Benefits of a Healthy Lifestyle
 In a talk at the 2015 meeting of the International Society for Bipolar Disorder, researcher Michael Berk suggested that a healthy lifestyle may improve mood disorder symptoms.
In a talk at the 2015 meeting of the International Society for Bipolar Disorder, researcher Michael Berk suggested that a healthy lifestyle may improve mood disorder symptoms.
Diet is important. A study of more than 20,000 mothers revealed that those with unhealthy diets had children with more externalizing disorders, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), oppositional defiant disorder, and mania. Diets high in fat and sugar were linked to depression. The Nurses’ Health Study, a long-term epidemiological study of 50,000 women, showed that people who exercised more were less likely to be depressed, while lower muscle mass was associated with greater depression. Exercise also has anti-inflammatory effects.
Avoiding smoking has benefits, too. A study by Pasco and colleagues showed that people who smoke are at increased risk for a new onset of a mood disorder. Smoking is associated with onset of a more severe mood disorder earlier in life, suicide attempts, alcohol and substance abuse, and decreased response to treatment. Fortunately, quitting smoking can reverse some of these risks.
Ultrabrief Right Unilateral ECT Similar in Efficacy to Brief ECT with Fewer Side Effects
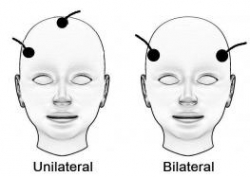 A new meta-analysis suggests that right unilateral ultrabrief electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) may be a better choice than standard brief pulse ECT for the treatment of severe depression. Researchers at the University of New South Wales in Australia led by Colleen Loo say that while standard ECT (with a pulsewidth of 1.0 ms) is recommended when urgency is paramount, ultrabrief ECT (with a pulsewidth of 0.3 ms) is better for patients at risk for cognitive side effects or those who do not require an urgent response. The researchers’ findings were reported in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry in July.
A new meta-analysis suggests that right unilateral ultrabrief electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) may be a better choice than standard brief pulse ECT for the treatment of severe depression. Researchers at the University of New South Wales in Australia led by Colleen Loo say that while standard ECT (with a pulsewidth of 1.0 ms) is recommended when urgency is paramount, ultrabrief ECT (with a pulsewidth of 0.3 ms) is better for patients at risk for cognitive side effects or those who do not require an urgent response. The researchers’ findings were reported in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry in July.
Loo and colleagues analyzed the findings of six different studies that compared right unilateral standard brief pulse ECT with ultrabrief pulse ECT and included a total of 689 patients. Standard ECT was more effective, producing more improvement in mood and more remissions, and working faster than ultrabrief ECT. However, standard ECT also produced greater cognitive side effects in every area tested, including thinking, learning and recall, and memory.
(When bilateral ECT is used, the cognitive effects are even worse, and researcher Harold Sacheim and colleagues have reported that the severity of the impairment in autobiographic memory is directly proportional to the number of bilateral ECT treatments a patient received, even when measured one year after the last session of bilateral ECT. This editor (Robert Post) believes bilateral ECT should be avoided if at all possible, as cognitive side effects can occasionally be severe.)
When Loo and colleagues removed nonrandomized trials from the analysis, the differences in efficacy between ultrabrief and standard right unilateral ECT were not statistically significant. Loo told Medscape Medical News that while the differences in efficacy between brief and ultrabrief ECT are minimal, the differences in side effects are greater. Right unilateral ultrabrief ECT works about as well as standard right unilateral brief pulse ECT, but preserves patients’ cognitive function better.
New TMS System Approved for Depression
In August the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the marketing of the MagVita TMS Therapy system from the company MagVenture. This machine can be used to provide transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) to patients with major depression that has not responded to antidepressant drugs. A TMS system uses magnets placed close to the head to stimulate the brain.
There are several existing systems that can provide TMS. The Neuronetics Neurostar TMS machine was the first one to be approved, in 2008. Then came Brainway’s Deep TMS machine. Now MagVenture says that the benefits of their new system include a simple design, low operating costs, no disposable components, and safety and efficacy rates comparable to those of other FDA-approved TMS devices.
Treatment with the MagVita system is typically provided five times per week for a duration of six weeks.
As TMS treatment becomes available to more patients, coverage by insurance companies is also increasing, but is still not guaranteed for patients in the US.
Treating Bipolar Disorder in Children and Adolescents
Bipolar disorder in childhood or adolescence can destroy academic, family, and peer relationships and increase vulnerability to drug use, unsafe sexual encounters, disability, and suicide. Treatment is critical to avoid cognitive decline. Given the potential tragic outcomes of undertreating bipolar illness, it is concerning that 40–60% of children and adolescents with bipolar disorder are not in treatment.
In a talk at the 2015 meeting of the International Society for Bipolar Disorder, researcher Cristian Zeni reviewed the existing research on the treatment of bipolar disorder in children and adolescents. A 2012 study by Geller reported response rates of 68% for the atypical antipsychotic risperidone, 35% for lithium and 24% for valproate. Risperidone was linked to weight gain and increases in prolactin, a protein secreted by the pituitary gland, while lithium was linked to more discontinuations and valproate to sedation.
For children or adolescents with aggression, researcher Robert Kowatch recommends quetiapine, aripiprazole, and risperidone. For those with a family history of bipolar disorder, he recommends lithium or alternatively, valproate plus an atypical antipsychotic.
Reseacher Robert Findling has found that lamotrigine has positive effects in childhood mania, and Duffy et al. found in a study of 21 children with mania that 13 remained stable on monotherapy with quetiapine for 40 weeks without relapse, while 5 others required combination treatment with more than one drug. In studies by Karen Wagner, oxcarbazepine was significantly better than placebo at reducing mania in younger children (ages 7–12), but not older children (13–18).
Studies by Duffy and colleagues in 2007 and 2009 recommend lithium for those with a family history of bipolar disorder, atypical antipsychotics for children with no family history of bipolar disorder, and lamotrigine for those with a family history of anxiety disorders.
In children with bipolar disorder and comorbid attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, there is universal agreement that mood should be stabilized first, and then small amounts of stimulants may be added for residual ADHD symptoms. Too often, the opposite occurs, with stimulants given prior to mood stabilization with lithium, anticonvulsants (valproate, lamotrigine, carbamazepine/oxcarbazepine) and/or an atypical antipsychotic. Read more
Cognitive Behavioral Prevention Program Can Reduce Incidence of Depression Among Teens
Adolescents whose parents have a history of depression are at greater risk for depression themselves. A new study suggests that a cognitive-behavioral prevention program aimed at these teens can reduce depression rates compared to the usual care.
The study, by David A. Brent and colleagues in the journal JAMA Psychiatry, included 316 participants aged 13–17, each of whom had a parent with a current or prior depression. Half of the participants participated in the cognitive-behavioral prevention program in addition to usual care initiated by their families. The program consisted of 8 weeks of 90-minute group sessions focused on developing positive thinking habits and improving problem solving, followed by six monthly sessions. The training was based on the Adolescents Coping with Depression program described in a June 2009 JAMA article by Garber et al.
The group who participated in the prevention program had a lower incidence of depression than the group who received only the usual care, and this difference persisted over six years of followup. Most of this effect was due to a reduced incidence of depression in the first nine months following the intervention. (Depression was roughly equal among the two groups at two later followups.)
Importantly, the benefit of the prevention program was only seen among adolescents whose parents were not depressed at the time of enrollment in the study, underscoring the importance of treating parents in order to keep the whole family healthy.
Benefits of the prevention program included reductions in onset of depression and days depressed, and improvement in interpersonal and academic competence.
Brent and colleagues say that the study shows that it is possible to prevent depression, and this can have long-term developmental consequences. They encourage focusing on the entire family’s mental health treatment.
While the main benefits came early, Brent suggests that booster sessions for teens who begin to show symptoms of depression might refresh the benefits of the prevention program at a later time.
Editor’s Note: This study has enormous health implications as depression in adolescents tends to recur and is associated with a more difficult course than depression beginning in adulthood. Preventing depressions would theoretically have positive consequences for both psychiatric and physical health, as depression is associated with increased risk of suicide and decreased longevity from increases in cardiovascular disease. Researcher Joan Luby recently reported that children with prepubescent onset of depression have decreased hippocampal volume in adolescence, so it is possible that preventing depression may have positive implications for brain volume and function.
Several Types of Psychotherapy Effective in Childhood Bipolar Disorder
Childhood onset bipolar disorder can be highly impairing. Treatment usually includes medication, but several types of psychotherapy have also been found to be superior to treatment as usual. These include family focused therapy, dialectical behavior therapy and multifamily psychoeducation groups, including Rainbow therapy.
Family focused therapy, developed by David Miklowitz, consists of psychoeducation about bipolar disorder and the importance of maintaining a stable medication routine. Families are taught to recognize early symptoms of manic and depressive episodes, and how to cope with them. Families also learn communication and problem solving skills that can prevent stressful interactions.
Dialectical behavior therapy was developed by Marsha Linehan, initially for the treatment of borderline personality disorder. It can be useful in bipolar disorder because participants learn how to manage stressors that might otherwise trigger depression or mania. DBT teaches five skills: mindfulness, distress tolerance, emotion regulation, interpersonal effectiveness, and self management.
Multifamily psychoeducation was developed by Mary Fristad. In groups, children and parents learn about mood disorders, including how to manage symptoms, and also work on communication, problem solving, emotion regulation, and decreasing family tension.
Rainbow therapy is a type of multifamily approach also known as child and family-focused cognitive-behavioral therapy (CFF CBT). It integrates individual cognitive-behavioral therapy with family psychoeducation and mindfulness skills training. In a recent article in the journal Evidence Based Mental Health, Miklowitz reviewed the current research on Rainbow therapy. While the research to date has many limitations, he highlighted some benefits of Rainbow therapy: its flexibility, and its focus on treating parents’ symptoms along with children’s illness.
Lithium Safely Reduces Mania in Kids 7–17
The first large, randomized, double-blind study of lithium in children and teens has shown that as in adults, the drug can reduce mania with minimal side effects. The study by researcher Robert Findling was published in the journal Pediatrics in October. Lithium is the best available treatment for adults, but until now little research had been done on treatments for children and teens with bipolar disorder.
In the study, 81 participants between the ages of 7 and 17 with a diagnosis of bipolar I disorder and manic or mixed episodes were randomized to receive either lithium or placebo for a period of eight weeks. By the end of the study, those patients taking lithium showed greater reductions in manic symptoms than those taking placebo. Among those taking lithium, 47% scored “much improved” or “very much improved” on a scale of symptom severity, compared to 21% of those taking placebo.
Dosing began at 900mg/day for most participants. (Those weighing less than 65 lbs. were started at 600mg/day.) Dosing could be gradually increased. The mean dose for patients aged 7–11 was 1292mg/day, and for patients aged 12–17 it was 1716mg/day.
Side effects were minimal. There were no significant differences in weight gain between the two groups. Those taking lithium had significantly higher levels of thyrotropin, a peptide that regulates thyroid hormones, than those taking placebo. If thyroid function is affected in people taking lithium, the lithium dosage may be decreased, or patients may be prescribed thyroid hormone.
Lithium Has Minimal Effects On Renal Function: Results Of Two New Large Controlled Studies
 Earlier this year we described a 2015 study by Harald Aiff and colleagues that suggested that long-term lithium use was associated with a risk of kidney failure. That study, published in the Journal of Psychopharmacology, included 630 patients who had taken lithium for at least 10 years. One-third of these patients had evidence of kidney dysfunction, and in 5%, the impairment was severe. Two new studies provide some data that suggest these risks may not be lithium-specific and are comparable to risks that come with taking other medications.
Earlier this year we described a 2015 study by Harald Aiff and colleagues that suggested that long-term lithium use was associated with a risk of kidney failure. That study, published in the Journal of Psychopharmacology, included 630 patients who had taken lithium for at least 10 years. One-third of these patients had evidence of kidney dysfunction, and in 5%, the impairment was severe. Two new studies provide some data that suggest these risks may not be lithium-specific and are comparable to risks that come with taking other medications.
The first, by Stefan Clos et al. in The Lancet Psychiatry, included 1,120 patients followed for up to 12 years. On average, these patients had been exposed to lithium for a little over 4.5 years. Clos and colleagues determined patients’ estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), a measure of how well the blood is filtered by the kidneys. The researchers concluded that there was “no effect of stable lithium maintenance therapy on the rate of change of eGFR over time” compared to other drugs such as quetiapine, olanzapine, or valproate.
The second new study, by Lars Vedel Kessing and colleagues in the journal JAMA Psychiatry, included 26,731 patients exposed to lithium and 420,959 exposed to anticonvulsants. Kessing and colleagues concluded that both exposure to lithium and exposure to an anticonvulsant were associated with an increased rate of chronic kidney disease, but lithium was not associated with end-stage kidney disease (the kind that requires dialysis or renal transplantation).
The three studies taken together suggest the following: Taking lithium for an average of 4–5 years does not affect kidney functioning, and longer exposure may not harm kidney function any more than other medications (such as anticonvulsants) would. However, kidney functioning (in terms of eGFR) does decline with age, and is also lower among those with higher baseline eGRF, those with other illnesses, those taking other drugs that affect the kidneys, and those who experience an episode of lithium toxicity. Read more
Saphris Reformulated for Kids with Bipolar I
The atypical antipsychotic asenapine has been reformulated for bipolar I disorder in children aged 10–17. The drug (trade name Saphris) was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2009 for adults with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. It is sometimes used as a treatment for mixed episodes (depression with some symptoms of mania).
The new formulation consists of 2.5mg tablets that are taken sublingually (under the tongue), and are available in a black cherry flavor. These can be prescribed as monotherapy for the acute treatment of manic or mixed episodes in children and teens.
Direct Current Stimulation Improves Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia
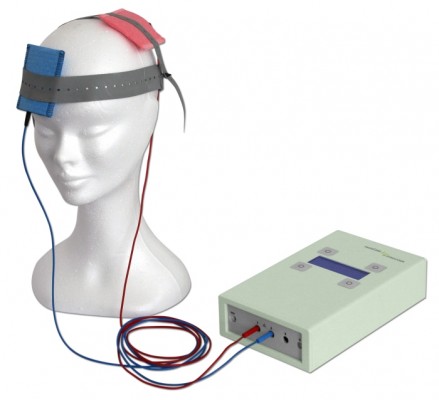 A new double-blind, randomized clinical trial has shown that transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) can reduce negative symptoms of schizophrenia. TDCS, a treatment in which an anode and a cathode electrode placed on the skull are used to apply a steady, low-level current of electricity to the brain, has been shown to improve neuroplasticity, such as neuronal remodeling, by depolarizing or hyperpolarizing neurons. People with schizophrenia have neuroplasticity deficits in parts of the cortex, so a few case reports and one previous randomized clinical trial have explored the use of tDCS in schizophrenia.
A new double-blind, randomized clinical trial has shown that transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) can reduce negative symptoms of schizophrenia. TDCS, a treatment in which an anode and a cathode electrode placed on the skull are used to apply a steady, low-level current of electricity to the brain, has been shown to improve neuroplasticity, such as neuronal remodeling, by depolarizing or hyperpolarizing neurons. People with schizophrenia have neuroplasticity deficits in parts of the cortex, so a few case reports and one previous randomized clinical trial have explored the use of tDCS in schizophrenia.
The current study, presented by Ulrich Palm at the 2015 meeting of the Society of Biological Psychiatry, included 20 patients with primarily negative symptoms of schizophrenia, such as thought disorders, poverty of speech, and withdrawal. The patients, who had stable medication regimes for at least three weeks, were randomized to receive either a sham procedure or tDCS with the anode over the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and the cathode over the right eye. TDCS stimulation was delivered at a current of 2 mA ten times over two weeks. The patients continued to take their medication and also received functional connectivity magnetic resonance imaging (fcMRI) before and after tDCS treatment.
Two weeks following the stimulation, scores on a scale of positive symptoms (hallucinations and delusions) and negative symptoms of schizophrenia had decreased significantly in those who received tDCS compared to the sham procedure. A measure of negative symptoms was significantly lower among the tDCS group throughout the study period and at the 2-week followup. The fcMRI revealed that those who received tDCS had a deactivated cluster in the brain region that includes the nucleus accumbens, the subgenual cortex, and the striatum.
This study suggests that tDCS is a promising treatment for otherwise difficult-to-treat symptoms of schizophrenia.