Baseline Levels of CRP Could Help Predict Clinical Response to Different Treatments
C-reactive protein, or CRP, is a marker or inflammation that has been linked to depression and other illnesses. People with high levels of CRP respond differently to medications than people with lower CRP, so assessing CRP levels may help determine which medications are best to treat a given patient.
High baseline levels of CRP (3–5pg/ml) predict a poor response to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressants (SSRIs) and to psychotherapy, and are associated with increased risk of recurrent depression, heart attack, and stroke.
However, high baseline CRP predicts a better response to the antidepressants nortriptyline and bupropion. High CRP is also associated with better antidepressant response to infliximab (a monoclonal antibody that inhibits the inflammatory cytokine TNF alpha), while low levels of CRP predict worsening depression upon taking infliximab.
High baseline CRP also predicts good antidepressant response to intravenous ketamine (which works rapidly to improve treatment-resistant depression), minocycline (an anti-inflammatory antibiotic that decreases microglial activation), L-methylfolate (a supplement that can treat folate deficiency), N-acetylcysteine (an antioxidant that can improve depression, pathological habits, and addictions), and omega-3 fatty acids (except in people with low levels of DHA).
High baseline CRP also predicts a good response to the antipsychotic drug lurasidone (marketed under the trade name Latuda) in bipolar depression. In people with high baseline CRP, lurasidone’s positive results have a huge effect size of 0.85, while in people with low CRP (<3pg/ml) the improvement on lurasidone has a smaller effect size (0.35).
In personal communications with this editor (Robert M. Post) in 2018, experts in the field (Charles L. Raison and Vladimir Maletic) agreed that assessing baseline CRP levels in a given patient could help determine optimal strategies to treat their depression and predict the patient’s responsiveness to different treatment approaches.
At a 2018 scientific meeting, researchers Cynthia Shannon, Thomas Weickert, and colleagues reported that high baseline levels of CRP were associated with symptom improvement in patients with schizophrenia when they were treated with the drug canakinumab (marketed under the trade name Ilaris). Canakinumab is a human monoclonal antibody that targets the inflammatory cytokine interleukin-1 beta (Il-1b). Il-1b is elevated in a subgroup of patients with depression, bipolar disorder, or schizophrenia, and CRP levels are an indication of the associated inflammation.
Ketamine May Enhance the Effects of Cognitive Training Therapy
Rebecca B. Price, a professor of Psychiatry and Psychology at the University of Pittsburgh, and colleagues reported at a recent scientific meeting that the combination of intravenous ketamine treatment and four days of cognitive training to enhance positive self-representations improved depression better than either intervention alone (IV ketamine plus a sham training or a non-medicated saline drip plus 4 days of cognitive work).
Price and colleagues suggested that priming brain plasticity with ketamine could enhance cognitive training focused on increasing positive self-representations. Psychologists have theorized that self-representations (or assessments of one’s strengths and other qualities) can be a resource that helps people cope with life stress.
Il-6 Inhibitor Sirukumab May Improve Anhedonia, But Not General Depression
 At a 2018 scientific meeting, researcher Giacomo Salvadore and colleagues reported that the drug sirukumab, a monoclonal antibody that targets the inflammatory marker Il-6 and that was originally developed to treat rheumatoid arthritis, did not have a statistically significant effect on overall depression compared to placebo. However, by the twelfth week of treatment, sirukumab did have a significant effect on anhedonia (loss of interest or pleasure in activities that one previously enjoyed).
At a 2018 scientific meeting, researcher Giacomo Salvadore and colleagues reported that the drug sirukumab, a monoclonal antibody that targets the inflammatory marker Il-6 and that was originally developed to treat rheumatoid arthritis, did not have a statistically significant effect on overall depression compared to placebo. However, by the twelfth week of treatment, sirukumab did have a significant effect on anhedonia (loss of interest or pleasure in activities that one previously enjoyed).
The degree of improvement in anhedonia was significantly correlated with patients’ baseline levels of the inflammatory marker CRP. Since the inflammatory marker that sirukumab targets, Il-6, is one of those most often elevated in depression, it appears that more study of sirukumab would be warranted.
Low Levels of Acetyl-L-Carnitine Associated with Insulin Resistance in Traumatized Children
 Researcher Carla Nasca and colleagues from the Rockefeller University reported at a late-2018 scientific meeting that depressed patients with a history of childhood adversity had low levels of the amino acid acetyl-L-carnitine and also exhibited insulin resistance. This is noteworthy because in a series of small studies, acetyl-L-carnitine supplements have had antidepressant effects. In laboratory animals, acetyl-L-carnitine also sensitizes insulin receptors. This suggests the possibility that the supplements could provide a two-for-one benefit in depressed patients with a history of adversity in childhood.
Researcher Carla Nasca and colleagues from the Rockefeller University reported at a late-2018 scientific meeting that depressed patients with a history of childhood adversity had low levels of the amino acid acetyl-L-carnitine and also exhibited insulin resistance. This is noteworthy because in a series of small studies, acetyl-L-carnitine supplements have had antidepressant effects. In laboratory animals, acetyl-L-carnitine also sensitizes insulin receptors. This suggests the possibility that the supplements could provide a two-for-one benefit in depressed patients with a history of adversity in childhood.
Vitamin D3 Improves Depression in Older Adults
Researcher Negin Masoudi Alavi and colleagues reported in the journal Clinical Nutrition in 2018 that compared to placebo, 50,000 IU of vitamin D3 taken weekly for eight weeks improved depression in depressed patients over the age of 60.
Although the literature about vitamin D3’s effects on depression are mixed, a 2014 meta-analysis by Simon Spedding in the journal Nutrients found that in studies of vitamin D-deficient depressed participants whose vitamin D levels were restored to normal levels by the end of the study, vitamin D significantly improved depression. (Spedding attributed earlier mixed results to studies that did not clearly correct a vitamin D deficiency.) A 2013 study by Nayereh Khoraminya and colleagues in the Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry suggested that a 1500 IU dose of vitamin D3 combined with the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressant fluoxetine improved depression more than fluoxetine plus placebo in depressed patients who were not necessarily deficient in vitamin D. Another study by Jacqueline A. Pettersen in the journal Experimental Gerontology found that in healthy adults, 4,000 IU of vitamin D3 improved cognitive functioning (namely visual memory) more than 400 IU.
Editor’s Note: Given these promising studies, the safety of D3, and fact that psychiatric patients are often deficient in vitamin D3, taking vitamin D3 supplements to improve depression might be worth trying.
Inflammation is Associated with Antidepressant Treatment Resistance
Researcher Ebrahim Haroon and colleagues report in a 2018 issue of Psychoneuroendocrinology that people whose depression failed to respond to at least three different antidepressants in their current episode of depression had higher levels of inflammation than those who had fewer than three failed antidepressant trials.
The researchers found that patients who had not responded to antidepressants had higher levels of the inflammatory markers TNF-alpha, TNF-alpha receptor 2, and Il-6. The inflammatory marker CRP was also significantly elevated in these patients when statistical analyses that excluded body mass index (BMI) were used.
Haroon and colleagues reported that a third of all patients with major depressive disorder fail to respond to currently available antidepressant treatments, and that inflammation may be to blame because it interferes with the neurotransmitter systems that antidepressants target.
Editor’s Note: These data indirectly support the use of anti-inflammatory drugs to augment the effects of antidepressants in patients with treatment resistant depression. A caution that may be very important is to assess evidence of inflammation at baseline, as some data suggest that people with low CRP may, for example, do more poorly with a blocker of TNF-alpha, while people with high CRP at baseline (over 3 pg/ml) show good improvement.
Inflammatory Marker IL-6 is Elevated in People with Depression and Those with a History of Childhood Trauma
In a 2018 article in the journal Psychiatry Research, researcher Ana Munjiza and colleagues reported that the inflammatory marker IL-6 was higher in 64 depressed people than in 53 non-depressed people, and that levels of IL-6 among people in the depressed group were significantly correlated with scores on a questionnaire in which participants reported traumas experienced in childhood. They reported more physical abuse, physical neglect, and emotional abuse.
Munjiza and colleagues indicate that trauma in childhood is a risk factor for depression in adulthood, as other researchers have suggested, and that inflammation could mediate the relationship between childhood adversity and depression.
Editor’s Note: IL-6 has been associated with antidepressant treatment resistance. IL-6 is secreted from white cells in the blood and from monocytes from the bone marrow in response to stress. It enters the brain and starts an inflammatory cascade that induces depressive behaviors. Animal studies have shown that if IL-6 secretion is blocked, depressive-like behaviors do not occur.
Another indicator of inflammation is CRP, and elevations in CRP have been associated with poor response to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressants, and better response to the noradrenergic tricyclic antidepressant nortriptyline and the dopamine active antidepressant bupropion.
Treatments for depressed people with histories of childhood trauma may include psychotherapy, somatic therapies such as repeated transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) and transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), and medication. More research is needed to determine the optimal treatment regimens for this subgroup of depression sufferers, including whether anti-inflammatory drugs could play a helpful role in preventing or treating depression. People with elevated inflammatory markers (such as IL-6, CRP, IL-1, or TNF-alpha) are likely to be better candidates for adjunctive anti-inflammatory treatments than those with normal or low baseline levels of inflammation.
Inflammation and Depression: Treatment Implications
 Vladimir Maletic of the University of South Carolina School of Medicine Greenville gave a plenary talk at the 2018 meeting of the North Carolina Psychiatric Association that described a variety of ways that inflammation can drive depression.
Vladimir Maletic of the University of South Carolina School of Medicine Greenville gave a plenary talk at the 2018 meeting of the North Carolina Psychiatric Association that described a variety of ways that inflammation can drive depression.
Maletic explained that stress can increase neurotransmitters that activate brain macrophages, increase NFkB (a protein that controls DNA transcription and cell survival), and increase brain inflammation, evidenced by elevated levels of the inflammatory markers IL-1b, IL-6, TNF-alpha, and C-reactive protein (CRP). These signs of inflammation are associated with changes in brain function and connectivity that are consistent with depression, fatigue, and cognitive slowing.
Inflammation measured outside of the brain and spinal cord is associated with increased activity of the insula (a key brain sensor and modulator of emotions), disconnection between the prefrontal cortex and the reward circuits in the nucleus accumbens, and decreased function and structural changes to the hippocampus (critical for memory).
Maletic also explained that inflammation changes the way the amino acid tryptophan is metabolized. Normally tryptophan is converted into kyneurenic acid, which prevents excitotoxicity and has anticonvulsant effects. Stress can lead to tryptophan being metabolized instead into quinolinic acid, which is neurotoxic and has been linked to certain psychiatric disorders and neurodegenerative processes. This in turn impairs synaptic functioning, including increasing glutamate and decreasing brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), impairing a type of glia called oligodendroglia (which produce myelin), and the formation of new neural connections.
These findings have several important implications for treatment. Increases in inflammation have been linked to the atypical type of depression characterized by increased appetite, weight gain, and increased sleep rather than the more classic presentation of depression that includes loss of appetite, weight loss and insomnia. Thus, weight gain, waist circumference, and body mass index (BMI) are correlated with inflammation and can signal a poor response to medications (including the rapid-acting antidepressant ketamine and some other antidepressants). If someone with unipolar depression has high levels of CRP, they tend to have a poorer response to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressants, and may respond better to the noradrenergic tricyclic antidepressant nortryptyline, the serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), and the dopamine active antidepressant bupropion.
There is some good news. Read more
Using Light to Improve Sleep and Depression
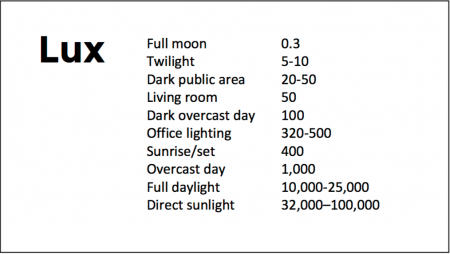
At the 2018 meeting of the North Carolina Psychiatric Association, researcher Chris Aiken described the phenomenon of sleep inertia, when people are awakened from deep sleep by an alarm, rather than waking at the end of a sleep cycle, and are groggy for 15 minutes. Depressed people may stay groggy for 4 hours. A dawn simulator may help. These lights turn on gradually over the course of 30 to 60 minutes, reaching 250 lux while the patient is still asleep. Dawn simulators have worked in eight out of ten controlled clinical trials to help people with seasonal affective disorder, adolescents, and normal adults wake up more easily. They range in cost from $25 to $90 and some brands include PER2LED or LightenUp. Aiken says dawn simulators can improve depression, sleep quality, and cognition.
Evening and nighttime light: Bright lights and blue light, like the light that comes from electronic screens, can shut down the body’s secretion of melatonin, making people awake and alert in the evening when they should be getting sleepy. Dim light or glasses that filter out blue light allow increases in melatonin secretion in the evening, while bright light suppresses it. Missing this early melatonin pulse creates “night owls” who have delayed sleep onset.
Because light still reaches our eyes through our eyelids as we sleep, even low-level light during the night impairs sleep, cognition, and learning, and increases the risk of depression by a hazard ratio of 1.8 (about double the risk). A 2017 study by Kenji Obayashi in the American Journal of Epidemiology found that bedroom light above 5 lux elevated rates of depression in older adults after two years of followup. Living room light averaged around 50 lux and increased depression further.
The treatment is turning off TVs, electronic screens, and cellphones in the evening or wearing blue-blocking glasses, which can be found for less than $10. Blue-blocking glasses can increase calmness and reduce anxiety, and even are effective in treating mania. Then, during sleep, wear an eye mask or get light-blocking blinds or curtains for windows. For a complete blackout, use blackout curtains, aluminum foil over windows, electric tape over LED lights, or try sleeping in the basement.
Aiken suggests that to re-instate healthy sleep patterns, people should institute virtual darkness from 6pm to 8am, including wearing blue-blocking glasses when out of bed. Then they should institute total darkness or wear an eye mask when in bed. When symptoms improve, this routine can gradually be shifted to begin later in the evening, such as two hours before bedtime.
Blue light filters are also available for smartphones and tablets including Apple Nightshift mode, Kindle BlueShade, and Android Twilight and Blue Light Filter.
Glasses that filter out blue light include Uvex Ultraspec 2000, 50360X ($7 on Amazon) and Uvex Skyper 351933X ($7-10 on Amazon). The website lowbluelights.com sells blue-blocking glasses from $45 and a variety of other blue-free lighting products such as lightbulbs and flashlights.
Bright light therapy for unipolar and bipolar depression: 30 minutes of bright light (7,500 to 10,000 lux) in the morning can help treat depression in unipolar and bipolar disorder and seasonal affective disorder. The effects usually take 3 to 7 days to set in, but they only last while a patient continues using the bright light in the morning. Researcher Dorothy K. Sit and colleagues found that bright light therapy in the morning sometimes caused hypomanic reactions in people with bipolar disorder, and reported in a 2018 article in the American Journal of Psychiatry that midday light therapy (from noon to 2:30pm) was also effective without this unwanted effect. However, a 2018 article by Ne?e Yorguner Küpeli and colleagues in the journal Psychiatry Research suggested that a half hour of morning light for two weeks was sufficient to bring about improvement in 81% of patients with bipolar disorder and did not cause serious side effects.
Melatonin regimen for sleep onset delay: Melatonin can be used to treat severe night-owls with a very late onset of sleep (for example, going to bed at 2 or 3am and sleeping late into the morning). Melatonin can help with sleep onset to some extent when used at bedtime, but in those with an extreme phase shift, researcher Alfred J. Lewy recommends a regimen of low dose priming with 400–500 micrograms of melatonin at 4pm and then a full dose of 3 milligrams of melatonin at midnight. The 4pm priming dose helps pull back the delayed onset of the body’s secretion of melatonin toward a more normal schedule.
Recent Cannabis Use Linked to Greater Symptoms of Anxiety and Mood Disorders and Less Response to Treatment
 In a 2018 systematic literature review published in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, researcher George Mamman and colleagues reported that across 12 studies of people with anxiety and mood disorders, participants who had used cannabis in the previous six months had more symptoms than those who had used less cannabis or no cannabis during that period.
In a 2018 systematic literature review published in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, researcher George Mamman and colleagues reported that across 12 studies of people with anxiety and mood disorders, participants who had used cannabis in the previous six months had more symptoms than those who had used less cannabis or no cannabis during that period.
The 12 studies reviewed included a total of 11,959 participants. Four studies looked at post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), one at panic disorder, five at bipolar disorder, and 2 at depressive disorder. In addition to finding that recent cannabis use was associated with greater symptoms, the authors of the review also found that in 10 of the 12 studies, recent cannabis use was associated with less symptom improvement in response to treatment for bipolar disorder, depression, and PTSD; including both medication and psychotherapy.
In bipolar disorder, cannabis use was associated with greater symptom severity. Cannabis use for more than one year was linked to more recurrences of mania and shortened time to a recurrence. Compared to participants with no prior use of cannabis, those with a cannabis use disorder had more depressive symptoms, including sleep troubles and loss of interest in activities one had previously enjoyed.
In PTSD, any cannabis use at the beginning of the analysis period and sustained use of cannabis over time were both linked to greater symptom severity in the four months following the beginning of the analysis.
Mammen and colleagues cautioned that these results are limited based on the differences in measurements across the 12 studies, the inpatient populations under study, and the uncontrolled nature of the cannabis the participants accessed on their own time. However, the authors suggest that the findings may inform patients’ and doctors’ conversations about whether or not to use cannabis.