Bipolar Disorder Patients Respond to Ketamine, Esketamine Treatment
(Reposted from the Yale School of Medicine blog)
A small sample of patients with bipolar disorder displayed noteworthy improvement in their depressive symptoms after being treated with the rapid-acting antidepressant intravenous ketamine and the nasal spray esketamine, according to a new Yale led-study.
The study, published October 2 in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, also found that patients were not at higher risk of suffering a manic episode during the acute phase of treatment.
Review: Reconsideration of bipolar disorder as a developmental disorder
Reconsideration of bipolar disorder as a developmental disorder: Importance of the time of onset
Pierre Alexis Geoffroy et al, J Physiology Paris, 2013
Eight admixture studies have demonstrated three homogeneous subgroups of patients with bipolar disorder, identi?ed by their age at onset (early, intermediate and late age at onset), with two cutoff points, at 21 and 34 years.
The early onset group had more: Suicide attempts, rapid cycling, drug and alcohol abuse, psychotic symptoms, panic disorder, OCD, and a positive family history for affective disorder. Early onset illness should be recognized and treated earlier.
Accelerated iTBS Treats Bipolar Depression in 5 Days
Yvette Sheline, of the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, reported that 10 intermittent theta burst stimulations (iTBS) per day for 5 days yielded dramatic improvement in patients with bipolar depression – both immediately after the iTBS as well as at 4 weeks.
Resting-state functional MRI was used to individually target the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (dlPFC), the region most anticorrelated with the subgenual anterior cingulate cortex (sgACC).
Influence of Childhood Maltreatment on Morphometry and Brain Network Architecture in Bipolar Disorder
Martin Teicher of McLean Hospital, Harvard Medical School, reported on the influence of childhood maltreatment on morphometry and brain network architecture in Bipolar Disorder.
“Childhood maltreatment (MAL) is common in individuals with bipolar disorder (BP) and is associated with earlier onset, more severe course, and more comorbidities.” They found that reduced hippocampal volume and white matter alterations were present in those with a history of childhood maltreatment. They concluded that “MAL may act as a sensitizer promoting the emergence of bipolar symptoms in individuals with less severe network abnormalities” than in BP patients with no MAL.
Lithium Is Unparalleled in It Range of Efficacy in the Mood Disorders
Most clinicians are aware of lithium’s superiority over other mood stabilizers in bipolar illness prophylaxis. New data suggests this might also apply to the atypical antipsychotics.
Lithium is also not only an effective adjunct to antidepressant in unipolar depression, but has some of the best data for its use in long term prevention. In bipolar disorder prophylaxis it is particularly effective in those with classical presentations of discrete episodes of euphoric mania, treatment early in the course of illness, lack of anxiety and substance comorbidities, and a positive history of mood disorder in first-degree relatives.
New data indicates that it is also effective in childhood onset mania, and open long term follow ups indicate that it is more effective than other mood stabilizers or atypical antipsychotics.
Despite the compelling effectiveness data and many ancillary benefits, survey data indicates very low levels of current lithium use in both adult and child bipolar disorder. The conventional view, shared by most patients and many clinicians, underestimates its range of effectiveness and potential benefits while overestimating it is side effects. A more balanced view is needed as neglect of wider use of lithium is detrimental to the long term outcome of immense numbers of patients.
Robert M. Post, MD
Lithium vs Anticonvulsants Lamotrigine and Valproate on 10 year physical illness
In a study by lars Kessing in (European Neeuropsychopharmcology Volume 84, July 2024, Pages 48-56) on 169,285 patients taking either lithium or the anticonvulsants Lamotrigine (LTG) or Valproate (VPA) for at least 10 years, there was no difference in physical outcome in any physical outcome, including chronic kidney disease, except for a higher incidence of myxedema.
Other diagnoses that showed no difference included stroke, arteriosclerosis, angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, diabetes mellitus, osteoporosis, dementia, Parkinson’s disease, chronic kidney disease and cancer (including subtypes).
Editors Note: This data further supports an already robust existing literature that lithium is not more likely to cause chronic kidney disease or other physical illnesses than other anticonvulsant treatments with the exception of hypothyroidism. Patient should be made aware of these and the related long term data that lithium is no more likely to cause chronic kidney disease than other treatments and, in some cases, these other treatments cause more end-stage renal failure. The misapprehension that lithium is more toxic than other treatments has led to the vast underutilization of this treatment. Lithium is the treatment of choice for bipolar illness and should be used earlier, more often, and more persistently. When this is done illness outcomes and patient’s well being are significantly improved.
Quotes from Kay Jamison, PhD, Professor of Psychiatry at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine
“There’s this notion that mania and depression are uncommon or certainly that mania is uncommon, and that is not true. The bipolar illness spectrum is associated with a lot of very damaging things, most importantly suicide, but also alcohol and drug use and violence. It’s a very early onset illness, so unlike dementia or heart disease, which hit people much later in life, these hit people when they’re young. They have to cope with [bipolar disorder] when they’re young, and they don’t have the experience of life to help them out. That tends to be overlooked, what it does to people and their families, and how devastating it is. First and foremost, I would want people to know that it’s treatable, imperfectly treatable, but treatable, and it’s important to get it treated….It’s completely reasonable to extend hope to somebody who has bipolar illness but to also make it very clear that it’s hard. But draw upon what you know. Read, read, read. Learn about it. Badger your doctors. Why are they doing this? What’s the point of this drug rather than that drug? Always question what’s happening to you. “
Editor’s Note: One of the most important things that people with mood disorder can do, is to every night chart chart their mood, functioning, sleep, medications, and other symptoms so that this graphic longitudinal assessment can be shown to their physician/therapist at each visit. This will help most efficiently refining the treatment regimen for an optimal long term outcome. See www.bipolarnews.org (click on Personal Calendar or Life Chart) for a good format for doing these daily ratings.
Parents of children (age 2-12) with mood and behavioral disorders can each week rate the severity of their child’s symptoms of anxiety, depression, ADHD, oppositional behavior, and mania on a secure website. This can be printed out to assist physicians with the assessment of need for treatment and of how well treatment is working. Informed consent for this system is available at www.bipolarnews.org (click on Child Network).
LITHIUM IS VASTLY UNDER-UTILIZED IN BIPOLAR DISORDER LEADING TO PREMATURE DEATH AND DISABILITY: WE WANT YOU TO HELP REVERSE THIS ANOMALOUS TREND
We are looking for people who have had a good course of illness with lithium included in their treatment regimen to help spread the word that lithium works extremely well and its side effects are erroneously overestimated.
We are hoping that you, as a good responder to lithium, will start a positive chain letter to fellow patients, family members, and friends suggesting that earlier and greater use of lithium would be overwhelmingly likely to improve the lives of many individuals with bipolar illness.
Why do we need you? It is because every expert in the treatment of bipolar illness of whom I am aware of has long advocated for greater and earlier use of lithium, but with little success. Lithium is widely recognized as a first line and treatment of choice for bipolar disorder, yet its use remains miniscule. In the US somewhere between only 10 to 27% of bipolar patients are given lithium. This has tragic consequences.
Treatment outcomes of the illness remain poor with vast numbers of patients experiencing pain, disability, memory loss, and loss of many years of life expectancy from suicide, cardiovascular disease, and many other psychiatric and medical disabilities. Compared to the general population, people with bipolar illness lose between 10-15 years of life expectancy. A new study by Carvalho et al (Psychother Psychosom, 2024) of more than 50,000 patients with a first episode of mania compared to more than 250,000 matched controls have a significantly higher rate of all cause mortality and a 10 fold increase of suicide. Those treated with lithium have a significantly lower rate of both all cause mortality and of suicide.
In addition, lithium has many other assets, besides the treatment of mania, of which most people are unaware and the liabilities of its side effects profile are over estimated. Some of the positive’s of lithium are listed below. Please print this ‘list of assets of lithium out and give it to everyone who might be interested. Patients with bipolar disorder should also print it out for their treating physicians, particularly if they do not as yet have lithium in their treatment regimen.
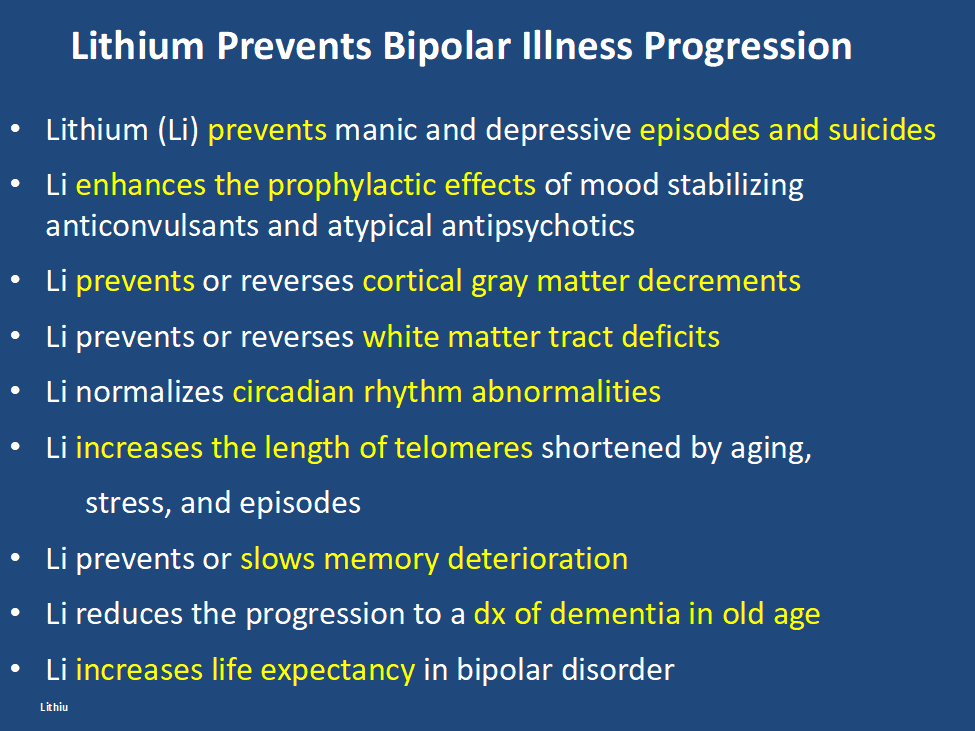
At the same time lithium’s side effects are over emphasized. The biggest concern is that lithium causes end stage kidney dysfunction eventually leading to dialysis. This is likely based on findings that individuals with bipolar disorder have an increase in most medical illnesses including chronic kidney disease compared to the general population. However, two very large trans-national studies of bipolar patients in Denmark and in Israel have found that bipolar patients treated with lithium are no more likely to get end stage renal disease than those treated with anticonvulsants such as valproate (Depakote). Lithium does cause low thyroid function in 15-25% of patients, but this is easily corrected with replacement of thyroid hormone. Many other side effects of lithium such as tremor can be managed by using lower doses.
Bottom line: Lithium gets a bad rap.
Please tell everyone you know about the new data on lithium’s relative safety and its many assets including reducing all cause mortality and suicide and restoring many years of lost life expectancy. 14 of 15 studies indicate that if lithium is started early in course of bipolar disorder it is more effective than starting it after many episodes or rapid cycling have occurred. It also works well in youngsters with bipolar disorder and better in comparison to other treatments (Hafeman et al 2020). In addition, after a first mania, patients randomized to a year of treatment with lithium do better on all outcome measures than those given a year on quetiapine (Seroquel) including manic and depressive severity, functioning, cognition, and normality of brain imaging (Berk et al 2017).
One more conceptual breakthrough: Lithium is literally the original salt of the earth. It was generated just 20 minutes after the big bang origin of the universe and is considered an essential element. Common table salt, sodium chloride, emerged only many millions of years after the big bang. Also in six studies across multiple countries, higher minute levels of lithium in the drinking water have been shown to reduce the incidence of suicide in the general population. A very low dose of lithium 150-300mg/day has also been shown to reduce the progression of mild cognitive impairment in otherwise well elderly volunteers.
Do a good thing for other people. Relay this new view of lithium to everyone you can think of in hope that they will help get the word out to many others and improve the life, functioning, and longevity of those with bipolar disorder.
Suggest and promulgate a new mantra:
“LITHIUM PREVENTS EPISODES OF BIPOLAR ILLNESS, AND PROTECTS THE BRAIN AND BODY”
Vitamin B6 Plus Lithium Helps Ease Mania Symptoms in Patients With Bipolar Disorder
Daily vitamin B6 (40mg/day), but not B1 (100mg/day), as an adjunctive therapy to lithium was associated with the improvement of mood symptoms in hospitalized patients with bipolar disorder experiencing a manic episode, according to a study published in the Journal of Affective Disorders 2024; 345 103-111: Zandifar et al.
Cannabis and Cannabinoids Don’t Work for Pain or Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
Aaron S. Wolfgang, MD and Charles W. Hoge, MD reviewed data on cannabis in JAMA Psychiatry and found that there were big placebo effects and no evidence for effectiveness of cannabis in military personal.
This negative data, along will all the liability of cannabis potentially causing or triggering psychosis, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia (as well as possibly contributing to cognitive dysfunction, worsening anxiety and depression in patients with mood disorders) makes the use of pot for medical purposes an entirely foolhardy proposition, as well as a waste of money.
Legalization of pot has helped people avoid jail but precipitated a rash of use and over use.
So the bottom line from this editor is: Get Your Priorities Straight. Cannabis and Cannabinoids Don’t Work for Pain or Posttraumatic Stress Disorder and they Worsen Most Everything Else. Save your Money and Do Something Nice for Yourself and Others Instead.

