Meta-Analysis Shows Inflammation is Common in Unipolar Depression, Bipolar Depression, and Schizophrenia
In a symposium at the 2016 meeting of the Society of Biological Psychiatry, Mark Hyman Rapaport described the results of his research group’s meta-analysis of studies comparing levels of inflammation in the blood of people with unipolar depression, bipolar depression, and schizophrenia. Rapaport and colleagues determined that people acutely ill with any of the three illnesses showed abnormally high levels of certain inflammatory proteins. These included: interleukin-1beta, interleukin-6, TNF alpha, and c-reactive protein. Those who were chronically ill showed elevations in interleukin-6.
These data are consistent with increasing evidence that inflammation also occurs in the brain. Brain inflammation can be observed by measuring translocator protein binding, a measure of brain microglial activation, using positron emission tomography (PET) scans.
Meta-Analysis Shows Anti-Inflammatory Treatments Improve Bipolar Depression
 It has been clear for some time that depression and inflammation are linked. This has led researchers to explore a variety of anti-inflammatory agents to treat depression. A meta-analysis of studies examining anti-inflammatory treatments for bipolar depression was published in the journal Bipolar Disorders in 2016.
It has been clear for some time that depression and inflammation are linked. This has led researchers to explore a variety of anti-inflammatory agents to treat depression. A meta-analysis of studies examining anti-inflammatory treatments for bipolar depression was published in the journal Bipolar Disorders in 2016.
Researcher Joshua D. Rosenblat and colleagues identified eight randomized controlled trials that met their criteria for anti-inflammatory treatments of bipolar disorder. These treatments included nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs such as ibuprofen and aspirin), omega-3 fatty acids, the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine, and pioglitazone (used to treat diabetes). Overall, the anti-inflammatory treatments had a moderate and statistically significant antidepressant effects. No serious side effects were reported, and the anti-inflammatory treatments did not cause a switch into mania in any of the participants.
The diversity of the anti-inflammatory treatments reviewed in this meta-analysis limit the extent to which it can be interpreted, but it is clear that more research on anti-inflammatory treatments for bipolar depression is needed. An open question is whether patients with particularly elevated levels of inflammatory markers in their blood would respond better to these anti-inflammatory treatments.
Methylene Blue May Help Bipolar Depression
 We have previously reported on the research by Martin Alda and colleagues that the chemical compound methylene blue had positive effects in patients with bipolar depression. The research was published in the British Journal of Psychiatry in 2016.
We have previously reported on the research by Martin Alda and colleagues that the chemical compound methylene blue had positive effects in patients with bipolar depression. The research was published in the British Journal of Psychiatry in 2016.
Now a new article by Ashley M. Feen and colleagues in the Journal of Neurotrauma reports that methylene blue has an antidepressant-like effect in mice with traumatic brain injury (TBI). Methylene blue reduced inflammation and microglia activation in the animals. Methylene blue reduced levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokine Il-1b and increased levels of the anti-inflammatory cytokine Il-10.
These findings are of particular interest as many patients with classical depression (and no brain injury) have abnormal levels of these inflammatory markers. It remains to be seen whether methylene blue is more helpful in those patients with elevated inflammatory markers and if levels of the markers can predict treatment response or not.
Methylene blue causes urine to turn blue, so low doses of the compound are used as a placebo. Alda and colleagues reported that the active dose 195mg reduced depression and anxiety significantly more than the placebo dose (15mg) in a 13-week crossover study. In that study, methylene blue was added to lamotrigine which had not had a complete enough effect.
In a 1986 study by G.J. Naylor and colleagues in the journal Biological Psychiatry, patients were treated with either 15mg/day or 300mg/day of methylene blue for one year and crossed over to the other dose in the second year. Participants had significantly less depression during the year of taking the active 300mg/day dose.
The FDA has issued a warning about the danger of a serotonin syndrome if methylene blue is combined with serotonin active agents (presumably because it inhibits MAO-A). Symptoms of the serotonin syndrome can include lethargy, confusion, delirium, agitation, aggression, decreased alertness, and coma. Neurological symptoms, such as jerky muscle contractions, loss of speech, muscle tension, and seizures; or autonomic symptoms, such as fever and elevated blood pressure, are also common. Patients should call their doctor if they are taking a serotonergic psychiatric medication and develop any of the above symptoms.
Anti-Inflammatory Treatments Look Promising for Bipolar Depression
Inflammation has been linked to both unipolar and bipolar depression. New research shows that anti-inflammatory treatments may reduce bipolar depression, for which few treatments exist.
Researchers led by Jonathan Savitz divided people with bipolar depression into four groups. One group received two placebos, another received minocycline (a drug with neuroprotective and immune-modulating properties) plus a placebo, the third received aspirin plus a placebo, and the final group received both minocycline and aspirin. Of the 64 participants, those who took both minocycline and aspirin were most likely to respond to treatment and to enter remission. In people with body mass indexes (BMIs) above the median of 30, a sign of greater inflammation, 100% of those who received both anti-inflammatory drugs responded to treatment, compared to 36% of those who received aspirin alone, 33% of those who received minocycline alone, and 25% of those who received two placebos.
Dosages of the drugs were 100mg twice a day for minocycline and 81mg twice a day for aspirin. Savitz and colleagues believe that aspirin and minocycline must work particularly well together, and are modifying their study to more directly compare use of the two anti-inflammatory drugs together to the absence of anti-inflammatory treatments.
Clarifying the Effects of a Diabetes Drug that Improves Bipolar Depression
Research continues on pioglitazone, a drug typically used to treat diabetes but with other positive effects on depression and stroke risk. Some researchers are working on determining whether the drug increases the risk of developing certain cancers, including bladder, prostate, and pancreatic cancers. A recent study by James D. Lewis and colleagues in the journal JAMA found no statistically significant increase in risk of bladder cancer among patients taking the drug, but the researchers said they also couldn’t rule out that the drug may increase this risk, as has been seen in previous studies. The study by Lewis did show an increase in pancreatic and prostate cancers in patients taking pioglitazone, but the researchers did not determine whether this was caused by the drug.
Another recent study by Walter N. Kernan and colleagues in the New England Journal of Medicine reported that pioglitazone reduced the incidence of stroke and heart attack in patients with a history of stroke or blocked blood vessels in the brain but without a diagnosis of diabetes. Patients who received pioglitazone also experienced side effects including weight gain, edema (an increase in fluids in the body’s tissues) and serious bone fractures.
Pioglitazone has had positive effects in bipolar depression and may one day be used as a treatment for bipolar disorder. For now, it may be worthy of consideration for the treatment of diabetes in patients who also have bipolar depression.
Approaches to Restoring Cognition in Unipolar and Bipolar Depression
Many people with bipolar disorder suffer cognitive difficulties, and these may progress as a function of the number of mood episodes they experience. At the 2015 meeting of the International Society for Bipolar Disorders, researcher Eduard Vieta described the importance of directly prescribing diet, exercise, good sleep hygiene, smoking avoidance, and cognitive exercises designed to maintain cognitive reserves in people with bipolar disorder. Vieta stressed that one of the most important approaches to maintaining cognition is to help patients achieve and maintain remission. He also noted that those patients with lithium levels of .6meq/l or greater did not see cognitive deterioration.
Some treatments for bipolar disorder can contribute to cognition problems. Topiramate and benzodiazepines can impair cognition, as can atypical antipsychotic drugs and certain antidepressants that block the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Avoiding these treatments and those with sedative side effects may also be helpful.
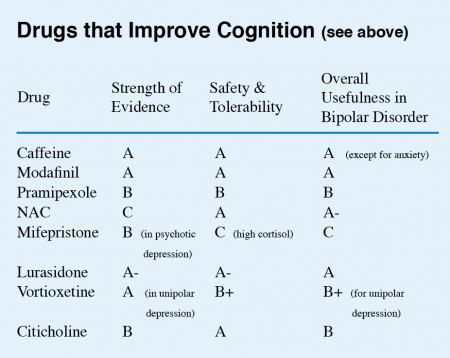
Vieta listed a series of drugs with some promise for improving cognition. (These did not include treatments for dementia, which include memantine and a group of drugs that increase acetylcholine by inhibiting its breakdown.)
This editor (Robert M. Post) has taken the liberty of giving a letter grade (A to D) to each drug on Vieta’s list on the basis of the strength of the data supporting its efficacy, its safety and tolerability, and its overall usefulness for patients with bipolar disorder. These recommendations, like other material in the BNN, are subjective and likely to change as more systematic studies on these treatments are published.
Lamotrigine potentiates the antidepressant effects of quetiapine in bipolar depression
At the 2015 meeting of the International Society for Bipolar Disorders, researcher John Geddes presented an important study showing in inadequate responders to quetiapine that compared to adding placebo, adding the anticonvulsant lamotrigine to their treatment improved depression rapidly and lastingly. Some psychiatrists have been prescribing this combination to patients for some time, but this is the first formal clinical trial documenting its efficacy. The article was published online in December in the journal Lancet Psychiatry.
Researcher Guy Goodwin described details of the study, called CEQUEL, at the meeting. It included 202 patients with bipolar I or II disorder who required treatment for a depressive episode. Participants who did not respond completely to 14 days of treatment with quetiapine were prescribed either an additional dose of lamotrigine or a placebo. Lamotrigine was very slowly titrated up to maximum doses of 200mg/day. Its antidepressant effects were striking. They began early and persisted for 50 weeks. (The published article covers only the first 12 weeks.) Response rates for the combination of quetiapine and lamotrigine were 52%, compared to 22% for quetiapine alone. Remission rates were 35% for quetiapine and lamotrigine and 12% for quetiapine alone.
Folic acid interaction
Another part of the study assessed whether folic acid supplements could improve outcomes, but in fact they did the opposite, reversing the benefits of adding lamotrigine. Geddes did not have an explanation for why this might be the case. Lamotrigine can inhibit folate metabolism, and it had been thought that adding folate would be useful. Until further data are gathered on folate augmentation in patients taking the combination of lamotrigine and quetiapine, folate should be used cautiously if at all in these patients.
Possible combination with lithium
In Goodwin’s talk, he also noted lithium’s potential to lower suicide rates, premature mortality, and cognitive impairment, and to increase hippocampal and cortical volume.
Since lamotrigine was shown to potentiate the antidepressant effects of lithium in a study by Van der Loos and colleagues, and quetiapine is approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the prevention of depression as an adjunct to lithium (or valproate), there might be theoretical acute and long-term benefits to combining the three: lithium, quetiapine, and lamotrigine.
Preliminary Evidence That Anti-Inflammatory Celecoxib Helps in Bipolar Depression
A study currently in progress indicates that the anti-inflammatory COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib (better known as the arthritis treatment Celebrex) may aid in the treatment of bipolar depression. In a panel session on inflammation at the 2015 meeting of the Society of Biological Psychiatry, researcher Angelos Halaris reported results from the first 26 participants.
Participants were taking mood stabilizers for bipolar disorder and became depressed. They received either 20mg/day of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressant escitalopram (Lexapro) plus either 200mg twice a day of celecoxib or placebo for a total of eight weeks. Those participants who received celecoxib showed greater and more rapid reductions in depression symptoms than those who received placebo.
The study will continue, and Halaris and colleagues will also observe whether measures of inflammation in patients’ blood are correlated with the patients’ responsiveness to the combined treatment with escitalopram and celecoxib.
Another Antidepressant Fails in Bipolar Depression
Despite repeated studies, including meta-analyses, showing that antidepressants that work in unipolar depression do not work in bipolar depression as adjuncts to mood stabilizers, antidepressants remain widely used for the treatment of bipolar depression. A recent study of the antidepressant agomelatine has shown that it is not effective in bipolar depression. In patients taking lithium or valproate but still depressed, agomelatine was no better than placebo at reducing depression.
Agomelatine has an unusual mechanism of action (blockade of 5HT-2C receptors and activation of melatonin M1 and M2 receptors) that helps normalize sleep and circadian rhythms, but only in unipolar depression. Until this study by Lakshmi Yatham and colleagues in the British Journal of Psychiatry, it was thought that these properties would make the drug ideal for bipolar depression.
Three atypical antipsychotics are have been approved by the Federal Drug Administration for bipolar depression: quetiapine (Seroquel), lurasidone (Latuda), and the olanzepine-fluoxetine combination Symbyax. These, used alongside mood stabilizers (lithium, valproate, carbamazepine, and lamotrigine) are more effective treatments for bipolar depression. There are other adjunctive treatments that may be helpful, such as the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine, vitamin D3, and folate.
Diabetes Drug Pioglitazone May Improve Bipolar Depression
The hypoglycemic drug pioglitazone is typically used to treat diabetes, but a 2015 study by A. Zeinoddini and colleagues shows that it may improve depressive symptoms in patients with bipolar disorder who do not have type 2 diabetes or the metabolic syndrome (characterized by high weight, cholesterol, triglycerides, and blood pressure).
Forty-four patients with bipolar disorder and a major depressive episode were randomized to receive either 30 mg/day of pioglitazone or placebo as an adjunctive treatment to lithium. Depressive symptoms were lower in the pioglitazone group at weeks 2, 4, and 6 of the six-week study.
No serious side effect occurred in the study, but pioglitazone use is associated with some risks in those using it for diabetes treatment. People taking pioglitazone for longer than a year have shown increased rates of bladder cancer. There is an increased risk of fractures of the upper arms, hands, and feet in female patients. The drug lowers blood sugar, but not enough to be a problem in people not taking other drugs that lower blood sugar. Pioglitazone can also cause fluid retention, worsening congestive heart failure. It can also cause mild weight gain, anemia, and sinus problems.