High Baseline Levels Of C-Reactive Protein Predict Better Response To Lurasidone in Bipolar Depression
In a study presented at the 2017 meeting of the International Society for Affective Disorders, Charlies L. Raison and colleagues examined whether baseline levels of the inflammatory marker C-reactive protein (CRP) affected antidepressant response to the antipsychotic drug lurasidone in bipolar depression. The participants were divided into three double-blind groups: one received 20–60mg/day of lurasidone, another received 80–120 mg/day of lurasidone, and the third received placebo over a period of six weeks. The effect was dramatic—in people with CRP levels above 5 mg/L at the beginning of the study, lurasidone (at either dosage level) had a very large effect size (d=0.85), while in people with baseline CRP levels below 5 mg/L the effect size was smaller (d=0.35).
Interestingly, 118 of the participants (24.5%) had CRP levels above 5mg/L at baseline, indicating a substantial amount of inflammation was present in a quarter of the bipolar depressed patients. Higher levels of CRP at baseline were correlated with better improvement on specific items on the Montgomery–Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS): “lassitude” (or lack of energy), “apparent sadness,” “reported sadness,” and “pessimistic thoughts.” Raison and colleagues concluded: “These findings suggest that the efficacy of lurasidone in patients with bipolar depression may in part be linked to the inflammatory status of patients prior to treatment. If confirmed in prospective investigations, [the results of a wide-range CRP assay] may prove useful as a predictive biomarker that could help optimize the use of lurasidone for the treatment of patients with bipolar depression.”
Editor’s Note: In many instances, high levels of CRP predict a poor response to treatment (such as to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressants (SSRIs) in unipolar depression), so these findings are of considerable interest. They also suggest the untested possibility that lurasidone has anti-inflammatory effects, as those with high levels of inflammation at baseline often respond better to drugs with direct anti-inflammatory effects such as celecoxib (Celebrex) or the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (NAC).
Inflammation is Associated with Antidepressant Treatment Resistance
Researcher Ebrahim Haroon and colleagues report in a 2018 issue of Psychoneuroendocrinology that people whose depression failed to respond to at least three different antidepressants in their current episode of depression had higher levels of inflammation than those who had fewer than three failed antidepressant trials.
The researchers found that patients who had not responded to antidepressants had higher levels of the inflammatory markers TNF-alpha, TNF-alpha receptor 2, and Il-6. The inflammatory marker CRP was also significantly elevated in these patients when statistical analyses that excluded body mass index (BMI) were used.
Haroon and colleagues reported that a third of all patients with major depressive disorder fail to respond to currently available antidepressant treatments, and that inflammation may be to blame because it interferes with the neurotransmitter systems that antidepressants target.
Editor’s Note: These data indirectly support the use of anti-inflammatory drugs to augment the effects of antidepressants in patients with treatment resistant depression. A caution that may be very important is to assess evidence of inflammation at baseline, as some data suggest that people with low CRP may, for example, do more poorly with a blocker of TNF-alpha, while people with high CRP at baseline (over 3 pg/ml) show good improvement.
Using Light to Improve Sleep and Depression
At the 2018 meeting of the North Carolina Psychiatric Association, researcher Chris Aiken described the phenomenon of sleep inertia, when people are awakened from deep sleep by an alarm, rather than waking at the end of a sleep cycle, and are groggy for 15 minutes. Depressed people may stay groggy for 4 hours. A dawn simulator may help. These lights turn on gradually over the course of 30 to 60 minutes, reaching 250 lux while the patient is still asleep. Dawn simulators have worked in eight out of ten controlled clinical trials to help people with seasonal affective disorder, adolescents, and normal adults wake up more easily. They range in cost from $25 to $90 and some brands include PER2LED or LightenUp. Aiken says dawn simulators can improve depression, sleep quality, and cognition.
Evening and nighttime light: Bright lights and blue light, like the light that comes from electronic screens, can shut down the body’s secretion of melatonin, making people awake and alert in the evening when they should be getting sleepy. Dim light or glasses that filter out blue light allow increases in melatonin secretion in the evening, while bright light suppresses it. Missing this early melatonin pulse creates “night owls” who have delayed sleep onset.
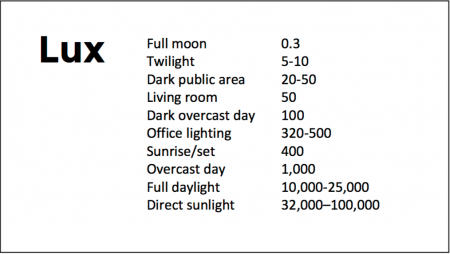
Because light still reaches our eyes through our eyelids as we sleep, even low-level light during the night impairs sleep, cognition, and learning, and increases the risk of depression by a hazard ratio of 1.8 (about double the risk). A 2017 study by Kenji Obayashi in the American Journal of Epidemiology found that bedroom light above 5 lux elevated rates of depression in older adults after two years of followup. Living room light averaged around 50 lux and increased depression further.
The treatment is turning off TVs, electronic screens, and cellphones in the evening or wearing blue-blocking glasses, which can be found for less than $10. Blue-blocking glasses can increase calmness and reduce anxiety, and even are effective in treating mania. Then, during sleep, wear an eye mask or get light-blocking blinds or curtains for windows. For a complete blackout, use blackout curtains, aluminum foil over windows, electric tape over LED lights, or try sleeping in the basement.
Aiken suggests that to re-instate healthy sleep patterns, people should institute virtual darkness from 6pm to 8am, including wearing blue-blocking glasses when out of bed. Then they should institute total darkness or wear an eye mask when in bed. When symptoms improve, this routine can gradually be shifted to begin later in the evening, such as two hours before bedtime.
Blue light filters are also available for smartphones and tablets including Apple Nightshift mode, Kindle BlueShade, and Android Twilight and Blue Light Filter.
Glasses that filter out blue light include Uvex Ultraspec 2000, 50360X ($7 on Amazon) and Uvex Skyper 351933X ($7-10 on Amazon). The website lowbluelights.com sells blue-blocking glasses from $45 and a variety of other blue-free lighting products such as lightbulbs and flashlights.
Bright light therapy for unipolar and bipolar depression: 30 minutes of bright light (7,500 to 10,000 lux) in the morning can help treat depression in unipolar and bipolar disorder and seasonal affective disorder. The effects usually take 3 to 7 days to set in, but they only last while a patient continues using the bright light in the morning. Researcher Dorothy K. Sit and colleagues found that bright light therapy in the morning sometimes caused hypomanic reactions in people with bipolar disorder, and reported in a 2018 article in the American Journal of Psychiatry that midday light therapy (from noon to 2:30pm) was also effective without this unwanted effect. However, a 2018 article by Ne?e Yorguner Küpeli and colleagues in the journal Psychiatry Research suggested that a half hour of morning light for two weeks was sufficient to bring about improvement in 81% of patients with bipolar disorder and did not cause serious side effects.
Melatonin regimen for sleep onset delay: Melatonin can be used to treat severe night-owls with a very late onset of sleep (for example, going to bed at 2 or 3am and sleeping late into the morning). Melatonin can help with sleep onset to some extent when used at bedtime, but in those with an extreme phase shift, researcher Alfred J. Lewy recommends a regimen of low dose priming with 400–500 micrograms of melatonin at 4pm and then a full dose of 3 milligrams of melatonin at midnight. The 4pm priming dose helps pull back the delayed onset of the body’s secretion of melatonin toward a more normal schedule.
Cannabidiol Drug Approved For Rare and Severe Types of Epilepsy
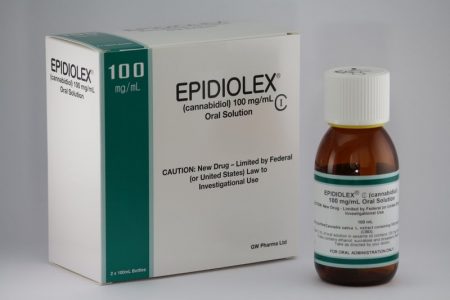
In June, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the first time approved a drug derived completely from the cannabis plant. The drug, Epidiolex, a syrup, contains cannabidiol, the cannabis component that has been found to treat certain ailments. In a news release, the FDA stated that cannabidiol does not cause intoxication or a ‘high’. Tetrahydrocannabinol, or THC, is the cannabis component that makes people high, impairs cognition, and can induce paranoia.
The approval led, in September, to the Drug Enforcement Agency re-classifying FDA-approved drugs containing cannabidiol derived from cannabis and less than 0.1% THC as schedule V controlled substances. So far only Epidiolex meets these criteria. Cannabis had previously been classified as a schedule I controlled substance, in the same legal category as heroin, LSD, or ecstasy.
Epidiolex is now approved to treat two rare, severe types of epilepsy, Lennox-Gastaut syndrome and Dravet syndrome, in patients aged two years and older. It is the first FDA-approved treatment for Dravet syndrome, a genetic condition that appears in the first year of life when babies develop fever-related seizures. Other types of seizures, even including a continuous seizure state, can occur later.
Lennox-Gastaut syndrome also develops in young children, usually between the ages of three and five. They have multiple types of seizures with debilitating consequences.
In three randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials that included a total of 516 patients with either Lennox-Gastaut syndrome or Dravet syndrome, the drug reduced the frequency of patients’ seizures compared to placebo.
Side effects of Epidiolex include sleepiness, sedation and lethargy; elevated liver enzymes; decreased appetite; diarrhea; rash; fatigue, malaise and weakness; insomnia, sleep disorder and poor quality sleep; and infections. The FDA also warned in its approval that “[a]s is true for all drugs that treat epilepsy, the most serious risks include thoughts about suicide, attempts to commit suicide, feelings of agitation, new or worsening depression, aggression and panic attacks.” The drug is produced by GW Pharmaceuticals, which has already gained approval outside the US for a cannabis-based drug to treat multiple sclerosis.
Editor’s Note: It is important for readers to know that most marijuana available in the US contains mostly THC with minimal cannabidiol.
Early Intervention Works in Schizophrenia: Also Needed in Bipolar Disorder
For twenty years, evidence has shown that early intervention can ameliorate many of the adverse consequences of schizophrenia. In a 2018 article in the journal Annual Review of Clinical Psychiatry titled “Transforming the treatment of schizophrenia in the United States: The RAISE Initiative,” Lisa B. Dixon and colleagues described the importance of early intervention in schizophrenia. RAISE stands for Recovery After an Initial Schizophrenia Episode. Dixon and colleagues emphasize that shortening the time that a patient’s psychosis goes untreated, which averages 74 months, is critical to achieving good outcomes. In parallel to these consistent findings, researchers of bipolar disorder (including this editor Robert M. Post and colleagues) have found that an increased length of the interval before treatment is initiated in childhood-onset bipolar disorder is associated with a poor outcome in adulthood.
The RAISE program consists of four interventions: personalized psychopharmacology using a computerized decision support system, individual resilience therapy, family psychoeducation and therapy, and supportive employment and education. Compared with patients receiving standard treatments, patients who participated in the RAISE program showed greater improvements on almost all measures, including the Heinrichs-Carpenter Quality of Life Scale (main outcome), the Calgary Depression Scale for Schizophrenia, the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale, treatment duration, and engagement in work and school. Moreover, the improvements were more substantial among patients with a shorter duration of untreated psychosis.
Editor’s Note: These findings are of great importance in their own right, but they also have great implications for treatment and research efforts in bipolar disorder. A 2013 randomized study by Lars Kessing and colleagues published in the British Journal of Psychiatry found that in bipolar patients hospitalized for a first or second episode of mania, two years of comprehensive treatment with psychotherapy, pharmacotherapy, and illness education that included mood monitoring and early symptom recognition was vastly superior to typical treatment, and this held true even six years later. In a 2014 article in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry and a 2016 article in the journal Bipolar Disorders, researcher Jan Marie Kozicky and colleagues reported that in patients hospitalized with a first episode of mania, cognitive functioning and brain imaging abnormalities, respectively, returned to normal over the next year only if the patients experienced no further mood episodes. The message is clear: we must treat the first episode of mania comprehensively to avoid long-term deterioration, which occurs as a function of the number of episodes of mania or depression a patient experiences. However, this early multimodal approach is rarely taken in the US.
In schizophrenia, Dixon and colleagues noted that: “After the RAISE study reports were made available, Congress allocated additional funding to the community mental health …program, leading to growth in the number of…programs across the United States; they were expected to reach 48 states in 2018.”
The contrast between these efforts in schizophrenia and their virtual absence in bipolar disorder is incomprehensible and tragic. Studies in early schizophrenia have been funded for 25 years, while almost none have been funded in bipolar disorder, even in recent years. Community mental health programs for early schizophrenia will soon exist in 48 states; for patients with bipolar disorder there are no programs available in any state that I am aware of. The incidence of bipolar is about three times that of schizophrenia, and the long-term outcomes are often as devastating in bipolar disorder as in schizophrenia. There is a high incidence of drug abuse; social, educational and occupational deficits; and suicide in bipolar disorder. Early intervention with the many safe supplements, nutraceuticals, and well-tolerated drugs that are currently available to adult patients should be studied in young people with bipolar disorder, but such studies neither being funded nor conducted.
The reality is that childhood-onset bipolar disorder is poorly recognized and treated in the US, largely because of a paucity of treatment-related studies and knowledge about the best options for these young patients. If a reader of the BNN knows how to influence advocacy groups, leaders in the Substance Abuse Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) and the National Institutes of Mental Health (NIMH), or influential politicians, it would be useful to take the initiative in bringing some of these deficits and disparities to their attention. Something must be done; ideas about how to do it are welcome. My own efforts to get funding for a childhood-onset bipolar research network in collaboration with such luminaries in the field as David Miklowitz (UCLA), Kiki D. Chang (Stanford University), Boris Birmaher (University of Pittsburg), Benjamin Goldstein (Stonybrook Research Institute), Eric Youngstrom (UNC, Chapel Hill), Soledad Romero (Hospital Clinic of Barcelona), and Josefina Castro Fornieles (University of Barcelona) have not been successful. We will keep trying, but the field needs to reach beyond the many investigators who are advocating for more treatment research to other people with more influence.
20-Year Study Finds Clozapine and Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics Most Effective at Preventing Re-Hospitalizations for Schizophrenia
Few studies have evaluated the comparative long-term effectiveness of antipsychotics in preventing relapse, but a 2017 study from Finland published in the journal Schizophrenia Bulletin by Heidi Taipale and colleagues did just that, and found that clozapine and long-acting injectable antipsychotic drugs were most effective at preventing psychiatric re-hospitalizations.
The Finnish health care registry was used to prospectively collect data on the treatment of every person who received inpatient care for schizophrenia between 1972 and 2014. The patients totaled 62,250 including 8,719 in their first episode of schizophrenia. Follow-up to evaluate antipsychotic use began at 1996 for those with ongoing treatment, and upon first discharge from the hospital for those patients in their first episode. The follow-up time ranged from 6.9 to 20 years with an average of 14.1 years. During the follow-up period, 59% of patients were readmitted to psychiatric inpatient care.
Among the drugs with the lowest rates of relapse, olanzapine long-acting injection, clozapine, and paliperidone long-acting injection were associated with the least risk of psychiatric re-hospitalization. Among patients in a first episode, taking flupentixol long-acting injection, olanzapine long-acting injection, or perphenazine long-acting injection had the lowest risk of psychiatric re-hospitalization. Clozapine and the long-acting injections also had the least risk of hospitalization for any cause.
Early Intervention Improves Outcomes in Early-Stage Schizophrenia
A recent meta-analysis of 10 studies found that early intervention after a first episode of psychosis or in the early stages of a schizophrenia spectrum disorder led to better patient outcomes than treatment as usual.
The meta-analysis by researcher Christoph U. Correll and colleagues appeared in the journal JAMA Psychiatry in 2018. The 10 studies that were included had randomized a total of 2,176 patients to receive either treatment as usual or early intervention services, which typically include efforts at early detection of symptoms, early treatment with low doses of antipsychotic medication, interventions to prevent relapse, and strategies to help patients return to normal work and social activities.
Those patients who received early intervention services were less likely to discontinue treatment, were less likely to have a psychiatric hospitalization, were more involved in school or work, and had less severe symptoms, including both positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia.
The authors called for better funding and implementation of early intervention services in early psychosis or the beginning stages of schizophrenia.
Editor’s Note: This finding with regard to schizophrenia spectrum disorders emphasizes the enormous disparity in allocation of research resources for the study of early psychosis versus early bipolar disorder, where almost no studies of this kind have been done.
The mean age of the patients in this psychosis meta-analysis was 27.5 years. Symptoms of bipolar disorder can often begin earlier, in childhood, and early onset of bipolar disorder predicts poor long-term outcomes into adulthood and is associated with a high risk of substance abuse and suicide. This editor (Robert M. Post) and many colleagues have witnessed two decades of scientific literature on early-onset bipolar disorder. We know that early intervention is necessary, but more treatment studies are needed at the early stages of the illness, and calls for funding treatment-focused research have gone unheeded.
More advocacy is needed among families affected by bipolar disorder and advocacy groups interested in better treatment of bipolar disorder. We must try to change the abysmal status quo and campaign publicly, privately, and politically for more funds and public health attention to be directed toward early intervention in bipolar disorder.
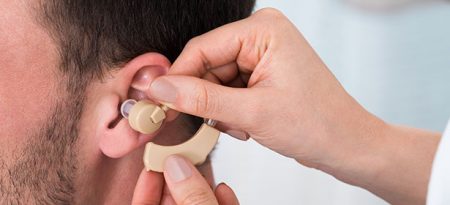
Hearing Aids May Lessen Cognitive Decline, Memory Loss
A 2018 article by researcher Asri Maharani and colleagues in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society reports that using a hearing aid was associated with better scores on a test of episodic memory, and that declines in episodic memory slowed after participants began using hearing aids.
The study included 2,040 adults aged 50 years and up. Maharani and colleagues used data from the Health and Retirement Study, which measured participants’ cognitive functioning every two years for 18 years. Participants were asked to recall 10 words both immediately and after some delay.
The authors suggested that improving access to hearing aids earlier in the course of hearing impairment might help to stem the rise of dementia.
Meta-Analysis Finds Antidepressants More Effective Than Placebo
In a 2018 article in the journal The Lancet, researchers led by Andrea Cipriani compared the efficacy of 21 different antidepressants and established that antidepressants are more effective than placebo at reducing unipolar depression. To date, this is the largest meta-analysis of double-blind, randomized controlled studies of antidepressant efficacy, including 522 trials and a total of 116,477 participants. All 21 of the antidepressants were found to be more effective than placebo.
Looking at head to head studies, Cipriani and colleagues found that the most effective antidepressants were agomelatine, amitriptyline, escitalopram, mirtazapine, paroxetine, venlafaxine, and vortioxetine. The least effective antidepressants were fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, reboxetine, and trazodone.
In terms of tolerability, agomelatine, citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, sertraline, and vortioxetine were most tolerable to patients, while amitriptyline, clomipramine, duloxetine, fluvoxamine, reboxetine, trazodone, and venlafaxine caused the most study dropouts due to side effects. Only agomelatine and fluoxetine had better dropout rates than placebo.
Interestingly, agomelatine, the medication found to be most effective and most tolerable, is unavailable in the US. Pharmaceutical company Novartis, which owns the rights to the drug, was disappointed by some lackluster studies of the drug and never applied for Food and Drug Administration approval to sell it in the US. The studies found potential problems regarding drug interactions related to the metabolic enzyme CYP1A2 and a risk of liver damage with longer-term use.
Editor’s Note: This meta-analysis should end any remaining controversy about the efficacy of antidepressants in the acute treatment of unipolar depression.
This study did not address maintenance treatment for the prevention of depressive episodes. Researcher John R. Geddes and colleagues have found robust, statistically significant data that continuation treatment with antidepressants can prevent depressive relapse, suggesting that if patients continue taking effective antidepressants, rather than switching to placebo, the antidepressants can reduce depressive occurrences by about 70%.
It is now recommended in most guidelines that patients with two or three prior episodes of depression consider staying on antidepressants indefinitely over their lifetime in order to prevent recurrence. Antidepressants increase the creation of new neurons and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which protects neurons and is important for learning and memory. Antidepressants can also prevent loss of hippocampal volume.
Large Finnish Study Finds Lithium is Best at Preventing Re-Hospitalizations in Bipolar Disorder
A 2018 article in the journal JAMA Psychiatry reports that lithium and long-acting antipsychotic injections were most effective at preventing re-hospitalizations among people with bipolar disorder.
The study by Markku Lähteenvuo and colleagues included 18,018 Finnish patients with bipolar disorder. A national database contained information on any hospitalizations that occurred among the patients and what medications were dispersed to patients.
Among the participants, 54% (9,721 patients) were re-hospitalized at least once over a study period of 16 years. Medications associated with the smallest risk of re-hospitalization for psychiatric reasons were long-acting injections of risperidone, gabapentin, long-acting injections of perphenazine, and lithium carbonate.
When the researchers looked at hospitalizations for any cause (not just psychiatric illness), lithium was associated with the least risk of re-hospitalization, while benzodiazepines had the greatest risk, both for psychiatric re-hospitalization and re-hospitalization for any cause.
Long-acting injectable medications were associated with less risk of re-hospitalization compared to the identical medications delivered orally.
Lähteenvuo and colleagues concluded, “Lithium…should remain as the first line of treatment for bipolar disorder, after decades of underprescription.” They suggest that long-acting injectable medications may be a good alternative to prevent relapse in patients for whom lithium is unsuitable.
Editor’s Note: In addition to lithium’s ability to prevent depressions and manias, it also increases the volume of the hippocampus and protects against a diagnosis of dementia in old age. Lithium decreases the risk for suicide and also increases the length of telomeres, bits on the ends of DNA strands that protect them as they replicate, which are important to the maintenance of both physical and psychiatric health. When lithium is used cautiously to maintain doses below a given patient’s side effects threshold, it is very well tolerated by most individuals.