TDCS May Improve ADHD Symptoms
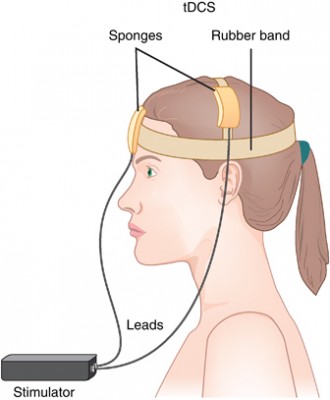 Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) is a therapy in which electrodes placed on the skull deliver a steady, low level current to the brain, changing its threshold for electrical activity. Anodal tDCS to the prefrontal cortex can improve working memory. In a small 2017 study in the Journal of Neural Transmission, Cornelia Soff and colleagues found for the first time that tDCS may improve symptoms of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) is a therapy in which electrodes placed on the skull deliver a steady, low level current to the brain, changing its threshold for electrical activity. Anodal tDCS to the prefrontal cortex can improve working memory. In a small 2017 study in the Journal of Neural Transmission, Cornelia Soff and colleagues found for the first time that tDCS may improve symptoms of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
People with ADHD tend to have underactivation of the prefrontal cortex and deficits in working memory. The study randomized 15 young people aged 12–16 (three girls and twelve boys) to receive either real tDCS or a sham stimulation. The anodal tDCS was delivered at 1 mA targeting the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex for 5 days. Those participants who received tDCS showed a reduction in inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity compared to those who received the sham stimulation. The effects were more pronounced 7 days after the stimulation, suggesting that tDCS’ effects may be long-term. Larger, more definitive trials are needed to clarify the effects of tDCS on ADHD, but these preliminary findings are promising.

