Track Your Moods with Life Charting
If you have unipolar depression or bipolar disorder and are having trouble stabilizing your mood, we recommend nightly charting of mood, medications and side effects on the easy-to-use Monthly Mood Chart Personal Calendar (pictured below) or the National Institute of Mental Health Life Chart (NIMH-LCM), both of which are available for download.

Sample Mood Chart
Click on the Life Charts tab above to download the personal calendar, which includes space for rating mood, functioning, hours of sleep, life events, side effects, and other symptoms such as anxiety. Then bring the chart to each visit with your physician to help in the assessment of treatments.
Life charting can help determine which medications are working partially and need to be augmented further, and which need to be eliminated because of side effects. Since there are now many potential treatments for depression and bipolar disorder (some FDA-approved and some not), a careful assessment of how well each new treatment works for a particular patient is essential to finding the optimal treatment regimen.
Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Bipolar Disorder
A number of studies presented at the 4th Biennial Conference of the International Society for Bipolar Disorders conference in Sao Paulo, Brazil in March reported new data relevant to inflammation and oxidative stress. Both inflammation and oxidative stress increase risk of cardiovascular disorders, and patients with inadequately treated mood disorders lose 10 or more years of life expectancy from cardiovascular disorders compared to the general population. Inflammation and oxidative stress may also contribute to the symptoms, evolution, and progression of the mood disorders themselves.
It is possible that these two processes could become new targets for therapeutic intervention in addition to more traditional psychopharmacological drugs that primarily target the neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin, and the neurotrophic factor BDNF. Read more
Thyroid Augmentation Helps Depression (And Bipolar Disorder in Women)
Low dose thyroid replacement treatment with T3 (Cytomel) (25-37.5 µg) is typically recommended for acute antidepressant augmentation in unipolar and bipolar depression. This approach has few side effects and works even in those with normal thyroid function at baseline.
Some data also supports the use of relatively high (supraphysiological) doses of T4 (Synthroid) late in the treatment of highly treatment-resistant patients with unipolar and bipolar disorder. These supra-physiological doses of T4 typically ranged from 300-500 µg/day, producing a free thyroxine index of 150% of normal. This is usually moderately well tolerated, although minor degrees of sweating, tachycardia (fast heartbeat), and other signs of hyperthyroidism can accompany this regimen. If this approach is employed, it is particularly important to increase the dose of T4 (Synthroid) very slowly because of its relatively long half-life—about 12 days. (That is, if a patient takes a high dose of T4 and then stops their medication completely, 12 days later blood levels will only have decreased to half of what they originally were.)
Findings about high-dose T4 for women with treatment-resistant bipolar illness after the jump. Read more
5 Myths About Unipolar Depression
 Early this year, news stories such as Newsweek’s “The Depressing News About Antidepressants” and “Antidepressant Drug Effects and Depression Severity” in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) created an inadequate picture of the seriousness of clinical depression, and the importance of preventing recurrent episodes with long-term antidepressant treatment. (For a rebuttal, see Psychiatric Times.)
Early this year, news stories such as Newsweek’s “The Depressing News About Antidepressants” and “Antidepressant Drug Effects and Depression Severity” in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) created an inadequate picture of the seriousness of clinical depression, and the importance of preventing recurrent episodes with long-term antidepressant treatment. (For a rebuttal, see Psychiatric Times.)
The consequences of this distorted depiction of depression and its treatment are potentially dire for individuals’ health. Some of the popular myths about depression deserve critical review so that patients can make more informed decisions about their own treatment.
Myth 1: Depression is all in your mind
Myth 2: Depression is over-treated
Myth 3: Antidepressant efficacy barely exceeds that of placebo
Myth 4: Antidepressants should be stopped as soon as possible
Myth 5: Depression is a minor medical problem
Myth 1: Depression is all in your mind
This might seem valid, since depression is classified as a mental illness. But depression is not abstract, imaginary, or lacking a solid physical foundation. There is now overwhelming evidence that depression coincides with disturbances in multiple brain and body systems.
Quetiapine is Effective Across a Spectrum of Illnesses
The atypical antipsychotic quetiapine (Seroquel or Seroquel XR) has a range of efficacy in a number of illnesses, depending on the size of the dose given. Read about some of its uses below, including as an adjunct to antidepressants in unipolar depression; as a treatment for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD); and, at higher doses, as a treatment for mania and depression. Some of its potential mechanisms of action are described as well.
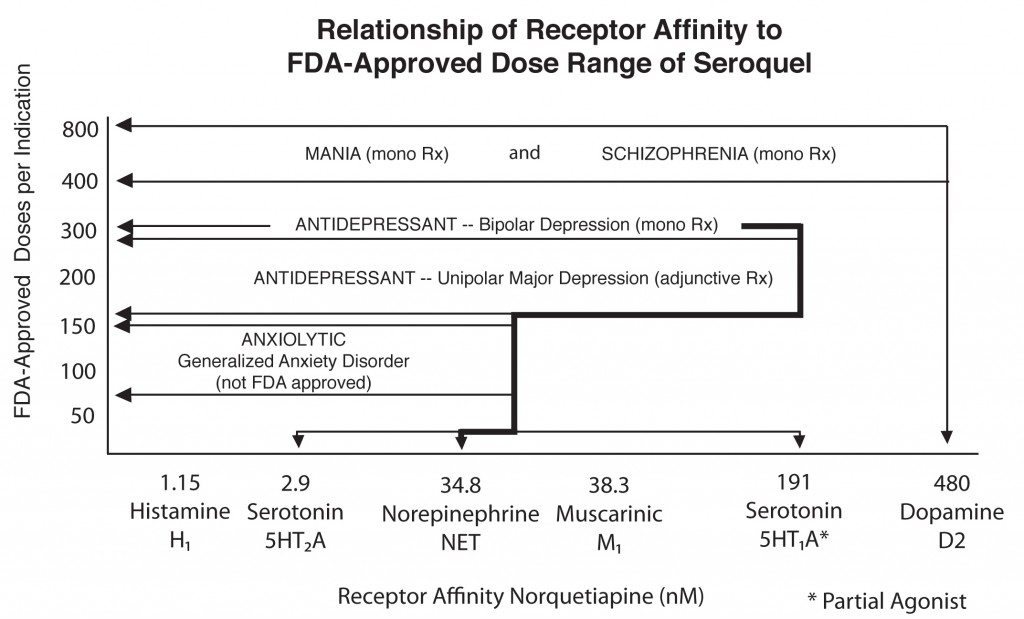
Quetiapine's actions on various receptors in the brain (bottom axis) are responsible for its effects in different illnesses
Quetiapine as an adjunct to antidepressants in unipolar depression
Posters at the American Psychiatric Association meeting in San Francisco in May 2009 showed new data from a series of studies of quetiapine in unipolar depression that showed the drug in monotherapy (at 150mg & 300mg) was significantly more effective than placebo. Studies were also positive when quetiapine was used as an adjunct compared with placebo for patients showing inadequate or incomplete responses to antidepressants such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
Read more


