Bipolar Disorder and Its Comorbidities in Youth
A symposium on bipolar disorder and its comorbidities in children and adolescents was held at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry in 2011. The following findings were reported there.
ADHD
Researcher Janet Wozniak discussed the relationship of bipolar illness and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Based on interviews of family members of children with bipolar illness alone, bipolar illness plus ADHD, ADHD alone, and controls, she concluded that bipolar illness occurred more often in families of children with bipolar illness with or without ADHD. Similarly, she showed that there was more ADHD in relatives of children with either ADHD alone or ADHD comorbid with bipolar illness. She concluded that the comorbidity of bipolar illness and ADHD is a unique subtype of bipolar disorder and requires further study.
Emotional Dysregulation and Substance Abuse
In another presentation, Tim Wilens indicated that those with bipolar disorder and emotional dysregulation had an 8- to 20-fold increased risk of having a substance abuse comorbidity with their bipolar disorder.
Substance Abuse Comorbidity
In a third presentation, Ben Goldstein reported that the onset of bipolar illness predates the onset of substance abuse in 60 to 83% of instances of comorbid illness. He emphasized the dramatic negative impact of comorbid substance use in children with bipolar disorder in terms of increasing legal entanglements, pregnancy, academic failure, suicide, and decreased compliance with medications. He reported that in the multi-site, National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)-funded Course and Outcome of Bipolar Illness in Youth (COBY) study, the largest longitudinal study to date of youth with bipolar disorder, the risk of new onset substance abuse over the course of 4 years of follow-up was 32%. These data taken with the 15% of children who already had substance abuse at intake indicates that in this study approximately half of the children with bipolar illness had or acquired a substance abuse problem near the beginning of their illness. Two-thirds of the children in the study had abused both alcohol and cannabis. Read more
Obesity and Bipolar Disorder: News from the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
 At the annual meeting of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry in Toronto in October 2011, a symposium on the impact of obesity on the course of childhood onset bipolar illness was held.
At the annual meeting of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry in Toronto in October 2011, a symposium on the impact of obesity on the course of childhood onset bipolar illness was held.
Typical Treatment of Bipolar Disorder in Youth
David Axelson described the typical outcome of bipolar illness and the medications used during naturalistic treatment. The data came from the large collaborative Course and Outcome of Bipolar Illness among Youth (COBY) study, in which he and his colleagues followed 255 patients with bipolar I disorder (BP I), 30 patients with bipolar II (BP II), and 153 patients with bipolar not otherwise specified (BP NOS) for a mean of 5 years. He discussed only BP I children at the symposium.
The study initially followed 270 BP I children for a mean of 582 weeks. They ranged in age from 7 to 17 years (average 14.4 years). Ninety-three percent of the children were treated with one or more antimanic (AM) agents. These included atypical antipsychotics (AA) in 77%, valproate or carbamazepine in 44%, and lithium in 47%. Antidepressants (ADs) were used in 46% of the children, stimulants in 43%, and benzodiazepines in 21%. Sixty percent had been on two classes of antimanic medications concurrently at some point.
A univariate analysis showed that older children received smaller amounts of antipsychotics and more anticonvulsants and lithium. Variables associated with better response, that is, a rating of either much or very much improved on the Clinical Global Impressions scale for bipolar disorder (CGI-BP), included older age and treatment with atypical antipsychotics. Those who had comorbid attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) or psychosis at baseline did more poorly. Mean symptom scores were better when the children received any anti-manic treatment including an atypical or lithium, but worse when they received valproate or carbamazepine.
These data are similar to those from other prospective treatment outcome studies in childhood-onset bipolar I illness. Taken together they all suggest that the illness is difficult to treat and stabilize even when multiple medicines are used in combination.
Obesity and Mood Disorders in Youth
Another speaker, Ben Goldstein, indicated that in the scientific literature, obesity has been associated with a higher number of depressive episodes and longer length of depression, more recurrences of depression, more anxiety disorders, increased numbers of hospitalization, more suicide attempts, and worse functional outcomes. In the same group of patients discussed by Axelson above, 42% were overweight or obese, compared to a 34% incidence in the general population of children in this age range.
Factors associated with overweight included substance abuse, a history of physical abuse, prior hospitalization, and being on 2 or more medications. Those who were overweight or obese spent more time ill in a manic or depressive episode. Read more
Heading Off Early Symptoms of Bipolar Disorder in Children at High Risk
 At the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (AACAP) annual meeting in Toronto in October 2011, there was a symposium on risk and resilience factors in the onset of bipolar disorder in children who have a parent with the disorder.
At the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (AACAP) annual meeting in Toronto in October 2011, there was a symposium on risk and resilience factors in the onset of bipolar disorder in children who have a parent with the disorder.
Family Focused Therapy Highly Encouraged
Amy Garrett reported that family focused therapy (FFT) in those at risk for bipolar disorder was effective in ameliorating symptomatology compared to treatment as usual. Family focused therapy, pioneered by Dave Miklowitz, PhD of UCLA involves three components. The first component is education about the illness and methods of self-management. The second is enhancement of communication in the family with practice and rehearsal of new modes of conversation. The third component is assistance with problem solving.
In Garrett’s study, 50 children aged 7 to 17 were randomized to family focused treatment or treatment as usual. These children were not only at high risk for bipolar disorder, they were already prodromal, meaning they were already diagnosable with bipolar not otherwise specified (BP-NOS), cyclothymia, or major depressive disorder, and had also shown concurrent depressive and/or manic symptoms in the two weeks prior to the study. At baseline, compared to controls, these children at high risk for full-blown bipolar disorder by virtue of a parental history of the illness showed increased activation of the amygdala and decreased activation of the prefrontal cortex. Most interestingly, after improvement with the family focused therapy (FFT), amygdala reactivity to emotional faces became less prominent and dorsolateral prefrontal cortical activity increased in proportion to the degree of the patient’s improvement.
The discussant for the symposium was Kiki Chang of Stanford University, who indicated that the results of this study of family focused therapy were already sufficient to convince him that FFT was a useful therapeutic procedure in children at high risk for bipolar disorder by virtue of having a parent with a history of bipolar illness. Chang is now employing the therapy routinely in all of his high-risk patients.
Editors Note: This is an extremely important recommendation as it gives families a specific therapeutic process in which to engage children and others in the family when affective behavior begins to become abnormal, even if it does not meet full criteria for a bipolar I or bipolar II disorder.
FFT also meets all the important criteria needed for putting it into widespread clinical practice. Family focused therapy has repeatedly been shown to be effective in adults and adolescents with bipolar illness and now also in these children who are prodromal. The psychoeducational part of FFT is common sense, and dealing with communication difficulties and assisting with problem solving also have merit in terms of stress reduction. Finally, this treatment intervention appears to be not only safe but also highly effective in a variety of different prodromal presentations of affect disorders even if children do not meet full criteria for bipolar disorder. While the few studies of early intervention with psychopharmacological agents have not yet identified efficacious medications for the prodromes of bipolar disorder and in particular medications with a high degree of safety, such family focused therapy appears to be an ideal early intervention.
I would concur with Dr. Chang’s assessment. Family focused therapy (FFT) should be offered to all children with this high-risk status who have begun to be symptomatic. Early onset of unipolar depressive disorder or of bipolar disorder carries a more adverse prognosis than the adult onset variety and thus should not be ignored. If more serious illness is headed off early, it even raises the possibility that the full-blown illness will not develop at all.
Gray Matter Volume Abnormalities
Tomas Hajek of Dalhousie University in Halifax presented data indicating that in children at high risk for bipolar disorder, gray matter volume in the right inferior frontal gyrus is increased. Read more
Inflammation and Mood Disorders
There is increasing evidence of a link between inflammation, brain function, and treatment resistance in the mood disorders. Obesity is also linked to inflammatory processes and thus may contribute to the development of treatment resistance in both unipolar and bipolar mood disorders.
Causes of Inflammation
 Obesity is one factor that can lead to increases in inflammation. When people gain weight, the size of fat cells can increase to the point that the cells are deprived of oxygen and disintegrate. Then macrophages and other cells come in to sweep up the remaining particles of the fat cells. These scavenger cells then become activated and produce more regulatory chemicals called cytokines. The cytokines produced in the periphery (in the body outside the brain) can then enter the brain and affect brain function in a process that may ultimately be linked to fatigue, depression, and other adverse mood and behavior states that contribute to treatment resistance. There is a two-way street: the brain can influence the body and what goes on in the body can influence the brain.
Obesity is one factor that can lead to increases in inflammation. When people gain weight, the size of fat cells can increase to the point that the cells are deprived of oxygen and disintegrate. Then macrophages and other cells come in to sweep up the remaining particles of the fat cells. These scavenger cells then become activated and produce more regulatory chemicals called cytokines. The cytokines produced in the periphery (in the body outside the brain) can then enter the brain and affect brain function in a process that may ultimately be linked to fatigue, depression, and other adverse mood and behavior states that contribute to treatment resistance. There is a two-way street: the brain can influence the body and what goes on in the body can influence the brain.
Other factors that can lead to increases in inflammation and eventually to treatment resistance in the unipolar and bipolar mood disorders include early life stress, medical illness, and anxiety and personality disorders.
Anti-Inflammatory Treatments
Given the close links between inflammation and depression (discussed in BNN Volume 15, Issue 1 from 2011), Andrew H. Miller of Emory University decided to test a specific anti-inflammatory agent called infliximab (a TNF monoclonal antibody that inhibits TNF alpha actions) as an antidepressant. One sign of inflammation is a C-reactive protein (CRP) level of 2mg/L or greater. The effect of infliximab on the population of treatment refractory depressed patients who participated in Miller’s study was not significant on the whole, but the drug did have significantly greater antidepressant effects than placebo in those patients with the highest levels of CRP. The investigators believe this demonstrates the principle that a drug that inhibits TNF alpha may be useful in patients with the greatest degree of inflammation.
Other approaches to anti-inflammatory mechanisms are also being pursued, including use of aspirin, COX-2 inhibitors, and the antibiotic minocycline. Minocycline has anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects and has been reported to have positive effects in cognition and negative symptoms of schizophrenia.
Psychosis Risks with Marijuana Use
 At a recent conference Robin Murray, a researcher based in London, gave a talk about the potential adverse effects of tetrahydrocanabinol (THC). Considerable data indicate that chronic long-term smoking of marijuana is associated with the doubling of the risk of psychosis. Moreover, if a marijuana user has a common genetic variant in the catechol-o-methyltransferase enzyme (COMT), they are at substantially increased risk for the development of psychosis. New data also indicate that frequent use of marijuana can also be associated with an earlier onset of schizophrenic psychosis than would ordinarily occur without the substance use. Data also suggest that the psychosis associated with THC use is more difficult to treat than that without such use.
At a recent conference Robin Murray, a researcher based in London, gave a talk about the potential adverse effects of tetrahydrocanabinol (THC). Considerable data indicate that chronic long-term smoking of marijuana is associated with the doubling of the risk of psychosis. Moreover, if a marijuana user has a common genetic variant in the catechol-o-methyltransferase enzyme (COMT), they are at substantially increased risk for the development of psychosis. New data also indicate that frequent use of marijuana can also be associated with an earlier onset of schizophrenic psychosis than would ordinarily occur without the substance use. Data also suggest that the psychosis associated with THC use is more difficult to treat than that without such use.
Murray also reported on a new risk that is associated with more potent new products. Older, natural forms of marijuana contained a compound called cannabidiol, which is associated with calming effects and possible antipsychotic effects. In a new synthetic preparation of THC called skank or spice, there is a higher amount of THC, but none of the positive diol compound. Thus there are some important caveats to the prevailing view that marijuana is relatively harmless.
Editor’s Note: Marijuana use brings a clear-cut increased risk for psychosis, which appears to interact with a common gene polymorphism and which is increased with use of a new synthetic preparation called skank or spice. If a marijuana user has a concurrent mood disorder, the risks appear to be even greater. The one sure pharmacological effect of marijuana is an amotivational syndrome, and motivational deficits are one of the core components of depression.
Given the difficulty of treating the mood and schizophrenic disorders, a patient should not risk worsening their illness with marijuana. N-acetylcysteine is one treatment option that may bring about decreased craving for and avoidance of marijuana and a number of other abused substances, as well as being helpful for mood and negative symptoms in schizophrenia.
Puberty Occurs at Younger Ages
Experts disagree about the data that show an earlier onset of depression and bipolar disorder in every successive generation since the first World War (this change is called the cohort effect). Nonetheless, it is interesting that so many other medical conditions are increasingly seen in young children. These include asthma, arthritis, obesity, allergy, diabetes, and a host of other conditions. WebMD reported that menarche and the onset of puberty are also occurring at younger ages. Puberty used to be a largely teenage occurrence, and now it occurs in many children as early as age 7.
Common Genetic Variation Linked to Response to Antidepressants
 Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) protects neurons and is important for long-term learning and memory. There are several genetic variations in BDNF depending on which amino acid—valine or methionine—falls at a particular position when the proBDNF protein is being made. Most people have the val-66-val allele, some have the val-66-met, and a few have the met-66-met allele.
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) protects neurons and is important for long-term learning and memory. There are several genetic variations in BDNF depending on which amino acid—valine or methionine—falls at a particular position when the proBDNF protein is being made. Most people have the val-66-val allele, some have the val-66-met, and a few have the met-66-met allele.
Researcher Jessica C. Levenson, working with David Kupfer and Ellen Frank at the University of Pittsburgh, reported at the 51st Annual Meeting of the National Institute of Mental Health’s New Clinical Drug Evaluation Unit (NCDEU) in 2011 that patients with unipolar depression who have the val-66-val allele of proBDNF have better clinical responsiveness to antidepressants than those with the slightly less common variant, val-66-met.
Editor’s note: The val-66-val allele is more effective in enhancing synaptic plasticity and is more easily transported from the nucleus to the dendrites of neurons (where it is necessary for learning and memory) than the val-66-met allele or the least effective met-66-met variant.
These findings are intriguing because antidepressant treatments tend to increase BDNF, regardless of their mechanisms of action. Moreover, BDNF levels are low in patients with depression, usually in direct relationship to the severity of depression. Thus, the ability of antidepressants to increase BDNF may lead to a more effective treatment response in those with the better functioning val-66-val allele of BDNF. This remains to be further documented, but the study provides a preliminary example of how genotyping may eventually be able to help predict individual clinical response to a given treatment and thus foster the development of personalized medicine.
Neurological Biomarkers May Eventually Predict Response to Antidepressants
 T.L. Lauriat reported at the 51st Annual Meeting of the National Institute of Mental Health’s New Clinical Drug Evaluation Unit (NCDEU) in 2011 that low baseline levels of the neurotransmitter GABA in the brains of depressed patients were associated with greater response to antidepressants. GABA was measured using magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS).
T.L. Lauriat reported at the 51st Annual Meeting of the National Institute of Mental Health’s New Clinical Drug Evaluation Unit (NCDEU) in 2011 that low baseline levels of the neurotransmitter GABA in the brains of depressed patients were associated with greater response to antidepressants. GABA was measured using magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS).
These data raise the possibility that easily observed neurobiological markers, such as levels of GABA or the neurotransmitter glutamate, may ultimately be helpful in predicting clinical response to particular treatments.
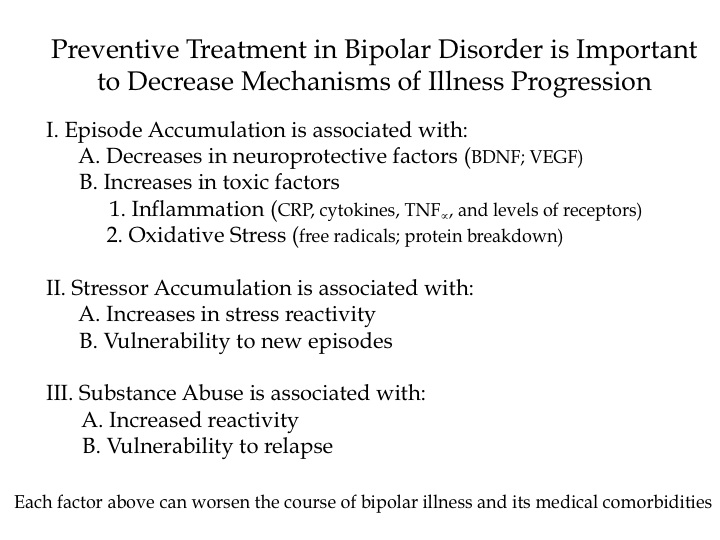
Risks and Difficulties of Treating Childhood-Onset Bipolar Disorder
 Early treatment is needed in childhood onset bipolar disorder
Early treatment is needed in childhood onset bipolar disorder
Multiple factors make childhood-onset bipolar disorder a difficult problem for affected children and families. Early onset is common, and treatment is often delayed or inappropriate. It takes an average of nine months to achieve remission, and relapses are common. In studies children have remained symptomatic for an average of two-thirds of the time they receive naturalistic follow up treatment, and the illness impairs social and educational development. Episodes and stressors tend to accumulate, and substance abuse is a frequent complication. Dysfunction and disability occur at a high rate among children with the illness, and suicidal ideation and acts are common.
When we surveyed adults in our treatment network, the Bipolar Collaborative Network (BCN), about the history of their illness, we found that the duration of the time lag between illness onset and first treatment was independently related to a poor outcome in adulthood. A longer delay to first treatment was associated in adulthood with greater depression severity, more days depressed, fewer days euthymic, more episodes, and more ultradian cycling (or cycling within a single day). Because treatment delay is a risk factor that can be avoided or prevented, efforts should be made to initiate treatment early in the course of bipolar illness. Read more