New Atypical Antipsychotic Lurasidone Appears To Improve Schizophrenia Without Weight-Gain Side Effects
 A study by a research group that included Antony Loebel of pharmaceutical company Sunovion; Steven Potkin of the University of California, Irvine; and Herbert Meltzer from Vanderbilt University summarizes data on a new atypical antipsychotic FDA-approved for treatment of schizophrenia. This agent, lurasidone (Latuda), was studied in a double-blind, placebo-controlled six-week trial in patients with schizophrenia.
A study by a research group that included Antony Loebel of pharmaceutical company Sunovion; Steven Potkin of the University of California, Irvine; and Herbert Meltzer from Vanderbilt University summarizes data on a new atypical antipsychotic FDA-approved for treatment of schizophrenia. This agent, lurasidone (Latuda), was studied in a double-blind, placebo-controlled six-week trial in patients with schizophrenia.
The drug is a new psychotropic agent that has a high affinity for dopamine D2 receptors and serotonin 5HT2A, 5HT1A, and 5HT7 receptors. (New data suggest that antagonistic effects on 5HT7 receptors may be related to antidepressant efficacy.)
In the study, patients were randomized to receive lurasidone at 80mg/day, lurasidone at 160mg/day, quetiapine XR at 600mg/day, or placebo. Evening dosing was used. Both dose levels of lurasidone resulted in significant degrees of improvement compared with quetiapine XR and placebo.
The side effects profile for lurasidone was also promising; patients were no more likely to gain weight on lurasidone than on placebo, while there was a mean 2kg weight increase on quetiapine XR. In addition, total cholesterol and triglycerides on both doses of lurasidone were similar to that on placebo, in contrast to small but significant increases on quetiapine XR.
There were significant increases in levels of prolactin (a hormone related to lactation, sex function, and bone demineralization) on lurasidone at both 80mg (+ 0.8mg/dl) and 160mg (+ 3mg/dl), while small decreases in prolactin were observed on quetiapine XR (-0.3 mg/dl) and on placebo (-0.8 mg/dl).
The data suggest that lurasidone is effective in the treatment of patients with acute exacerbation of schizophrenia, with significant effects occurring as early as day 4. This study had a low rate of adverse events. Read more
Dopamine D2 and D3 Agonist Pramipexole May Enhance Cognitive Function in Bipolar I Disorder
Anil Malhotra from the Zucker Hillside Hospital found that pramipexole (Mirapex), a dopamine D2 and D3 agonist used in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease, improved measures of processing speed and working memory in euthymic bipolar patients (whose average age was 42) when compared with placebo in an adjunctive clinical trial.
Editor’s Note: Bipolar patients in a euthymic phase have consistently been shown to have some degree of cognitive dysfunction that is typically correlated with the number of prior depressive and/or manic episodes they have experienced. This is one of the first studies to directly target this cognitive dysfunction with a pharmacotherapeutic agent.
Pramipexole may be of additional value among depressed patients, because in two small, placebo-controlled studies, one led by Carlos Zarate at the National Institute of Mental Health and one led by Joseph F. Goldberg in New York, pramipexole has been shown to exert acute antidepressant effects in bipolar patients in the depressive phase of the illness. The new data from Malhotra raise the possibility that there could be a two-for-one benefit when pramipexole is used in the depressive phase of bipolar illness—improvement in both depression and cognition.
Other approaches to improving cognition in patients with bipolar disorder
Preventing Recurrent Mood Episodes
Psychotherapy and psychoeducational approaches, long-term psychopharmacology, and combination therapy all play a role in preventing recurrent mood episodes.
Psychotherapeutic and Psychoeducational Approaches Are Critical
A number of studies presented at the 4th Biennial Conference of the International Society for Bipolar Disorders in Sao Paulo, Brazil in March indicated that cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and individual and group psychoeducational approaches enhance both short- and long-term outcomes for patients with bipolar illness. These studies add to an already substantial literature that shows that focused psychotherapies (such as cognitive/behavioral, interpersonal, and social rhythms therapies) and psychoeducation are superior to treatment as usual.
These therapies can provide a variety of approaches to stress management and reduction, and can enhance family and interpersonal communication. Another way these focused psychotherapeutic approaches help patients is by demonstrating the benefits of effective long-term preventive treatment and encouraging its consistent use.
Without consistent prophylactic treatment, patients are at high risk for recurrences and their subsequent psychosocial and neurobiological consequences. Greater number of prior episodes is associated with an increased risk of psychosocial dysfunction, treatment resistance, cognitive dysfunction, medical comorbidities, and even dementia in old age.
After the jump: preventive psychopharmacology and combination therapy. Read more
One Expert’s Personal Treatment Algorithm for Bipolar Disorder in Young Children
EDITOR’S NOTE: Dr. Gagin Joshi of Massachusetts General Hospital, who presented the work on carbamazepine and lamotrigine on page 1 provided us with his own general treatment algorithm for youngsters with bipolar disorder.

Omega-3 Fatty Acids (photo from ironmagazine.com)
Joshi typically starts with 0.5 to 2 gms of omega-3 fatty acids because of their benign side-effects profile, the many studies suggesting they are effective in adult mood disorders, and a recent article indicating that they were effective in preventing the conversion of prodromal schizophrenia into full-blown illness in a randomized double-blind controlled study in Australia.
After the omega-3 fatty acids, Joshi’s second choice is typically the atypical antipsychotic aripiprazole (Abilify) because of its lesser degree of weight gain compared to atypicals quetiapine (Seroquel) or risperidone (Risperidol). Risperidone can be a third option if aripiprazole is not effective or tolerated.
Quetiapine is Effective Across a Spectrum of Illnesses
The atypical antipsychotic quetiapine (Seroquel or Seroquel XR) has a range of efficacy in a number of illnesses, depending on the size of the dose given. Read about some of its uses below, including as an adjunct to antidepressants in unipolar depression; as a treatment for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD); and, at higher doses, as a treatment for mania and depression. Some of its potential mechanisms of action are described as well.
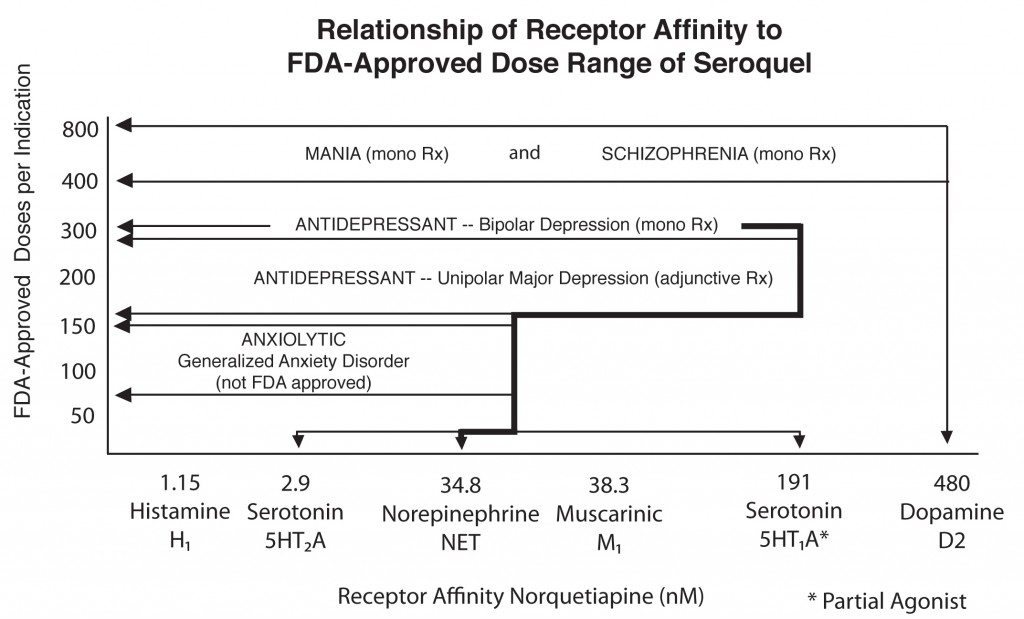
Quetiapine's actions on various receptors in the brain (bottom axis) are responsible for its effects in different illnesses
Quetiapine as an adjunct to antidepressants in unipolar depression
Posters at the American Psychiatric Association meeting in San Francisco in May 2009 showed new data from a series of studies of quetiapine in unipolar depression that showed the drug in monotherapy (at 150mg & 300mg) was significantly more effective than placebo. Studies were also positive when quetiapine was used as an adjunct compared with placebo for patients showing inadequate or incomplete responses to antidepressants such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
Read more
Treating Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is a prevalent illness often associated with considerable discomfort and dysfunction. It often co-occurs with bipolar disorder. Traditional treatments of the primary syndrome (occurring in the absence of bipolar disorder) involve serotonin-selective antidepressants and serotonin-noradrenergic reuptake inhibitors such as venlafaxine (Effexor) or duloxitine (Cymbalta). While these are often useful and lead to considerable improvement, they often do not lead to full remission of somatic or accompanying symptoms of insomnia.
Alternative treatment possibilities include the anticonvulsant pregabalin (Lyrica), which has been found effective in four placebo-controlled studies in GAD. A poster presentation by Joshi et al. at the American Psychiatric Association meeting in San Francisco in May 2009 also reported that pregabalin was more effective in reducing sleep disturbance than venlafaxine. Pregabaline is FDA-approved for seizures and fibromyalgia, but not for GAD or pain syndromes. Another treatment possibility is quetiapine (Seroquel), where not only have there been positive efficacy in placebo-controlled studies of patients with GAD, but the patients also experienced improvement in sleep.
Read more



