Lithium Is Unparalleled in It Range of Efficacy in the Mood Disorders
Most clinicians are aware of lithium’s superiority over other mood stabilizers in bipolar illness prophylaxis. New data suggests this might also apply to the atypical antipsychotics.
Lithium is also not only an effective adjunct to antidepressant in unipolar depression, but has some of the best data for its use in long term prevention. In bipolar disorder prophylaxis it is particularly effective in those with classical presentations of discrete episodes of euphoric mania, treatment early in the course of illness, lack of anxiety and substance comorbidities, and a positive history of mood disorder in first-degree relatives.
New data indicates that it is also effective in childhood onset mania, and open long term follow ups indicate that it is more effective than other mood stabilizers or atypical antipsychotics.
Despite the compelling effectiveness data and many ancillary benefits, survey data indicates very low levels of current lithium use in both adult and child bipolar disorder. The conventional view, shared by most patients and many clinicians, underestimates its range of effectiveness and potential benefits while overestimating it is side effects. A more balanced view is needed as neglect of wider use of lithium is detrimental to the long term outcome of immense numbers of patients.
Robert M. Post, MD
Quotes from Kay Jamison, PhD, Professor of Psychiatry at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine
“There’s this notion that mania and depression are uncommon or certainly that mania is uncommon, and that is not true. The bipolar illness spectrum is associated with a lot of very damaging things, most importantly suicide, but also alcohol and drug use and violence. It’s a very early onset illness, so unlike dementia or heart disease, which hit people much later in life, these hit people when they’re young. They have to cope with [bipolar disorder] when they’re young, and they don’t have the experience of life to help them out. That tends to be overlooked, what it does to people and their families, and how devastating it is. First and foremost, I would want people to know that it’s treatable, imperfectly treatable, but treatable, and it’s important to get it treated….It’s completely reasonable to extend hope to somebody who has bipolar illness but to also make it very clear that it’s hard. But draw upon what you know. Read, read, read. Learn about it. Badger your doctors. Why are they doing this? What’s the point of this drug rather than that drug? Always question what’s happening to you. “
Editor’s Note: One of the most important things that people with mood disorder can do, is to every night chart chart their mood, functioning, sleep, medications, and other symptoms so that this graphic longitudinal assessment can be shown to their physician/therapist at each visit. This will help most efficiently refining the treatment regimen for an optimal long term outcome. See www.bipolarnews.org (click on Personal Calendar or Life Chart) for a good format for doing these daily ratings.
Parents of children (age 2-12) with mood and behavioral disorders can each week rate the severity of their child’s symptoms of anxiety, depression, ADHD, oppositional behavior, and mania on a secure website. This can be printed out to assist physicians with the assessment of need for treatment and of how well treatment is working. Informed consent for this system is available at www.bipolarnews.org (click on Child Network).
LITHIUM IS VASTLY UNDER-UTILIZED IN BIPOLAR DISORDER LEADING TO PREMATURE DEATH AND DISABILITY: WE WANT YOU TO HELP REVERSE THIS ANOMALOUS TREND
We are looking for people who have had a good course of illness with lithium included in their treatment regimen to help spread the word that lithium works extremely well and its side effects are erroneously overestimated.
We are hoping that you, as a good responder to lithium, will start a positive chain letter to fellow patients, family members, and friends suggesting that earlier and greater use of lithium would be overwhelmingly likely to improve the lives of many individuals with bipolar illness.
Why do we need you? It is because every expert in the treatment of bipolar illness of whom I am aware of has long advocated for greater and earlier use of lithium, but with little success. Lithium is widely recognized as a first line and treatment of choice for bipolar disorder, yet its use remains miniscule. In the US somewhere between only 10 to 27% of bipolar patients are given lithium. This has tragic consequences.
Treatment outcomes of the illness remain poor with vast numbers of patients experiencing pain, disability, memory loss, and loss of many years of life expectancy from suicide, cardiovascular disease, and many other psychiatric and medical disabilities. Compared to the general population, people with bipolar illness lose between 10-15 years of life expectancy. A new study by Carvalho et al (Psychother Psychosom, 2024) of more than 50,000 patients with a first episode of mania compared to more than 250,000 matched controls have a significantly higher rate of all cause mortality and a 10 fold increase of suicide. Those treated with lithium have a significantly lower rate of both all cause mortality and of suicide.
In addition, lithium has many other assets, besides the treatment of mania, of which most people are unaware and the liabilities of its side effects profile are over estimated. Some of the positive’s of lithium are listed below. Please print this ‘list of assets of lithium out and give it to everyone who might be interested. Patients with bipolar disorder should also print it out for their treating physicians, particularly if they do not as yet have lithium in their treatment regimen.
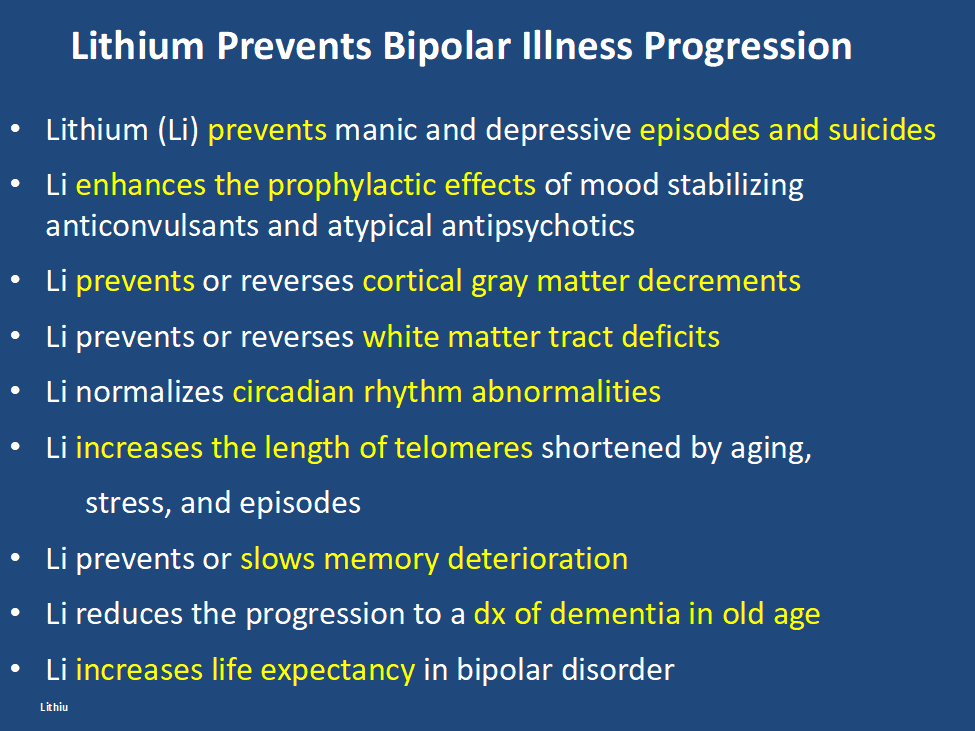
At the same time lithium’s side effects are over emphasized. The biggest concern is that lithium causes end stage kidney dysfunction eventually leading to dialysis. This is likely based on findings that individuals with bipolar disorder have an increase in most medical illnesses including chronic kidney disease compared to the general population. However, two very large trans-national studies of bipolar patients in Denmark and in Israel have found that bipolar patients treated with lithium are no more likely to get end stage renal disease than those treated with anticonvulsants such as valproate (Depakote). Lithium does cause low thyroid function in 15-25% of patients, but this is easily corrected with replacement of thyroid hormone. Many other side effects of lithium such as tremor can be managed by using lower doses.
Bottom line: Lithium gets a bad rap.
Please tell everyone you know about the new data on lithium’s relative safety and its many assets including reducing all cause mortality and suicide and restoring many years of lost life expectancy. 14 of 15 studies indicate that if lithium is started early in course of bipolar disorder it is more effective than starting it after many episodes or rapid cycling have occurred. It also works well in youngsters with bipolar disorder and better in comparison to other treatments (Hafeman et al 2020). In addition, after a first mania, patients randomized to a year of treatment with lithium do better on all outcome measures than those given a year on quetiapine (Seroquel) including manic and depressive severity, functioning, cognition, and normality of brain imaging (Berk et al 2017).
One more conceptual breakthrough: Lithium is literally the original salt of the earth. It was generated just 20 minutes after the big bang origin of the universe and is considered an essential element. Common table salt, sodium chloride, emerged only many millions of years after the big bang. Also in six studies across multiple countries, higher minute levels of lithium in the drinking water have been shown to reduce the incidence of suicide in the general population. A very low dose of lithium 150-300mg/day has also been shown to reduce the progression of mild cognitive impairment in otherwise well elderly volunteers.
Do a good thing for other people. Relay this new view of lithium to everyone you can think of in hope that they will help get the word out to many others and improve the life, functioning, and longevity of those with bipolar disorder.
Suggest and promulgate a new mantra:
“LITHIUM PREVENTS EPISODES OF BIPOLAR ILLNESS, AND PROTECTS THE BRAIN AND BODY”
Vitamin B6 Plus Lithium Helps Ease Mania Symptoms in Patients With Bipolar Disorder
Daily vitamin B6 (40mg/day), but not B1 (100mg/day), as an adjunctive therapy to lithium was associated with the improvement of mood symptoms in hospitalized patients with bipolar disorder experiencing a manic episode, according to a study published in the Journal of Affective Disorders 2024; 345 103-111: Zandifar et al.
Metabolic Changes in Brain of Bipolar at Autopsy
Highlights from the International Society for Bipolar Disorders Conference Posters and Presentations, Chicago, June 22-25, 2023
Graeme Preston reported on the brain of autopsied bipolar patients having increases aspartate and citrulline, while those with unipolar depression had decreases in the TCA cycle.
He saw increases in acetyl carnitine in manic bipolar patients versus bipolar depressed patients, which is of interest in relationship to the putative antidepressant effects of acetyl-L-carnitine in animal models of depression and in humans.
Positive Effects of Low-Dose Lithium (LDL)
Highlights from the International Society for Bipolar Disorders Conference Posters and Presentations, Chicago, June 22-25, 2023
Rebecca Strawbridge of the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience, King’s College London reported on 18 articles that were examined and grouped according to outcome domain (cognition, depression, mania, and related constructs e.g., suicidality). Significant benefits (versus placebo) were identified for attenuating cognitive decline, and potentially as an adjunctive therapy for people with depression/mania. Across studies, LDL (~serum level ?0.6 mmol/L) was reported to be safe.
The Systematic Treatment Optimization Program for Early Mania
Highlights from the International Society for Bipolar Disorders Conference Posters and Presentations, Chicago, June 22-25, 2023
A. Rathseesh and L. Yatham reported on the importance of systematic vigorous treatment of a first manic episode. If more episodes occurred, losses in cognition did not fully recover. All patients remitted within 1 year of their first mania. Recurrence occurred in 58% by year 1 and 74% by year 4. Predictors of functional recovery included sustained euthymia, especially absence of depressive symptoms, good cognitive functioning, and maintaining a normal weight. More aggressive treatment to prevent relapses in years 1-4 after a first manic episode appears needed and how exactly to achieve this requires further study.
Nighttime Bedroom Light Exposure Increases Episode Relapses in Bipolar Disorder
Highlights from the International Society for Bipolar Disorders Conference Posters and Presentations, Chicago, June 22-25, 2023
Yuichi Esaki of Okehazama Hospital reported that “Of the 172 participants, 39 (22%) experienced manic or hypomanic episodes (during 2 years of follow up). In the Cox proportional-hazards model, the hazard ratio (HR) for manic/hypomanic episode relapses was significantly higher when the average nighttime illuminance was ?3 lux (n = 71) than when it was <3 lux (n = 101; HR, 2.54; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.33–4.84)… Keeping the bedroom dark at night may prevent hypomanic and manic episodes.”
“Pharmacotherapy of Bipolar Depression”
Roger McIntyre gave a talk on the “Pharmacotherapy of Bipolar Depression” at the International Society for Bipolar Disorders Conference in Chicago, June 22-25, 2023
He pointed out that, contrary to the many approved agents for mania, there were few FDA-approved drugs for depression in patients with Bipolar Disorders. These approved drugs included: cariprazine (Vraylar); lumateperone (Caplyta); lurasidone (Latuda); quetiapine (Seroquel); and the olanzapine-fluoxetine combination (Symbyax). Other non-approved agents include: lithium, lamotrigine, antidepressants, MAOIs, pramipexole, carbamazepine, ketamine, bupropion+dextromethorphan, amantadine, memantine, and possibly minocycline and celecoxib. Surprisingly, more than 3,000 bipolar depressed patients have been reported to be taking ketamine and that this was not associated with the induction of hypomania or mania.
McIntyre reported on the antidepressant (AD) effects of intra-nasal (i.n.) insulin. The insulin receptor sensitizer metformin had AD effects, but only in those who converted to insulin sensitivity.
McIntyre reported on the mixed effects of the GLP-1 agonists in the prevention of depression (Cooper et al J. Psychiatric Res, 2023). This is of interest in relationship to the bidirectional relationship of diabetes mellitus and depression.
Liraglutide appeared to have an anti-anhedonia effect. Semaglutide had AD and antianxiety effects in animal models of depression.
Recent studies have explored the antidepressant effect of psilocybin. Small studies have indicated that it has rapid onset of AD effects, and, in contrast to ketamine where rapid onset AD and anti-suicidal effects are short lived, the AD effect of psilocybin may be more prolonged.
Ketamine repairs structure and function of prefrontal cortical neurons via glutamate NMDA receptor blocking action, while psilocybin and other psychedelics act via stimulating 5HT2A receptors. One single case study suggested that blocking 5HT2A receptors with trazodone could achieve a rapid onset of AD effects of psilocybin without the psychedelic effects, a very interesting finding that requires replication.
Sleep Disturbances in Pediatric Bipolar NOS is the Same as in BP I
Gianni Faedda reported in Frontiers in Psychiatry (2012) that decreased need for sleep is as prominent in BP NOS children as in those with BP I. So it appears that with the exception of only brief periods of mania in BP NOS, these children have similar characteristics to those with full blown BP I. Thus in addition to the briefer periods of mania, one should be on the look out for all the symptoms of bipolar disorder that are not typical of ADHD, including brief or extended periods of euphoria, decreased need for sleep, more extreme degrees of irritability and poor frustration tolerance, hallucination, delusions, suicidal and homicidal ideation, more severe depression, and increases in sexual interest and actions. When these are present, the bipolar mood instability should be treated first and only then small doses of psychomotor stimulants can be used to treat what ever residual ADHD remains. The typical symptoms of ADHD are very of present and comorbid in childhood onset bipolar disorder and cannot be used to discriminate the two diagnoses. The children with BP NOS are as dysfunctional as those with BP I and take longer to stabilize, so pharmacological treatment may need to be intensive, multimodal, and supplemented by Family Focused Therapy (FFT) or a related family therapy. It is most often not conceptualized as such, but BP NOS as well as BP I should be considered as a medical emergency and handled by a sophisticated pediatrician and/or referred for psychiatric consultation and therapy. The longer bipolar disorder is not treated, the worse the outcome is in adulthood.

