Using Light to Improve Sleep and Depression
At the 2018 meeting of the North Carolina Psychiatric Association, researcher Chris Aiken described the phenomenon of sleep inertia, when people are awakened from deep sleep by an alarm, rather than waking at the end of a sleep cycle, and are groggy for 15 minutes. Depressed people may stay groggy for 4 hours. A dawn simulator may help. These lights turn on gradually over the course of 30 to 60 minutes, reaching 250 lux while the patient is still asleep. Dawn simulators have worked in eight out of ten controlled clinical trials to help people with seasonal affective disorder, adolescents, and normal adults wake up more easily. They range in cost from $25 to $90 and some brands include PER2LED or LightenUp. Aiken says dawn simulators can improve depression, sleep quality, and cognition.
Evening and nighttime light: Bright lights and blue light, like the light that comes from electronic screens, can shut down the body’s secretion of melatonin, making people awake and alert in the evening when they should be getting sleepy. Dim light or glasses that filter out blue light allow increases in melatonin secretion in the evening, while bright light suppresses it. Missing this early melatonin pulse creates “night owls” who have delayed sleep onset.
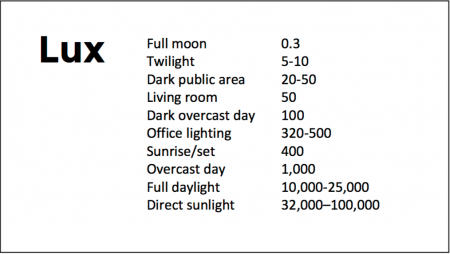
Because light still reaches our eyes through our eyelids as we sleep, even low-level light during the night impairs sleep, cognition, and learning, and increases the risk of depression by a hazard ratio of 1.8 (about double the risk). A 2017 study by Kenji Obayashi in the American Journal of Epidemiology found that bedroom light above 5 lux elevated rates of depression in older adults after two years of followup. Living room light averaged around 50 lux and increased depression further.
The treatment is turning off TVs, electronic screens, and cellphones in the evening or wearing blue-blocking glasses, which can be found for less than $10. Blue-blocking glasses can increase calmness and reduce anxiety, and even are effective in treating mania. Then, during sleep, wear an eye mask or get light-blocking blinds or curtains for windows. For a complete blackout, use blackout curtains, aluminum foil over windows, electric tape over LED lights, or try sleeping in the basement.
Aiken suggests that to re-instate healthy sleep patterns, people should institute virtual darkness from 6pm to 8am, including wearing blue-blocking glasses when out of bed. Then they should institute total darkness or wear an eye mask when in bed. When symptoms improve, this routine can gradually be shifted to begin later in the evening, such as two hours before bedtime.
Blue light filters are also available for smartphones and tablets including Apple Nightshift mode, Kindle BlueShade, and Android Twilight and Blue Light Filter.
Glasses that filter out blue light include Uvex Ultraspec 2000, 50360X ($7 on Amazon) and Uvex Skyper 351933X ($7-10 on Amazon). The website lowbluelights.com sells blue-blocking glasses from $45 and a variety of other blue-free lighting products such as lightbulbs and flashlights.
Bright light therapy for unipolar and bipolar depression: 30 minutes of bright light (7,500 to 10,000 lux) in the morning can help treat depression in unipolar and bipolar disorder and seasonal affective disorder. The effects usually take 3 to 7 days to set in, but they only last while a patient continues using the bright light in the morning. Researcher Dorothy K. Sit and colleagues found that bright light therapy in the morning sometimes caused hypomanic reactions in people with bipolar disorder, and reported in a 2018 article in the American Journal of Psychiatry that midday light therapy (from noon to 2:30pm) was also effective without this unwanted effect. However, a 2018 article by Ne?e Yorguner Küpeli and colleagues in the journal Psychiatry Research suggested that a half hour of morning light for two weeks was sufficient to bring about improvement in 81% of patients with bipolar disorder and did not cause serious side effects.
Melatonin regimen for sleep onset delay: Melatonin can be used to treat severe night-owls with a very late onset of sleep (for example, going to bed at 2 or 3am and sleeping late into the morning). Melatonin can help with sleep onset to some extent when used at bedtime, but in those with an extreme phase shift, researcher Alfred J. Lewy recommends a regimen of low dose priming with 400–500 micrograms of melatonin at 4pm and then a full dose of 3 milligrams of melatonin at midnight. The 4pm priming dose helps pull back the delayed onset of the body’s secretion of melatonin toward a more normal schedule.
Midday Bright Light Therapy Improved Bipolar Depression
A study by Dorothy K. Sit and colleagues published in the American Journal of Psychiatry in 2017 found that delivering bright white light therapy to patients with bipolar depression between the hours of noon and 2:30pm improved their depression compared to delivering inactive dim light, and did not cause mood switches into mania. The study included 46 patients with moderate bipolar depression, no hypomania and no psychosis.
The active therapy group was exposed to broad-spectrum bright white fluorescent light at 7,000 Lux while the inactive group received dim red light at 50 Lux. Both groups were instructed to sit 12 inches from the light and face it without looking directly at it. The therapy began with 15-minute afternoon sessions and increased to 60 minutes per day by 4 weeks. Participants were assessed weekly. Remission rates increased dramatically in the active group beginning in the fourth week. At weeks 4 through 6, the remission rate for those in the active bright light group was 68.2% compared to only 22.2% in the dim light group.
Mean depression scores were better in the treated group, as were global functioning and response rates.
Some participants were taking antidepressants concurrently, and these participants were evenly distributed across the two study groups.
An earlier pilot study by the same researchers had found that bright light therapy delivered in the morning was followed by some hypomanic reactions or bipolar cycling. The midday sessions did not cause any mood switching.
Bright light therapy is often used to treat seasonal affective disorder (SAD) using a 10,000 Lux light box. This study took place mostly during the fall and winter months.
Editor’s Note: Bright light therapy is generally safe and boasts a high remission rate. Light boxes can be acquired without a prescription and are portable and easy to use. Midday light may have the best results and the least risk of provoking a mood switch into mania.
In Small Study, High Intensity Light Therapy Boosts Libido in Men
The same type of high-intensity light therapy used to treat seasonal affective disorder (SAD) and as an adjunctive treatment for non-seasonal depression has been found to boost testosterone and improve sexual satisfaction in men with low libido.
In a study by Andrea Fagiolini and colleagues, men with low sexual desire or trouble getting aroused were exposed to the high intensity light (10,000 Lux) for a half hour upon waking. Compared to men who used a lightbox that filtered the light to only 100 Lux, men exposed to the high-intensity light for two weeks showed increased testosterone in the blood and reported greater sexual satisfaction. Testosterone levels increased from around 2.1 ng/ml to 3.6 ng/ml in the high-intensity light group. (There were no significant changes in the comparison group.) Light therapy is quite safe for people without eye problems.
Fagiolini explained that in the Northern hemisphere, testosterone production declines from November to April and then rises again through the spring and summer, peaking in October. He suggests that the light therapy mimics the effect of summer light on the body, perhaps by inhibiting the pineal gland, which secretes hormones.
Fagiolini and colleagues hope to replicate the study with a greater number of participants and to determine how long the results may last.The study of 38 participants was presented at the 29th Congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology in 2016.
Midday Bright Light Therapy Effective in Bipolar Disorder
A recent study of 93 adults with bipolar disorder suggests that midday bright light therapy can be an effective adjunctive treatment for bipolar depression. The study by Dorothy Sit and colleagues was presented at the 2015 meeting of the Society for Biological Psychiatry. Participants had been diagnosed with bipolar I or II disorder, were in a current episode of depression, and were taking stable doses of mood stabilizing medication. They were randomized to receive either 7000-lux broad spectrum light for 45 to 60 minutes each day for six weeks or 50 lux dim red light. The comparison was dramatic: remission rates were 56.5% among those exposed to the 7000-lux light, and 14.3% among those who were exposed to the dim light. Those who received the bright light also reported better sleep quality and less suicidality.
Editor’s Note: These results are striking and raise the issue of whether midday bright light is more effective than early morning bright light, the usual recommendation for seasonal affective disorder (SAD) and other forms of depression. Until comparative studies are available, using midday light may be the way to go.
Bright Light Therapy Adds to Venlafaxine’s Antidepressant Effects
A study by Pinar Güzel Özdemir and colleagues in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry indicates that bright light therapy may improve the effects of antidepressant venlafaxine (Effexor) in patients diagnosed with major depression for the first time. In the study of 50 inpatients, half received 150mg of venlafaxine at 7am each morning, while half received 150mg of venlafaxine plus 60 minutes of 7000 lux bright light therapy at 7am each morning. Beginning after the first week of treatment, both groups showed significant improvement in depression and negative mood states throughout the eight-week study. However, at weeks 2 and 4, the patients who received bright light therapy showed greater reductions in depression, with 76% reaching the target goal of treatment after four weeks compared to 44% of the venlafaxine-only group.
Both venlafaxine and combined treatment with venlafaxine and bright light therapy reversed symptoms of depression, but adding bright light therapy may produce more rapid, stronger effects. Larger studies are needed to replicate these effects and determine whether they are long-lasting.