Transcranial Near-Infrared Light May Treat Brain Injury and Neurodegeneration
At the 2021 meeting of the Society of Biological Psychiatry, there was a symposium on treatment with near-infrared light chaired by researchers Paolo Cassano and Dan Iosifescu. The treatment is known as transcranial photobiomodulation (PBM) with near-infrared light. A device worn on the head delivers infrared light that penetrates the cerebral cortex and can modulate cortical excitability. It has a variety of effects including promoting neuroplasticity, improving oxygenation, and decreasing inflammation and oxidative stress.
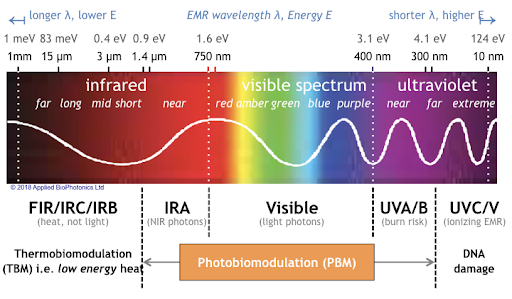
A number of studies exploring the possibility that PBM could be used as a clinical treatment for conditions such as depression, brain injury, or dementia were presented at the symposium.
Researcher Lorelei Tucker discussed promising findings from an animal model in which rats with stroke or brain injuries showed improvement after being treated with PBM.
Cassano discussed studies aimed at refining which brain areas should be targeted with PBM and how much light should be delivered in order to improve depression. In double-blind, sham-controlled studies in people with major depression, targeting the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex with PBM improved their symptoms.
Researcher Benjamin Vakoc discussed a study of low-level light therapy (LLLT) using near-infrared light compared to a sham procedure in 68 people with moderate traumatic brain injury. The researchers used magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to assess changes in white matter in the brain over time in people recovering from an acute brain injury. Patterns of changes in white matter were different for those who received LLLT compared to those who received the sham procedure.
Researcher Linda Chao described a very small study to determine whether PBM could improve symptoms of dementia. Four patients received typical dementia care while four others underwent home treatments with the commercially available Vielight Neuro Gamma device, which delivers PBM via both the scalp and an insert in the nose. After 12 weeks, the PBM group showed improvements in cognition and brain connectivity.

Editor’s Note: We will be watching the literature to follow advances in this promising novel method of neuromodulation.
Left Prefrontal Strokes Linked to Depression

In a 2021 article in the journal Stroke, researcher Julian Klingbeil and colleagues reported that left, but not right, ventrolateral prefrontal stroke lesions were associated with increased risk of depression at six months post-stroke.
The study included 270 participants who had their first-ever stroke. Six months following their strokes, 19.6% of the participants had depression. Those who scored higher on a scale of depression and anxiety symptoms in the first month after their stroke were more likely to have depression six months after the stroke.
The researchers identified a cluster of locations for stroke lesions, mostly within the left ventrolateral prefrontal cortex, that they linked to depression symptoms six months post-stroke. Klingbeil and colleagues hope that recognizing lesions in this region as risk factors for depression will help with early diagnosis of depression among people who recently had a stroke.
Editor’s Note: Antidepressants have been shown to improve post-stroke recovery of neurological functional (and depression) that is caused by the cutoff of blood supply during a stroke (ischemia). Patients and their family members should talk with their neurologist about treatment of ischemic strokes with antidepressants, especially when the lesions occur on the left side of the brain.
Baseline Levels of CRP Could Help Predict Clinical Response to Different Treatments
C-reactive protein, or CRP, is a marker or inflammation that has been linked to depression and other illnesses. People with high levels of CRP respond differently to medications than people with lower CRP, so assessing CRP levels may help determine which medications are best to treat a given patient.
High baseline levels of CRP (3–5pg/ml) predict a poor response to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressants (SSRIs) and to psychotherapy, and are associated with increased risk of recurrent depression, heart attack, and stroke.
However, high baseline CRP predicts a better response to the antidepressants nortriptyline and bupropion. High CRP is also associated with better antidepressant response to infliximab (a monoclonal antibody that inhibits the inflammatory cytokine TNF alpha), while low levels of CRP predict worsening depression upon taking infliximab.
High baseline CRP also predicts good antidepressant response to intravenous ketamine (which works rapidly to improve treatment-resistant depression), minocycline (an anti-inflammatory antibiotic that decreases microglial activation), L-methylfolate (a supplement that can treat folate deficiency), N-acetylcysteine (an antioxidant that can improve depression, pathological habits, and addictions), and omega-3 fatty acids (except in people with low levels of DHA).
High baseline CRP also predicts a good response to the antipsychotic drug lurasidone (marketed under the trade name Latuda) in bipolar depression. In people with high baseline CRP, lurasidone’s positive results have a huge effect size of 0.85, while in people with low CRP (<3pg/ml) the improvement on lurasidone has a smaller effect size (0.35).
In personal communications with this editor (Robert M. Post) in 2018, experts in the field (Charles L. Raison and Vladimir Maletic) agreed that assessing baseline CRP levels in a given patient could help determine optimal strategies to treat their depression and predict the patient’s responsiveness to different treatment approaches.
At a 2018 scientific meeting, researchers Cynthia Shannon, Thomas Weickert, and colleagues reported that high baseline levels of CRP were associated with symptom improvement in patients with schizophrenia when they were treated with the drug canakinumab (marketed under the trade name Ilaris). Canakinumab is a human monoclonal antibody that targets the inflammatory cytokine interleukin-1 beta (Il-1b). Il-1b is elevated in a subgroup of patients with depression, bipolar disorder, or schizophrenia, and CRP levels are an indication of the associated inflammation.
Taking SSRI Antidepressants May Increase Stroke Risk
 A Taiwanese study published in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry in 2017 finds that taking selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressants can increase risk of stroke. The study by Chin-Hong Chan and colleagues analyzed eight years of data from Taiwan’s National Health Insurance Research Database, comparing people who had taken SSRIs for at least two consecutive months to those who had not. First onset strokes were more common among people who had taken SSRIs, and the higher stroke rates in this group persisted for three years after exposure.
A Taiwanese study published in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry in 2017 finds that taking selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressants can increase risk of stroke. The study by Chin-Hong Chan and colleagues analyzed eight years of data from Taiwan’s National Health Insurance Research Database, comparing people who had taken SSRIs for at least two consecutive months to those who had not. First onset strokes were more common among people who had taken SSRIs, and the higher stroke rates in this group persisted for three years after exposure.
Ischemic strokes (which occur when a blood vessel carrying blood to the brain is obstructed) were more common than hemorrhagic strokes (which occur when a weak blood vessel ruptures). Younger adult participants exposed to SSRIs were more likely to have strokes, while people older than 65 saw only a slight increase in stroke risk from taking SSRIs. More strokes occurred during the first three years of SSRI treatment than later in treatment.
Chan and colleagues suggest that these strokes are caused by cerebral microbleeding or by overcorrection of hemostasis, the process by which the body slows or stops bleeding by constricting blood vessels and coagulating blood.
Best Antidepressants for Post-Stroke Depression
 A recent meta-analysis in the journal BMJ Open analyzes the efficacy and tolerability of 10 different antidepressants given to treat depression following a stroke. The meta-analysis incorporated data from 12 trials and a total of 707 participants. Reboxetine was the most effective antidepressant, followed by paroxetine, doxepin, and duloxetine. Sertraline, fluoxetine, and nefiracetam failed to outperform placebo in the treatment of post-stroke depression.
A recent meta-analysis in the journal BMJ Open analyzes the efficacy and tolerability of 10 different antidepressants given to treat depression following a stroke. The meta-analysis incorporated data from 12 trials and a total of 707 participants. Reboxetine was the most effective antidepressant, followed by paroxetine, doxepin, and duloxetine. Sertraline, fluoxetine, and nefiracetam failed to outperform placebo in the treatment of post-stroke depression.
In terms of tolerability, paroxetine had the least side effects and led to significantly fewer discontinuations than doxepin, citalopram, and fluoxetine. After paroxetine, the most tolerable drugs were sertraline and nortriptyline. The least tolerable drug was citalopram.
Researchers led by Yefei Sun suggested that paroxetine might be the best antidepressant to prescribe after a stroke due to its efficacy and good tolerability. Fluoxetine might be the worst due to its poor efficacy and poor side effects profile.
Editor’s Note: Multiple randomized controlled trials suggest that antidepressants can be helpful for anyone who has a stroke, both to decrease depression and to improve neurological and functional outcomes.
Marker of Heart Failure May Predict Brain Deterioration
 A protein released into the blood in response to heart failure may be able to predict brain deterioration before clinical symptoms appear. The protein, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), is released when cardiac walls are under stress. High levels of NT-proBNP in the blood are a sign of heart disease. A 2016 Dutch study indicated that high levels of NT-proBNP in the blood are also linked to smaller brain volume, particularly small gray matter volume, and to poorer organization of the brain’s white matter. The study by researcher Hazel I. Zonneveld and colleagues, published in the journal Neuroradiology, assessed heart and brain health in 2,397 middle-aged and elderly people with no diagnosed heart or cognitive problems.
A protein released into the blood in response to heart failure may be able to predict brain deterioration before clinical symptoms appear. The protein, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), is released when cardiac walls are under stress. High levels of NT-proBNP in the blood are a sign of heart disease. A 2016 Dutch study indicated that high levels of NT-proBNP in the blood are also linked to smaller brain volume, particularly small gray matter volume, and to poorer organization of the brain’s white matter. The study by researcher Hazel I. Zonneveld and colleagues, published in the journal Neuroradiology, assessed heart and brain health in 2,397 middle-aged and elderly people with no diagnosed heart or cognitive problems.
Researchers are working to clarify the relationship between cardiac dysfunction and preliminary brain disease, but researcher Meike Vernooij says it is likely cardiac dysfunction comes first and leads to brain damage. Measuring biomarkers such as NT-proBNP may help identify brain diseases such as stroke and dementia earlier and allow for earlier treatment and lifestyle changes that can slow or reverse the course of disease.
Inflammation Linked to Post-Stroke Depression
A 2016 study in the journal Psychoneuroendocrinology confirms that high levels of inflammatory cytokines in the blood are linked to higher risk of depression following a stroke.
The study, by Hee-Ju Kang and colleagues, followed 222 stroke sufferers for one year. Two weeks following the stroke, their levels of inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and IL-18 were measured. They were also assessed for depression both at the two-week point and one year later. The researchers also observed whether or not the participants were treated with statins, which are often prescribed to lower stroke risk and also have anti-inflammatory effects.
Those participants who had depression following their strokes (either at two weeks or at one year) tended to be older, to have a history of depression or stroke, to have a more severe stroke, and to have a stroke location toward the front of the brain.
Having any depression following the stroke was associated with higher levels of IL-6 and IL-18. This was particularly true of those participants who were not taking a statin. Among those taking statins, the statins may have interfered with the link between inflammatory cytokines and post-stroke depression. In the statin group, the only significant finding was a link between levels of IL-6 and depression at the two-week mark.
Depression Elevates Stroke Risk
Depression has been linked to increases in medical problems such as cardiovascular disease. A new study shows that depression is linked to increased risk of stroke, even when symptoms of depression are in remission.
The 2015 study, by Paola Gilsanz and colleagues in the Journal of the American Heart Association, focused on health and retirement. It included over 16,000 adults aged 50 and up who were interviewed every two years about their health history.
Previous studies have shown a link between depression and stroke risk. Like those studies, the study by Gilsanz and colleagues found that people who were depressed during two consecutive interviews were more than twice as likely to have a stroke in the subsequent two-year period than those who reported few depressive symptoms in the first two visits.
What is new is that in this study, people who were depressed in the first interview but not in the second interview were still at 66% greater risk for a stroke than those with no depression. Those who were depressed only during the second interview not at greater risk for a stroke, implying that depression takes more than two years to affect stroke risk.
Gilsanz and colleagues suggest that they don’t know how depression, remission, and stroke risk interact over the longer term. It is possible that stroke risk diminishes the longer a patient’s depression stays in remission.
It is not clear why depression increases strokes, though some have speculated that depression causes irregular heartbeats. There is not as yet any support for that theory, but high blood pressure, rigid veins, or sticky platelets may be other explanations.
Clarifying the Effects of a Diabetes Drug that Improves Bipolar Depression
Research continues on pioglitazone, a drug typically used to treat diabetes but with other positive effects on depression and stroke risk. Some researchers are working on determining whether the drug increases the risk of developing certain cancers, including bladder, prostate, and pancreatic cancers. A recent study by James D. Lewis and colleagues in the journal JAMA found no statistically significant increase in risk of bladder cancer among patients taking the drug, but the researchers said they also couldn’t rule out that the drug may increase this risk, as has been seen in previous studies. The study by Lewis did show an increase in pancreatic and prostate cancers in patients taking pioglitazone, but the researchers did not determine whether this was caused by the drug.
Another recent study by Walter N. Kernan and colleagues in the New England Journal of Medicine reported that pioglitazone reduced the incidence of stroke and heart attack in patients with a history of stroke or blocked blood vessels in the brain but without a diagnosis of diabetes. Patients who received pioglitazone also experienced side effects including weight gain, edema (an increase in fluids in the body’s tissues) and serious bone fractures.
Pioglitazone has had positive effects in bipolar depression and may one day be used as a treatment for bipolar disorder. For now, it may be worthy of consideration for the treatment of diabetes in patients who also have bipolar depression.
Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Reduces Depression Following Strokes
One-third of people who have strokes face depression afterward. New research is looking to expand the safe options for the treatment of depression following strokes. At the 2015 meeting of the Society of Biological Psychiatry, researchers led by Leandro Valiengo presented their successful randomized, sham-controlled double-blind study of transcranial direct current stimulation for post-stroke depression. Forty-eight people who had depression following a stroke were randomized to receive either a sham procedure or tDCS in twelve 30-minute sessions over a period of six weeks. After the six weeks, those who received tDCS had fewer symptoms of depression, more remission, and better response. There were no serious side effects.
TDCS is very low-level electrical current that has a positive (anode) or negative (cathode) electrode. Anodal stimulation of the cortex is usually associated with positive effects on mood and cognition. TDCS sessions in this study consisted of 2-mA anodal left/cathodal right dorsolateral prefrontal stimulation.
Editor’s Note: Placebo-controlled studies have repeatedly indicated that patients who have a stroke show better neurological and psychiatric response afterward when they are given an selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressant, whether or not they have depression or a prior history of depression. If a neurologist does not suggest treatment with an SSRI after a stroke, ask why not. Since antidepressants increase brain levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and increase neurogenesis, they could help with post-stroke recovery.