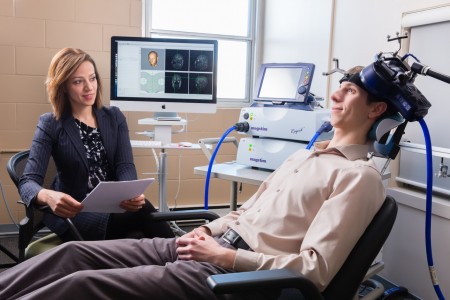
US Lags Behind Canada in Access to RTMS
At the 2015 meeting of the Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Society, Linda Carpenter, an American researcher who specializes in repeated transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS), a method of treating depression by using a magnetic coil placed near the scalp to stimulate neurons, compared notes with Jeff Daskalakis, a Canadian researcher who also studies rTMS.
Carpenter described the limited approval rTMS enjoys in the US. RTMS has been approved by the Federal Drug Administration for the treatment of unipolar depression under very limited parameters (only at a frequency of 10Hz). RTMS has limited availability in the US, and many healthcare companies do not cover it. Providers face scrutiny of study recruitment practices and recordkeeping by insurers and the Joint Commission (formerly the Joint Commission of Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations), which assesses healthcare quality.
In contrast, Daskalakis and his Canadian colleagues can and do use rTMS to treat a broader range of illnesses including bipolar disorder. In Canada rTMS is used to treat unipolar depression, schizophrenia, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and clinicians can adjust the parameters to treat adolescents and the elderly.
The situation in the US is unfair. Because rTMS has not been approved for the treatment of bipolar disorder, Carpenter and other clinicians in the US are unable to treat bipolar depression even though a wide range of experts and published studies report that rTMS is as effective (or possibly even more so) for patients with bipolar depression than for those with unipolar depression.
Few treatments are available for bipolar depression. The discrepancy is even sadder when one considers that there are already more than 20 FDA-approved antidepressants that can be used to treat unipolar depression, but only three approved medications for bipolar depression. Bipolar depression is an orphan illness, which lacks a powerful voice advocating for more treatment research about optimal therapeutic strategies. Read more
Anxiety and Depressive Disorders Often Precede the Onset of Bipolar Disorder in Those At High Risk Due to Family History
At the 2012 meeting of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (AACAP) meeting, Anne Duffy and Gabrielle A. Carlson sponsored a symposium on the association between anxiety and minor mood disorders and subsequent bipolar disorder in those at high risk. Researchers presenting at the symposium consistently found that there is a sequence in which young people at high risk for bipolar disorder develop increasingly severe illnesses: first anxiety, then mood disorders, then bipolar illness.
One difference: the incidence of childhood-onset bipolar disorders in those at high risk because a parent has the disorder was lower in Canada, Switzerland, and the Netherlands than it was in the US.
Duffy, a professor of psychiatry in Calgary, noted that bipolar disorder is highly heritable even though most adults with bipolar illness do not have a family history of bipolar illness among their first-degree relatives. She shared estimates that if one parent has bipolar disorder their offspring have a 5% lifetime risk of developing bipolar disorder. If both parents have bipolar disorder their offspring have a 25% risk of developing bipolar disorder and a 35% incidence of developing any affective disorder (although other data by Lapalme et al. suggest it may be as high as 60%).
Duffy found that when parents responded well to lithium, their children tended to do the same. Lithium-responsive patients tended to be those without anxiety disorder and substance abuse and who had classic bipolar episodes and clear well intervals between episodes. Read more