Anti-Alzheimers’s Drug Memantine (Namenda) May Augment the Antidepressant Effects of Lamotrigine
 At the 65th Annual Scientific Convention of the Society of Biological Psychiatry in May, Amit Anand reported that the anti-Alzheimer’s drug memantine (20 mg/day) was superior to placebo in augmenting the acute antidepressant effects of lamotrigine. These data are of particular interest since one of the assumed mechanisms of action of lamotrigine is to decrease the release of glutamate.
At the 65th Annual Scientific Convention of the Society of Biological Psychiatry in May, Amit Anand reported that the anti-Alzheimer’s drug memantine (20 mg/day) was superior to placebo in augmenting the acute antidepressant effects of lamotrigine. These data are of particular interest since one of the assumed mechanisms of action of lamotrigine is to decrease the release of glutamate.
Memantine is a drug approved for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease and is a partial antagonist (blocker) of glutamate NMDA receptors. This suggests that the dual actions of inhibiting glutamate’s release pre-synaptically (with lamotrigine) and blocking glutamate receptor activity post-synaptically (with memantine) combine to produce a better effect than that of lamotrigine alone.
Track Your Moods with Life Charting
If you have unipolar depression or bipolar disorder and are having trouble stabilizing your mood, we recommend nightly charting of mood, medications and side effects on the easy-to-use Monthly Mood Chart Personal Calendar (pictured below) or the National Institute of Mental Health Life Chart (NIMH-LCM), both of which are available for download.

Sample Mood Chart
Click on the Life Charts tab above to download the personal calendar, which includes space for rating mood, functioning, hours of sleep, life events, side effects, and other symptoms such as anxiety. Then bring the chart to each visit with your physician to help in the assessment of treatments.
Life charting can help determine which medications are working partially and need to be augmented further, and which need to be eliminated because of side effects. Since there are now many potential treatments for depression and bipolar disorder (some FDA-approved and some not), a careful assessment of how well each new treatment works for a particular patient is essential to finding the optimal treatment regimen.
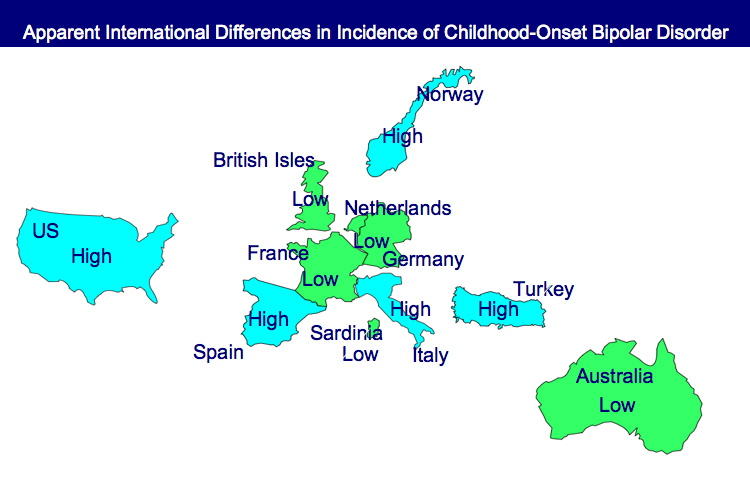
Bipolar Disorder Worse in US than Europe
New research shows that there are more early onsets of illness and more difficult courses of bipolar illness in the US than in the Netherlands or Germany.
This editor was invited to give a plenary presentation at the 4th Biennial Conference of the International Society for Bipolar Disorders in Sao Paulo, Brazil in March. The talk, titled “A greater incidence of early onset bipolar illness and poor prognosis factors in patients in the US compared with those in The Netherlands and Germany,” was based on studies in our Bipolar Collaborative Network.
We found that patients who were studied and treated at four sites in the US (Los Angeles, Dallas, Cincinnati, and Bethesda) had more poor-prognosis factors and indices of difficult courses of bipolar illness compared with patients studied in the same fashion at three sites in Utrecht, the Netherlands and Freiberg and Munich, Germany. We presented some of these data in a preliminary report in the British Journal of Psychiatry in 2008 and further analyzed these data for an article published last year in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. Read more
Almost 40% of Children with Bipolar Disorder May Not Receive Necessary Treatment
 An article by Geller et al. in Bipolar Disorders last year illustrates the crisis in the treatment of childhood-onset bipolar illness in the US. The article indicates that almost 40% of the children with a credible diagnosis of bipolar disorder in this study never received anything near the appropriate treatment for their illness.
An article by Geller et al. in Bipolar Disorders last year illustrates the crisis in the treatment of childhood-onset bipolar illness in the US. The article indicates that almost 40% of the children with a credible diagnosis of bipolar disorder in this study never received anything near the appropriate treatment for their illness.
It is unfortunate when children fail to receive appropriate treatment because of ambiguity about a diagnosis, but it is even more frustrating when one of the world’s experts makes a diagnosis, and a child still fails to receive treatment based on consensus guidelines.
Over 8 years of follow-up treatment in their communities, these very ill children not only did not receive helpful drugs such as atypical antipsychotics or mood stabilizers, but they often received treatments that can be counterproductive, such as antidepressants or psychomotor stimulants. Those children who did receive appropriate treatment with lithium fared better and recovered significantly earlier than the others. Read more
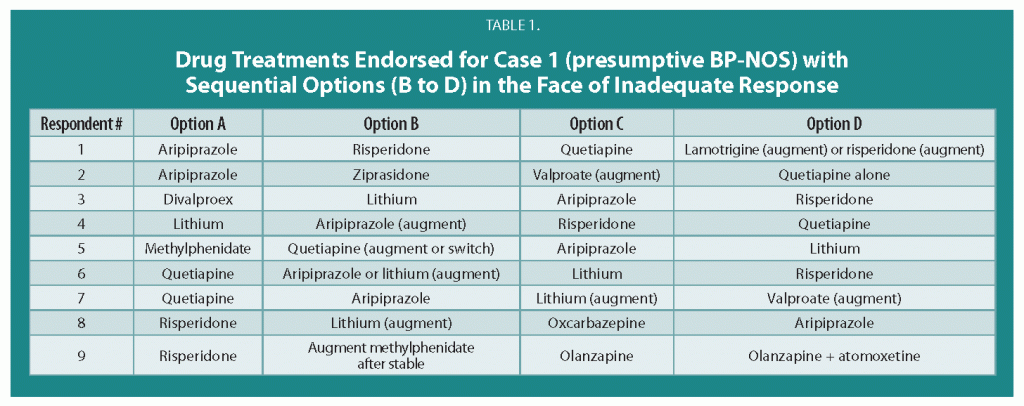
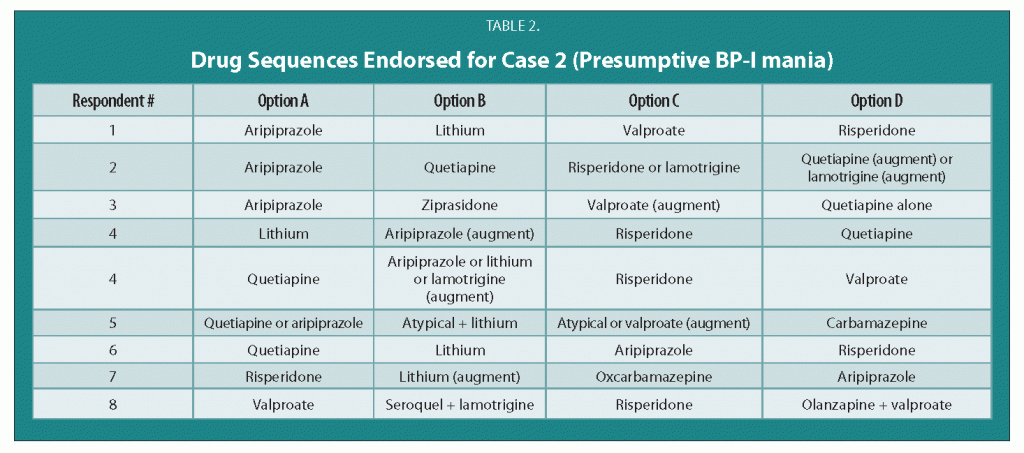
Treatment Guidelines for Two Hypothetical Cases in Children
There are no FDA-approved treatments for children under age 10 with bipolar disorder. For an article in Psychiatric Annals, this editor and Janet Wozniak asked experts how they would sequence treatment of a hypothetical case of a 6-year-old with extreme mood instability consistent with a diagnosis of BP -NOS (see Table I). We also asked how the experts would treat a different case of a 9-year-old with a full-blown psychotic BP-I mania (see Table II).
The results are presented and discussed in detail in the article, and are presented here to reinforce several points. The recommendations for children under 10 and for BP NOS are highly similar to consensus guidelines for older BP I children compiled by Kowatch et al.
Treatments in the face of non-response to option A or others are sequenced differently by different experts, but almost always involve an atypical antipsychotic (AA) or a mood stabilizer (MS) such as lithium, valproate, carbamazepine/oxcarbazepine, or rarely, lamotrigine. Revisions of atypical antipsychotics and mood stabilizers and use of combinations are the common next strategies.
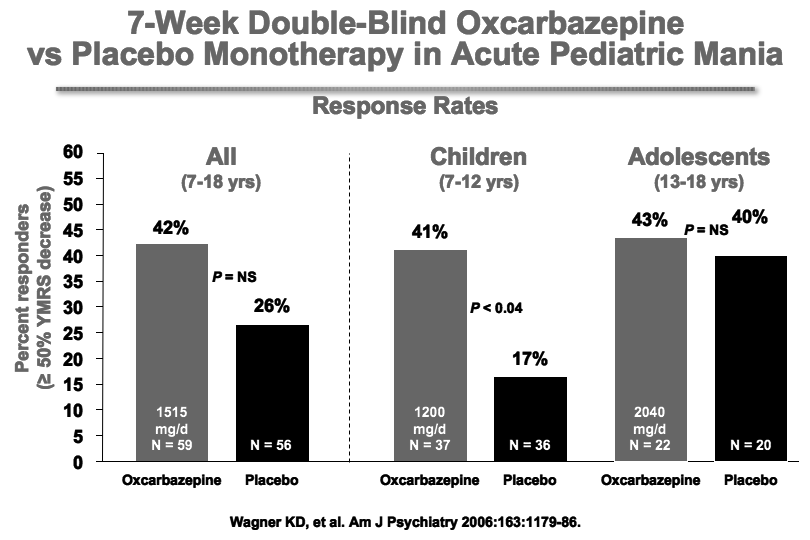
Oxcarbazepine May Be Helpful In Pediatric Mania
Oxcarbazepine (OXC; Trileptal) is a close structural relative of carbamazepine (CBZ; Tegretol; Equetro), but unlike CBZ, OXC is not an enzyme inducer, nor does it have CBZ’s risks of rare agranulocytosis or aplastic anemia.
Wagner et al.’s report on OXC in the American Journal of Psychiatry in 2006 is typically cited as evidence the drug is ineffective for pediatric mania. But observe the figure:
While this was true of OXC’s efficacy in adolescents (due to a large placebo response—see rightmost column), OXC worked significantly better than placebo in children ages 7-12. These younger children often have more chronic presentations and BP-NOS. This may explain the low placebo response rate in the younger children.
Oxcarbazepine is considered helpful by many clinicians (See Post and Wozniak’s survey of expert treatment approaches to childhood illness, published in Psychiatric Annals in 2009) and should not be dismissed altogether.
Faster, Better Response to Risperidone than Valproate in Adolescents with Bipolar Disorder
An article by Pavuluri et al. published in Bipolar Disorders in September reported that both divalproex sodium (valproate, or Depakote) and risperidone (Risperdol) were effective in youth with bipolar disorder, but improvements appeared more quickly with risperidone. Risperidone also produced higher response rates, higher remission rates, and fewer dropouts from side effects.
A presentation by the research group at an earlier conference suggested that it was particularly among those with comorbid disruptive behavioral disorders (DBD), which include attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), oppositional defiant disorder (ODD), and conduct disorder (CD), that risperidone worked faster and produced greater early results than divalproex.
 In the study, 66 children with type I bipolar disorder and a mean age of 11 years were assessed. Treatment with risperidone was initiated at 0.5 mg/day and titrated to 2 mg, while divalproex was initiated at 60 micrograms/mL and titrated up to 120 micrograms.
In the study, 66 children with type I bipolar disorder and a mean age of 11 years were assessed. Treatment with risperidone was initiated at 0.5 mg/day and titrated to 2 mg, while divalproex was initiated at 60 micrograms/mL and titrated up to 120 micrograms.
Editor’s Note: The possibility that children with different comorbid disorders respond differently to different antimanic agents suggests that more studies are needed to determine which subgroups of patients are most responsive to typical treatments.
Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Bipolar Disorder
A number of studies presented at the 4th Biennial Conference of the International Society for Bipolar Disorders conference in Sao Paulo, Brazil in March reported new data relevant to inflammation and oxidative stress. Both inflammation and oxidative stress increase risk of cardiovascular disorders, and patients with inadequately treated mood disorders lose 10 or more years of life expectancy from cardiovascular disorders compared to the general population. Inflammation and oxidative stress may also contribute to the symptoms, evolution, and progression of the mood disorders themselves.
It is possible that these two processes could become new targets for therapeutic intervention in addition to more traditional psychopharmacological drugs that primarily target the neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin, and the neurotrophic factor BDNF. Read more
Preventing Recurrent Mood Episodes
Psychotherapy and psychoeducational approaches, long-term psychopharmacology, and combination therapy all play a role in preventing recurrent mood episodes.
Psychotherapeutic and Psychoeducational Approaches Are Critical
A number of studies presented at the 4th Biennial Conference of the International Society for Bipolar Disorders in Sao Paulo, Brazil in March indicated that cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and individual and group psychoeducational approaches enhance both short- and long-term outcomes for patients with bipolar illness. These studies add to an already substantial literature that shows that focused psychotherapies (such as cognitive/behavioral, interpersonal, and social rhythms therapies) and psychoeducation are superior to treatment as usual.
These therapies can provide a variety of approaches to stress management and reduction, and can enhance family and interpersonal communication. Another way these focused psychotherapeutic approaches help patients is by demonstrating the benefits of effective long-term preventive treatment and encouraging its consistent use.
Without consistent prophylactic treatment, patients are at high risk for recurrences and their subsequent psychosocial and neurobiological consequences. Greater number of prior episodes is associated with an increased risk of psychosocial dysfunction, treatment resistance, cognitive dysfunction, medical comorbidities, and even dementia in old age.
After the jump: preventive psychopharmacology and combination therapy. Read more
Have you checked our archives lately?
We are currently posting articles from the 4th issue of 2010 and will soon begin posting articles from the 5th issue. But we also just updated our archives, so if you can’t wait, you can download the full PDF versions of the print newsletters in our archives.