeks of severe mania, depression, and ADHD, the child initially appeared to improve with the introduction of 4,800 micrograms per day of lithium orotate (a more potent alternative to lithium carbonate that is marketed as a dietary supplement), in combination with 1 mg per day of guanfacine, and 1 mg per day of melatonin.
Despite continued treatment with lithium orotate (up to 9,800 micrograms twice per day), the patient’s oppositional behavior worsened during the period from November 2015 to March 2016, and moderate depression re-emerged in April 2016. Anxiety was also generally less severe from December 2015 to July 2016, and weekly ratings of overall illness remained in the moderate severity range (not illustrated).
In June 2016, the patient began taking risperidone (maximum dose 1.7 mg/day) instead of lithium, and her mania improved from moderate to mild. There was little change in her moderate but fluctuating depression ratings, but her ADHD symptoms got worse.
The patient had been previously diagnosed with bipolar II disorder and anxiety disorders including school phobia, generalized anxiety disorder, and obsessive compulsive disorder.
Given the six weeks of moderate to severe mania that the patient experienced in October and November 2015, she would meet criteria for a diagnosis of bipolar I disorder.
Targeting Symptoms to Achieve Remission
General treatment goals would include: mood stabilization prior to use of ADHD medications, a drug regimen that maximizes tolerability and safety, targeting of residual symptoms with appropriate medications supplemented with nutraceuticals, recognition that complex combination treatment may be necessary, and combined use of medications, family education, and therapy.
Mood Stabilizers and Atypical Antipsychotics to Maximize Antimanic Effects
None of the treatment options in this section are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for use in children under 10 years of age, so all of the suggestions are “off label.” Further, they may differ from what other investigators in this area of medicine would suggest, especially since evidence-based medicine’s traditional gold standard of randomized placebo-controlled clinical trials is impossible to apply here, given the lack of research in children with bipolar disorder.
As we share in the original article, reintroducing lithium alongside risperidone could be effective, as “combinations were more effective than monotherapy in a study [by] Geller et al. (2012), especially when they involved an atypical antipsychotic such as risperidone. This might include the switch from lithium orotate to lithium carbonate,” the typical treatment for bipolar disorder, on which more research has been done. “Combinations of lithium and valproate were also more effective than either [drug alone]…in the studies of Findling et al. (2006),” and many patients needed stimulants in addition.
“Most children also needed combinations of mood stabilizers (lithium, carbamazepine, valproate) in the study [by] Kowatch et al. (2000).” In a 2017 study by Berk et al. of patients hospitalized for a first mania, randomization to lithium for one year was more effective than quetiapine on almost all outcome measures.
Targeting ADHD
“[The increased] severity of [the child’s] ADHD despite improving mania speaks to the…utility of adding a stimulant to the regimen that already includes…guanfacine,” which is a common non-stimulant treatment for ADHD. “This would be supported by the data of Scheffer et al. (2005) that stimulant augmentation for residual ADHD symptoms does not [worsen] mania, and that the combination of a stimulant and guanfacine may have more favorable effects than stimulants alone.”
However, the consensus in the field is that mood stabilization should be achieved first, before low to moderate (but not high) doses of stimulants are added. “Thus, in the face of an inadequate response to the lithium-risperidone combination in this child, stimulants could be deferred until better mood stabilization was achieved.”
Other Approaches to Mood Stabilization and Anxiety Reduction
“The anticonvulsant mood stabilizers (carbamazepine, lamotrigine, and valproate) each have considerable mood stabilizing and anti-anxiety effects, at least in adults with bipolar disorder. With inadequate mood stabilization of this patient on lithium and risperidone, we would consider the further addition of lamotrigine.
Lamotrigine appears particularly effective in adults with bipolar disorder who have a personal history and a family history of anxiety (as opposed to mood disorders), and it has positive open data in adolescents with bipolar depression and in a controlled study of maintenance (in teenagers 13–17, but not in preteens 10–12) (Findling et al. 2015). With better mood stabilization, anxiety symptoms usually diminish…, and we would pursue these strategies [instead of using] antidepressants for depression and anxiety in young children with bipolar disorder.”
“Carbamazepine appears to be more effective in adults with bipolar who have [no] family history of mood disorders,” unlike lithium, which seems to work better in people who do have a family history of mood disorders.
“While the overall results of oxcarbazepine in childhood mania were negative, they did exceed placebo in the youngest patients (aged 7–12) as opposed to the older adolescents (13–18) (Wagner et al. 2006).
“There are long-acting preparations of both carbamazepine (Equetro) and oxcarbazepine (Oxtellar) that would allow for all nighttime dosing to help with sleep and reduce daytime side effects and sedation. Although data [on] anti-manic and antidepressant effects in adults are stronger for carbamazepine than oxcarbazepine,” there are good reasons to consider oxcarbazepine. First, there is the finding mentioned above that oxcarbazepine worked best in the youngest children. Second, there is a lower incidence of severe white count suppression on oxcarbazepine. Third, it has less of an effect on liver enzymes than carbamazepine. However, low blood sodium levels are more frequent on oxcarbazepine than carbamazepine.