Midday Bright Light Therapy Improved Bipolar Depression
A study by Dorothy K. Sit and colleagues published in the American Journal of Psychiatry in 2017 found that delivering bright white light therapy to patients with bipolar depression between the hours of noon and 2:30pm improved their depression compared to delivering inactive dim light, and did not cause mood switches into mania. The study included 46 patients with moderate bipolar depression, no hypomania and no psychosis.
The active therapy group was exposed to broad-spectrum bright white fluorescent light at 7,000 Lux while the inactive group received dim red light at 50 Lux. Both groups were instructed to sit 12 inches from the light and face it without looking directly at it. The therapy began with 15-minute afternoon sessions and increased to 60 minutes per day by 4 weeks. Participants were assessed weekly. Remission rates increased dramatically in the active group beginning in the fourth week. At weeks 4 through 6, the remission rate for those in the active bright light group was 68.2% compared to only 22.2% in the dim light group.
Mean depression scores were better in the treated group, as were global functioning and response rates.
Some participants were taking antidepressants concurrently, and these participants were evenly distributed across the two study groups.
An earlier pilot study by the same researchers had found that bright light therapy delivered in the morning was followed by some hypomanic reactions or bipolar cycling. The midday sessions did not cause any mood switching.
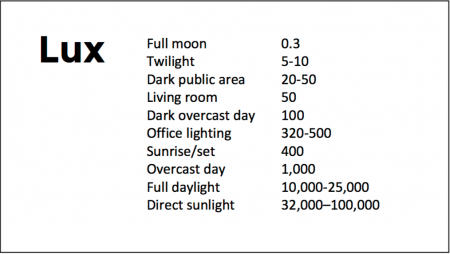
Bright light therapy is often used to treat seasonal affective disorder (SAD) using a 10,000 Lux light box. This study took place mostly during the fall and winter months.
Editor’s Note: Bright light therapy is generally safe and boasts a high remission rate. Light boxes can be acquired without a prescription and are portable and easy to use. Midday light may have the best results and the least risk of provoking a mood switch into mania.
Midday Bright Light Therapy Effective in Bipolar Disorder
A recent study of 93 adults with bipolar disorder suggests that midday bright light therapy can be an effective adjunctive treatment for bipolar depression. The study by Dorothy Sit and colleagues was presented at the 2015 meeting of the Society for Biological Psychiatry. Participants had been diagnosed with bipolar I or II disorder, were in a current episode of depression, and were taking stable doses of mood stabilizing medication. They were randomized to receive either 7000-lux broad spectrum light for 45 to 60 minutes each day for six weeks or 50 lux dim red light. The comparison was dramatic: remission rates were 56.5% among those exposed to the 7000-lux light, and 14.3% among those who were exposed to the dim light. Those who received the bright light also reported better sleep quality and less suicidality.
Editor’s Note: These results are striking and raise the issue of whether midday bright light is more effective than early morning bright light, the usual recommendation for seasonal affective disorder (SAD) and other forms of depression. Until comparative studies are available, using midday light may be the way to go.
Bright Light Therapy Adds to Venlafaxine’s Antidepressant Effects
A study by Pinar Güzel Özdemir and colleagues in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry indicates that bright light therapy may improve the effects of antidepressant venlafaxine (Effexor) in patients diagnosed with major depression for the first time. In the study of 50 inpatients, half received 150mg of venlafaxine at 7am each morning, while half received 150mg of venlafaxine plus 60 minutes of 7000 lux bright light therapy at 7am each morning. Beginning after the first week of treatment, both groups showed significant improvement in depression and negative mood states throughout the eight-week study. However, at weeks 2 and 4, the patients who received bright light therapy showed greater reductions in depression, with 76% reaching the target goal of treatment after four weeks compared to 44% of the venlafaxine-only group.
Both venlafaxine and combined treatment with venlafaxine and bright light therapy reversed symptoms of depression, but adding bright light therapy may produce more rapid, stronger effects. Larger studies are needed to replicate these effects and determine whether they are long-lasting.
Using Light to Improve Sleep and Depression
At the 2018 meeting of the North Carolina Psychiatric Association, researcher Chris Aiken described the phenomenon of sleep inertia, when people are awakened from deep sleep by an alarm, rather than waking at the end of a sleep cycle, and are groggy for 15 minutes. Depressed people may stay groggy for 4 hours. A dawn simulator may help. These lights turn on gradually over the course of 30 to 60 minutes, reaching 250 lux while the patient is still asleep. Dawn simulators have worked in eight out of ten controlled clinical trials to help people with seasonal affective disorder, adolescents, and normal adults wake up more easily. They range in cost from $25 to $90 and some brands include PER2LED or LightenUp. Aiken says dawn simulators can improve depression, sleep quality, and cognition.
Evening and nighttime light: Bright lights and blue light, like the light that comes from electronic screens, can shut down the body’s secretion of melatonin, making people awake and alert in the evening when they should be getting sleepy. Dim light or glasses that filter out blue light allow increases in melatonin secretion in the evening, while bright light suppresses it. Missing this early melatonin pulse creates “night owls” who have delayed sleep onset.
Because light still reaches our eyes through our eyelids as we sleep, even low-level light during the night impairs sleep, cognition, and learning, and increases the risk of depression by a hazard ratio of 1.8 (about double the risk). A 2017 study by Kenji Obayashi in the American Journal of Epidemiology found that bedroom light above 5 lux elevated rates of depression in older adults after two years of followup. Living room light averaged around 50 lux and increased depression further.
The treatment is turning off TVs, electronic screens, and cellphones in the evening or wearing blue-blocking glasses, which can be found for less than $10. Blue-blocking glasses can increase calmness and reduce anxiety, and even are effective in treating mania. Then, during sleep, wear an eye mask or get light-blocking blinds or curtains for windows. For a complete blackout, use blackout curtains, aluminum foil over windows, electric tape over LED lights, or try sleeping in the basement.
Aiken suggests that to re-instate healthy sleep patterns, people should institute virtual darkness from 6pm to 8am, including wearing blue-blocking glasses when out of bed. Then they should institute total darkness or wear an eye mask when in bed. When symptoms improve, this routine can gradually be shifted to begin later in the evening, such as two hours before bedtime.
Blue light filters are also available for smartphones and tablets including Apple Nightshift mode, Kindle BlueShade, and Android Twilight and Blue Light Filter.
Glasses that filter out blue light include Uvex Ultraspec 2000, 50360X ($7 on Amazon) and Uvex Skyper 351933X ($7-10 on Amazon). The website lowbluelights.com sells blue-blocking glasses from $45 and a variety of other blue-free lighting products such as lightbulbs and flashlights.
Bright light therapy for unipolar and bipolar depression: 30 minutes of bright light (7,500 to 10,000 lux) in the morning can help treat depression in unipolar and bipolar disorder and seasonal affective disorder. The effects usually take 3 to 7 days to set in, but they only last while a patient continues using the bright light in the morning. Researcher Dorothy K. Sit and colleagues found that bright light therapy in the morning sometimes caused hypomanic reactions in people with bipolar disorder, and reported in a 2018 article in the American Journal of Psychiatry that midday light therapy (from noon to 2:30pm) was also effective without this unwanted effect. However, a 2018 article by Ne?e Yorguner Küpeli and colleagues in the journal Psychiatry Research suggested that a half hour of morning light for two weeks was sufficient to bring about improvement in 81% of patients with bipolar disorder and did not cause serious side effects.
Melatonin regimen for sleep onset delay: Melatonin can be used to treat severe night-owls with a very late onset of sleep (for example, going to bed at 2 or 3am and sleeping late into the morning). Melatonin can help with sleep onset to some extent when used at bedtime, but in those with an extreme phase shift, researcher Alfred J. Lewy recommends a regimen of low dose priming with 400–500 micrograms of melatonin at 4pm and then a full dose of 3 milligrams of melatonin at midnight. The 4pm priming dose helps pull back the delayed onset of the body’s secretion of melatonin toward a more normal schedule.
Inflammation Predicts Poor Response to Sleep Deprivation with Light Therapy
A 2017 article by Francesco Benedetti and colleagues in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry reports that people with bipolar depression who have higher levels of certain inflammatory markers may have a poor antidepressant response to the combination of sleep deprivation and light therapy, compared to those with lower levels of inflammation.
The study included 37 participants with bipolar disorder who were in the midst of a major depressive episode. Of those, 31 participants (84%) had a history of poor response to antidepressant medication. The patients were treated with three cycles of total sleep deprivation and light therapy within one week, a combination that can often bring about a rapid improvement in depression.
Depression improved in a total of 23 patients (62%) following the therapy. Blood analysis showed that compared to those who had a good response, the non-responders had higher levels of five intercorrelated inflammatory markers: IL-8, MCP-1, IFN-gamma, IL-6, and TNF-alpha. Those with higher body mass index had more inflammation, indirectly decreasing response to the therapy.
Light Therapy Effectively Treats Non-Seasonal Depression
Doctors have known for some time that treatment with high-intensity light (7,000–10,000 Lux) can improve seasonal depression. In an 8-week study published in the journal JAMA Psychiatry in 2015, researcher Raymond Lam compared four different treatment options for non-seasonal major unipolar depression: bright light therapy for 30 minutes per day first thing in the morning, 20 mg of the antidepressant fluoxetine per day, combined bright light therapy and fluoxetine, and a placebo device paired with a placebo pill.
The combination of bright light therapy and fluoxetine produced remission in 58.6% of the participants who received it, compared to remission rates of 43.8% for bright light alone, 19.4% for fluoxetine alone, and 30% for placebo. It is notable that the effects of fluoxetine did not exceed those of placebo, but the effects of light alone did. There were few side effects in any group.
These data provide convincing evidence of the efficacy of light therapy in the treatment of non-seasonal unipolar depression. Use of light therapy for non-seasonal depression should now be more routinely considered, particularly when combined with antidepressant treatment.
Patients who had previously failed to respond to two or more antidepressants and patients with bipolar depression were excluded from the study. Bright light therapy administered in the morning can sometimes bring about mixed states in people with bipolar disorder. A 2007 case study by D. Sit and colleagues in the journal Bipolar Disorders found that midday light led to more improvement and less risk of mixed states than morning light among women with bipolar disorder.
One Night of Sleep Deprivation Can Rapidly Improve Depression
 One night of sleep deprivation can bring about rapid improvement in depression symptoms the following day. A 2017 meta-analysis by Elaine M. Boland and colleagues in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry summarizes the findings from 66 studies of sleep deprivation for unipolar and bipolar depression and finds that the technique produced a response rate of 45% in randomized controlled studies.
One night of sleep deprivation can bring about rapid improvement in depression symptoms the following day. A 2017 meta-analysis by Elaine M. Boland and colleagues in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry summarizes the findings from 66 studies of sleep deprivation for unipolar and bipolar depression and finds that the technique produced a response rate of 45% in randomized controlled studies.
It did not seem to matter whether patients experienced full or partial sleep deprivation, whether they had unipolar or bipolar depression, or whether or not they were taking medication at the time. Age and gender also did not affect the results of the sleep deprivation.
Extending the Effects
While sleep deprivation can rapidly improve depression, the patient often relapses after the next full night of sleep. There are a few things that can prevent relapse or extend the efficacy of the sleep deprivation. The first is lithium, which has extended the antidepressant effects of sleep deprivation in people with bipolar disorder.
The second strategy to prevent relapse is a phase change. This means going to sleep early in the evening the day after sleep deprivation and gradually shifting the sleep schedule back to normal. For example, after an effective night of sleep deprivation, one might go to sleep at 6pm and set their alarm for 2am. Then the next night, they would aim to sleep from 7pm to 3am, the following night 8pm to 4am, etc. until the sleep wake cycle returns to a normal schedule.
A 2002 article by P. Eichhammer and colleagues in the journal Life Sciences suggested that repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS), electromagnetic stimulation of the scalp over the prefrontal cortex, could help maintain improvement in depression following a night of partial sleep deprivation for up to four days.
Bright light therapy may also help. Read more
Rapid-Onset Antidepressant Treatments
At the International College of Neuropsychopharmacology (CINP) World Congress of Neuropsychopharmacology in 2014, several presentations and posters discussed treatments that bring about rapid-onset antidepressant effects, including ketamine, isoflurane, sleep deprivation, and scopolamine.
Ketamine’s Effects
Multiple studies, now including more than 23 according to researcher William “Biff” Bunney, continue to show the rapid-onset antidepressant efficacy of intravenous ketamine, usually at doses of 0.5 mg/kg over 40 minutes. Response rates are usually in the range of 50–70%, and effects are seen within two hours and last several days to one week. Even more remarkable are the six studies (two double-blind) reporting rapid onset of antisuicidal effects, often within 40 minutes and lasting a week or more. These have used the same doses or lower doses of 0.1 to 0.2mg/kg over a shorter time period.
Attempts to sustain the initial antidepressant effects include repeated ketamine infusions every other day up to a total of six infusions, a regimen in which typically there is no loss of effectiveness. Researcher Ronald Duman is running a trial of co-treatment with ketamine and lithium, since both drugs block the effects of GSK-3, a kinase enzyme that regulates an array of cellular functions, and in animals the two drugs show additive antidepressant effects. In addition, lithium has been shown to extend the acute antidepressant effects of one night of sleep deprivation, which are otherwise reversed by a night of recovery sleep.
Ketamine’s effects are related to the neurotransmitter glutamate, for which there are several types of receptors, including NMDA and AMPA. Ketamine causes a large burst of glutamate presumably because it blocks NMDA glutamate receptors on inhibitory interneurons that use the neurotransmitter GABA, causing glutamatergic cells to lose their inhibitory input and fire faster. While ketamine blocks the effects of this glutamate release at NMDA receptors, actions at AMPA receptors are not blocked, and AMPA activity actually increases. This increases brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which is also required for the antidepressant effects of ketamine. Ketamine also increases the effects of mTOR, a kinase enzyme that regulates cell growth and survival, and if these are blocked with the antibiotic rapamycin, antidepressant effects do not occur.
In animal studies, ketamine increases dendritic spine growth and rapidly reverses the effects of chronic mild unpredictable stressors on the spines (restoring their mature mushroom shape and increasing their numbers), effects that occur within two hours in association with its rapid effects on behaviors that resemble human depression.
About 50–70% of treatment-resistant depressed patients respond to ketamine. However, about one-third of the population has a common genetic variation of BDNF in which one or both valine amino acids that make up the typical val-66-val allele are replaced with methionine (producing val-66-met proBDNF or met-66-met proBDNF). The methionine variations result in the BDNF being transported less easily within the cell. Patients with these poorly functioning alleles of BDNF are less likely to get good antidepressant effects from treatment with ketamine.
Ketamine in Animal Studies
Researcher Pierre Blier reviewed the effects of ketamine on the neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. In rodents, a swim stress test is used to measure depression-like behavior. Researchers record how quickly the rodents give up trying to get out of water and begin to float instead. Blier found that ketamine’s effects on swim stress were dependent on all three neurotransmitters. For dopamine, ketamine’s effects were dependent on increases in the number of dopamine cells firing, not on the firing rate, and for norepinephrine, ketamine’s effects were dependent on increases in burst firing patterns. Each of these effects was dependent on glutamate activity at AMPA receptors. Given these effects, Blier believes that using ketamine as an adjunct to conventional antidepressants that tend to increase these neurotransmitters may add to its clinical effectiveness.
Important Anecdotal Clinical Notes
Blier reported having given about 300 ketamine infusions to 25 patients, finding that two-thirds of these patients responded, including one-third who recovered completely, while one-third did not respond to the treatment. Patients received an average of 12 infusions, not on a set schedule, but according to when they began to lose response to the last ketamine infusion. If a patient had only a partial response, Blier gave the next ketamine treatment at a faster rate of infusion and was able to achieve a better response. These clinical observations are among the first to show that more than six ketamine infusions may be effective and well tolerated. Read more