Vitamin Methyl B12 Improved Autism Symptoms in Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study
In a 2016 article in the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, Robert L. Hendren and colleagues described an 8-week study in which the vitamin methyl B12 improved symptoms of autism spectrum disorders in children.
Fifty-seven children were randomized to receive either 75??g/kg of methyl B12 injected under the skin every three days or saline injections as a placebo instead. Methyl B12 improved the children’s autism symptoms compared to placebo. The improvements correlated with increases in levels of the amino acid methionine in the blood and improvements in cellular methylation capacity. Children with autism spectrum disorders have reduced ability to methylate (i.e. add methyl groups to) DNA. The methylation process helps convert the toxic amino acid homocysteine into beneficial methionine. The children who received methyl B12 showed a reduction in homocysteine and a better ratio of methionine to homocysteine.
Homocysteine is bad for the heart, for cognition, and for fetal development, while methionine can help improve depression and is important to many cellular reactions. Converting homocysteine to methionine requires vitamin B12 and folate, another B vitamin found in foods such as green vegetables and beans.
Taking folate supplements can help make antidepressants more effective by aiding the methylation process. However, some people have a common variation in the MTHFR gene that makes it difficult for the body to make use of folate. These people would need to take the nutritional supplement L-methylfolate instead of regular folate to help in the conversion of homocysteine to s-adenosylmethionine (SAMe, which acts as an antidepressant).
Preventing Illness in the Offspring of a Parent with Bipolar Disorder
A 2018 article by researcher Robert Freedman and colleagues in the American Journal of Psychiatry reported that prenatal nutritional supplements can reduce mental illness in at-risk offspring. The article made a good case for supplementation with folate, phosphatidylcholine, and vitamins A and D.
Here we describe some additional ways to minimize risk of mental illness in children who are at risk for bipolar disorder or other mental illnesses.
Some efforts at prevention can begin even before a child is conceived. Avoiding smoking or drinking alcohol and maintaining a nutritious diet to prevent inflammation and excessive weight gain before conception could reduce adverse epigenetic effects on the offspring. Epigenetics refers to environmental influences on gene transcription. The impact of life experiences such as a mother or father’s substance use is not registered in their child’s DNA sequence, but can influence the structure of the child’s DNA or its packaging.
Maternal good health and wellbeing during pregnancy has also been shown to improve neonatal health and functioning.
Once a child is born, they can be encouraged in healthy habits, including a nutritious diet, good sleeping habits, regular vigorous exercise, and mindfulness/meditation training (which pediatric psychiatrist James Hudziak has suggested should be universal).
For a child who is beginning to develop mood or behavioral symptoms, more intensive intervention may be prudent. Research supports the effectiveness of family interventions such as family-focused therapy (FFT) for youth with depression, cyclothymia, or bipolar disorder not otherwise specified (BP-NOS) and a family history of bipolar disorder. Researcher David J. Miklowitz described the effects of this intervention in a 2013 article in the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.
Depression in children 3 to 6 years of age is as common as depression in older children (with rates around 1–2%), and robust improvements have been observed when families engage in parent child interaction therapy (PCIT) with a focus on emotional development. In PCIT, parents are coached while interacting with their children and encouraged to establish warm interactions while setting appropriate limits. In a study by Joan L. Luby and colleagues published in the American Journal of Psychiatry in 2018, using PCIT modified to include an emotional development component improved depression and associated symptoms in children aged 3 to 11, and it also improved mothers’ mood and behavior. Read more
Lithium Superior to Other Mood Stabilizers in a Longitudinal Study of Bipolar Youth
At a late-2018 scientific meeting, researcher Danella Hafeman and colleagues reported some results of the Course and Outcome of Bipolar Youth (COBY) study. The study includes long-term follow up of 413 youth with bipolar disorder, who ranged in age from 7 to 17 years old. Hafeman and colleagues reported that taking lithium more than 75% of the time was linked to fewer suicide attempts, fewer depressive symptoms, and fewer psychosocial difficulties than taking another mood stabilizer (such as an atypical antipsychotic, lamotrigine, or valproic acid) more than 75% of the time after adjusting for demographic variables.
Despite the limitations of observational studies such as this one, the authors concluded, “Our findings are consistent with studies in adult populations, showing that lithium (compared to other mood stabilizers) is associated with decreased suicidality, less depression, and better psychosocial functioning. Given the paucity of evidence regarding lithium in children and adolescents, these findings have important clinical implications for the pharmacological management of youth with [bipolar disorder].”
Editor’s Note: These observations are consistent with several other studies. Researcher Barbara Geller and colleagues observed in eight years of follow up of children diagnosed with bipolar disorder that those who were treated with lithium spent more time in remission than those who took other medicines. A randomized controlled study by researcher Robert Findling and colleagues documented that maintenance lithium treatment was more effective than placebo at preventing bipolar episodes. Together, these data suggest that lithium should be used more often in the long-term treatment of children with bipolar disorder.
Way ahead of his time in about 1993, the renowned child psychiatrist Dennis Cantwell said something like this: “If I had an adolescent child with a first manic episode, I would have him stay on lithium for the rest of his life.” He seems to have been prescient, as evidence of the many benefits of lithium over other alternatives in the treatment of both children and adults has been accumulating.
An open-access review article this editor (Robert M. Post) published in the journal Neuropsychopharmacology in 2017, “The New News about Lithium: An Underutilized Treatment in the United States,” argues that lithium’s many benefits have been underestimated, while its side effects have been overestimated. It is my view that it would be beneficial if lithium were more often included in the treatment regimen of adults as well as children and adolescents with bipolar disorder.
Lithium has an astounding range of effectiveness. It prevents recurrent depressions and suicide (even in those with unipolar depression), increases hippocampal and cortical volume, protects memory, and increases the length of telomeres (the end portions of chromosomes that protect them as they replicate). In multiple animal models of neurological diseases, it has also been found to be neuroprotective and to reduce the size of brain lesions.
Poll Finds 87% of US Adults Think Children Need More Mental Health Support
In a poll of 2,014 adults in the US, 87% believed that children need more mental health support. For over a decade, the editors of the BNN have been emphasizing the great need for earlier recognition and treatment of children with bipolar and related mood and behavioral disorders. With so many Americans in agreement, now could be the time to direct public health and research funds to the better support of children’s mental health. Sadly this does not yet seem to be the case, but this is an election year. We need stand-up leaders in Congress to marshal the resources to increase the well-being of current and future generations.
Treatment Approaches to Childhood-Onset Treatment-Resistant Bipolar Disorder
Dear readers interested in the treatment of young children with bipolar disorder and multiple other symptoms: In 2017, BNN Editor Robert M. Post and colleagues published an open access paper in the journal The Primary Care Companion for CNS Disorders titled “A Multi-Symptomatic Child: How to Track and Sequence Treatment.” The article describes a single case of childhood-onset bipolar disorder shared with us via our Child Network, a research program in which parents can create weekly ratings of their children’s mood and behavioral symptoms, and share the long-term results in graphic form with their children’s physicians.
Here we summarize potential treatment approaches for this child, which may be of use to other children with similar symptoms.
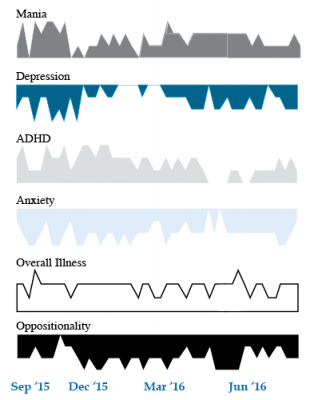
We present a 9-year-old girl whose symptoms of depression, anxiety, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), oppositional behavior, and mania were rated on a weekly basis in the Child Network under a protocol approved by the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Institutional Review Board. The girl, whose symptoms were rated consistently for almost one year, remained inadequately responsive to lithium, risperidone, and several other medications. We describe a range of other treatment options that could be introduced. The references for the suggestions are available in the full manuscript cited above, and many quotes from the original article are reprinted here directly.
As illustrated in the figure below, after many weeks of severe mania, depression, and ADHD, the child initially appeared to improve with the introduction of 4,800 micrograms per day of lithium orotate (a more potent alternative to lithium carbonate that is marketed as a dietary supplement), in combination with 1 mg per day of guanfacine, and 1 mg per day of melatonin.
Despite continued treatment with lithium orotate (up to 9,800 micrograms twice per day), the patient’s oppositional behavior worsened during the period from November 2015 to March 2016, and moderate depression re-emerged in April 2016. Anxiety was also generally less severe from December 2015 to July 2016, and weekly ratings of overall illness remained in the moderate severity range (not illustrated).
In June 2016, the patient began taking risperidone (maximum dose 1.7 mg/day) instead of lithium, and her mania improved from moderate to mild. There was little change in her moderate but fluctuating depression ratings, but her ADHD symptoms got worse.
The patient had been previously diagnosed with bipolar II disorder and anxiety disorders including school phobia, generalized anxiety disorder, and obsessive compulsive disorder.
Given the six weeks of moderate to severe mania that the patient experienced in October and November 2015, she would meet criteria for a diagnosis of bipolar I disorder.
Targeting Symptoms to Achieve Remission
General treatment goals would include: mood stabilization prior to use of ADHD medications, a drug regimen that maximizes tolerability and safety, targeting of residual symptoms with appropriate medications supplemented with nutraceuticals, recognition that complex combination treatment may be necessary, and combined use of medications, family education, and therapy.
Mood Stabilizers and Atypical Antipsychotics to Maximize Antimanic Effects
None of the treatment options in this section are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for use in children under 10 years of age, so all of the suggestions are “off label.” Further, they may differ from what other investigators in this area of medicine would suggest, especially since evidence-based medicine’s traditional gold standard of randomized placebo-controlled clinical trials is impossible to apply here, given the lack of research in children with bipolar disorder.
As we share in the original article, reintroducing lithium alongside risperidone could be effective, as “combinations were more effective than monotherapy in a study [by] Geller et al. (2012), especially when they involved an atypical antipsychotic such as risperidone. This might include the switch from lithium orotate to lithium carbonate,” the typical treatment for bipolar disorder, on which more research has been done. “Combinations of lithium and valproate were also more effective than either [drug alone]…in the studies of Findling et al. (2006),” and many patients needed stimulants in addition.
“Most children also needed combinations of mood stabilizers (lithium, carbamazepine, valproate) in the study [by] Kowatch et al. (2000).” In a 2017 study by Berk et al. of patients hospitalized for a first mania, randomization to lithium for one year was more effective than quetiapine on almost all outcome measures.
Targeting ADHD
“[The increased] severity of [the child’s] ADHD despite improving mania speaks to the…utility of adding a stimulant to the regimen that already includes…guanfacine,” which is a common non-stimulant treatment for ADHD. “This would be supported by the data of Scheffer et al. (2005) that stimulant augmentation for residual ADHD symptoms does not [worsen] mania, and that the combination of a stimulant and guanfacine may have more favorable effects than stimulants alone.”
However, the consensus in the field is that mood stabilization should be achieved first, before low to moderate (but not high) doses of stimulants are added. “Thus, in the face of an inadequate response to the lithium-risperidone combination in this child, stimulants could be deferred until better mood stabilization was achieved.”
Other Approaches to Mood Stabilization and Anxiety Reduction
“The anticonvulsant mood stabilizers (carbamazepine, lamotrigine, and valproate) each have considerable mood stabilizing and anti-anxiety effects, at least in adults with bipolar disorder. With inadequate mood stabilization of this patient on lithium and risperidone, we would consider the further addition of lamotrigine.
Lamotrigine appears particularly effective in adults with bipolar disorder who have a personal history and a family history of anxiety (as opposed to mood disorders), and it has positive open data in adolescents with bipolar depression and in a controlled study of maintenance (in teenagers 13–17, but not in preteens 10–12) (Findling et al. 2015). With better mood stabilization, anxiety symptoms usually diminish…, and we would pursue these strategies [instead of using] antidepressants for depression and anxiety in young children with bipolar disorder.”
“Carbamazepine appears to be more effective in adults with bipolar who have [no] family history of mood disorders,” unlike lithium, which seems to work better in people who do have a family history of mood disorders.
“While the overall results of oxcarbazepine in childhood mania were negative, they did exceed placebo in the youngest patients (aged 7–12) as opposed to the older adolescents (13–18) (Wagner et al. 2006).
“There are long-acting preparations of both carbamazepine (Equetro) and oxcarbazepine (Oxtellar) that would allow for all nighttime dosing to help with sleep and reduce daytime side effects and sedation. Although data [on] anti-manic and antidepressant effects in adults are stronger for carbamazepine than oxcarbazepine,” there are good reasons to consider oxcarbazepine. First, there is the finding mentioned above that oxcarbazepine worked best in the youngest children. Second, there is a lower incidence of severe white count suppression on oxcarbazepine. Third, it has less of an effect on liver enzymes than carbamazepine. However, low blood sodium levels are more frequent on oxcarbazepine than carbamazepine.
Other Atypical Antipsychotics That May Improve Depression
Playing Tackle Football Before Age 12 May Be Bad for the Brain
A 2017 study found that men who began playing American tackle football before age 12 were more likely to have depression, apathy, problems with executive functioning, and behavioral issues in adulthood than their peers who began playing football after age 12. Duration of football play did not seem to matter—those men who stopped playing football after high school were just as likely to be affected in adulthood as those who went on to play football in college or professionally.
The study by Michael L. Alosco and colleagues was published in the journal Translational Psychiatry. It included 214 men (average age 51) who had played football in their youth, but not other contact sports. The men reported their own experiences with depression, apathy, cognitive function, and behavioral regulation. Those who began football before age 12 were twice as likely to report impairment in behavioral regulation, apathy, and executive function than those who began playing later. Those who started younger were also three times more likely to have clinical depression in adulthood than those who started older.
According to Alosco and colleagues, between ages 9 and 12, the brain reaches peak maturation of gray and white matter volume, and synapse and neurotransmitter density also increases. The repeated head injuries that can occur during youth football play during this time may disrupt neurodevelopment, with lasting negative effects.
One drawback to the study was that recruitment was not random—men who volunteered for the study might have done so due to a recognition of their own cognitive problems. However, the results suggest more study is needed, and caution is encouraged when making decisions about youth football participation. Some youth football leagues have begun placing greater limits on the type of contact allowed during play.
Children Who Are Bullied Have Poorer Mental Health
A 2017 study of twins between the ages of 11 and 16 found that being bullied around age 11 caused anxiety, depression, hyperactivity and impulsivity, inattention, and conduct problems, some of which lasted for years. Participants recorded their experiences with physical or verbal bullying, social manipulation, and property attacks (trying to break one’s belongings, for example).
The effects of bullying decreased over time. The bullied children were still significantly more anxious than their non-bullied twins two years later, but this difference faded by the five-year mark. However, paranoid thoughts and cognitive disorganization did persist for 5 years.
The twin study design helped researchers zone in on the causal effect bullying might have on the children’s mental health, rather than other factors the twins shared, such as genetics or family environment. The study included 11,108 twins born in England and Wales.
The research by Timothy Singham and colleagues was published in the journal JAMA Psychiatry. Interestingly, the researchers found that prior mental health difficulties increased children’s likelihood of being bullied, such that being bullied could be considered a symptom of preexisting vulnerabilities. Singham and colleagues suggest that in addition to interventions to reduce bullying and address familial factors that might make children susceptible to bullying, children should also be taught resilience skills.
FDA Approves Lurasidone for Bipolar Depression in Children and Adolescents
 In March 2018, the US Food and Drug Administration approved the antipsychotic drug lurasidone (Latuda) for the treatment of bipolar depression in children and adolescents aged 10–17 years. Lurasidone was already approved for adults with bipolar depression, as an add-on treatment to the mood stabilizers lithium and valproate, and for schizophrenia in people aged 13 years and up.
In March 2018, the US Food and Drug Administration approved the antipsychotic drug lurasidone (Latuda) for the treatment of bipolar depression in children and adolescents aged 10–17 years. Lurasidone was already approved for adults with bipolar depression, as an add-on treatment to the mood stabilizers lithium and valproate, and for schizophrenia in people aged 13 years and up.
A 6-week clinical trial in 347 youth compared lurasidone (in doses ranging from 20 to 80 mg/day) to placebo and found that those who received lurasidone showed significant improvements in depression compared to those who received placebo. The average dose was below 40 mg/day. The research by Melissa P. DelBello and colleagues was published in the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry in 2017.
In the study, lurasidone was well-tolerated. Side effects included nausea, sleepiness, minimal weight gain, and insomnia. Lurasidone did not seem to affect glucose, triglycerides, cholesterol, or blood pressure.
Editor’s Note: This is the first drug to be approved for bipolar depression in this age range. This editor (Robert M. Post) has written extensively on the high incidence of childhood onset bipolar disorder in the US, and especially in the offspring of parents with bipolar disorder.
It is important to be alert to the possibilities of depression and bipolar disorder in children in the US (along with related illnesses such as anxiety, oppositional defiant disorder, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)), as early-onset illness tends to have a more severe long-term course than adult-onset depression and bipolar disorder. A longer delay between the emergence of symptoms and the first treatment for bipolar disorder is also a risk factor for more severe depression, more time depressed, and a poorer outcome in adulthood.
Parents of children aged 2-12 who have mood or behavioral problems are encouraged to consider joining the Child Network at our website, bipolarnews.org (click on the tab for the Child Network). By participating in this research network, parents are able to make a weekly rating of the severity of their children’s symptoms of anxiety, depression, ADHD, oppositional behavior, and mania via the secure website. The ratings can then be shared with the child’s clinicians for easy visualization of the course of symptoms over time, which may help with treatment decisions.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids Improve ADHD
 A 2017 systematic review and meta-analysis found that omega-3 fatty acid supplementation improves symptoms of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children and adolescents. The article by Jane Pei-Chen Chang and colleagues in the journal Neuropsychopharmacology identified seven randomized controlled trials in which omega-3 fatty acids improved clinical symptoms of ADHD, and three trials in which omega-3s improved cognitive measures associated with attention.
A 2017 systematic review and meta-analysis found that omega-3 fatty acid supplementation improves symptoms of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children and adolescents. The article by Jane Pei-Chen Chang and colleagues in the journal Neuropsychopharmacology identified seven randomized controlled trials in which omega-3 fatty acids improved clinical symptoms of ADHD, and three trials in which omega-3s improved cognitive measures associated with attention.
The meta-analysis also found that children and adolescents with ADHD have lower than normal levels of the omega-3s DHA and EPA, in addition to lower total levels of omega-3s measured in blood and cheek tissues.
Chang and colleagues suggest that omega-3 fatty acid supplementation is a potentially helpful and largely risk-free treatment option for ADHD in children and adolescents.
Reduced Functional Connectivity of Amygdala Linked to Autism in Pre-School Boys
A 2016 study in the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry found that preschool-aged boys with autism have weaker functional connectivity of the amygdala than typically-developing children of the same age. Researchers led by Mark D. Shen used resting-state functional connectivity magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to measure how connected the amygdala was to other regions of the brain in 72 young boys (average age 3.5).
The boys with autism had weaker connectivity between the amygdala and regions linked to social communication, language deficits, and repetitive behaviors. These areas include the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), bilateral temporal lobe, striatum, thalamus, cingulate cortex, and cerebellum.
The weaker the connectivity between these regions, the more severe the boys’ autism symptoms were. They showed impairments in overall cognitive ability and both verbal and nonverbal ability.